- Использование Android Search Dialog. Пример простого приложения
- Немного теории
- Конфигурационный файл
- Создаем Activity
- Выполнение поиска
- Исходный код
- How to scan QR Codes with Android phones without an app
- Table of Contents
- What are QR Codes? – Quick Recap
- Does Android have an in-built QR Code reader?
- How do I scan a QR Code without an app on Android?
- Scan QR Codes with Android 9 (PIE) and Android 10
- Activating Google Lens
- Scan QR Codes with Android 8 (Android OREO)
- Scan QR Codes with ANDROID 7 and below (Requires a QR Code reader app)
- What are the best QR Code reader apps for Android in 2021?
- How to scan QR Codes with Samsung Galaxy S10e, S10 and S10+
- How to scan QR Codes with Samsung Galaxy S9
- How to scan QR Codes with Vivo smartphones?
- Can Pixel scan QR Codes?
- How to scan QR Codes with Pixel 2 XL?
- Scanning QR Codes with Android: FAQs
- What happens when you scan QR Codes?
- Are QR Codes free?
- How far away can you scan a QR Code?
- How do I keep a QR Code on my phone?
- How do you use QR Codes?
- Are there any risks to scanning QR Codes?
- Can a phone with Android versions 8 and 9 scan QR Codes?
- GOOD READS:
Использование Android Search Dialog. Пример простого приложения
Данная статья предназначена для тех, кто уже написал свой HelloWorld для Android и знает, что такое Activity и Intent, а так же где находится манифест, и зачем нужны layout’ы. В противном случае, можно ознакомиться с этим материалом, например, на developer.android.com.
В статье описывается создание несложного приложения, которое использует механизм реализации поиска, основанный на возможностях встроенного фреймворка. После прочтения вы также сможете настроить свое приложение таким образом, чтобы оно осуществляло поиск по данным, используя стандартный Android Search Dialog.
Немного теории
Android Search Dialog (далее — «диалог поиска») управляется с помощью поискового фреймворка. Это означает, что разработчику не нужно задумываться над тем как его нарисовать или как отловить поисковый запрос. За вас эту работу сделает SearchManager.
Итак, когда пользователь запускает поиск, SearchManager создает Intent, и направляет его к Activity, которое отвечает за поиск данных (при этом сам запрос помещается в экстры). То есть по сути в приложении должно быть хотя бы одно Activity, которое получает поисковые Intent’ы, выполняет поиск, и предоставляет пользователю результаты. Для реализации потребуется следующее:
- Конфигурационный xml файл (в нем содержится информация о диалоге)
- Activity, которое будет получать поисковые запросы, выполнять поиск и выводить результаты на экран
- Механизм вызова поискового диалога (так как не все устройства с Android на борту имеют на корпусе кнопку поиска)
Конфигурационный файл
xml version =»1.0″ encoding =»utf-8″ ? >
searchable xmlns:android =»http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android:label =»@string/app_name»
android:hint =»@string/search_hint»
>
searchable >
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
Обязательным атрибутом является только android:label, причем он должен ссылаться на строку, которая является такой же, что и название приложения. Второй атрибут, android:hint используется для отображения строки в пустом диалоге. Например, это может быть «Поиск по Видео» или «Поиск контактов» и т.п. Этот атрибут указывает на то, по каким данным осуществляется поиск. Также важно знать, что элемент searchable поддерживает множество других атрибутов, подробнее можно прочесть Здесь.
Создаем Activity
Минимально, всё что нам нужно от пользовательского интерфейса Activity — это список для вывода результатов поиска и механизм вызова поискового диалога. Так и сделаем, добавив только поле для ввода текста и кнопку, чтобы мы сами могли заполнять базу. Забегая вперед, скажу, что данные будем хранить в БД SQLite.
Опишем интерфейс Activity следующим образом (файл находится в res/layout/main.xml).
xml version =»1.0″ encoding =»utf-8″ ? >
LinearLayout xmlns:android =»http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android:orientation =»vertical»
android:layout_width =»fill_parent»
android:layout_height =»fill_parent» >
LinearLayout
android:orientation =»horizontal»
android:layout_width =»fill_parent»
android:layout_height =»wrap_content»
android:gravity =»top» >
EditText
android:id =»@+id/text»
android:layout_width =»wrap_content»
android:layout_height =»wrap_content»
android:hint =»@string/text»
android:layout_weight =»100.0″/>
Button
android:id =»@+id/add»
android:layout_width =»wrap_content»
android:layout_height =»wrap_content»
android:text =»@string/add»/>
LinearLayout >
ListView
android:id =»@android:id/list»
android:layout_width =»fill_parent»
android:layout_height =»wrap_content»/>
TextView
android:layout_gravity =»left»
android:id =»@android:id/empty»
android:layout_width =»fill_parent»
android:layout_height =»fill_parent»
android:text =»@string/no_records»/>
LinearLayout >
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
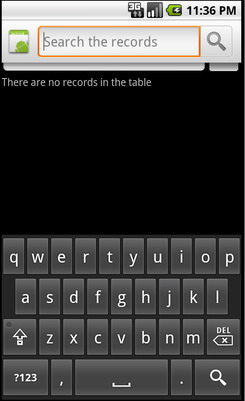
Выглядит следующим образом:
Также нам понадобится layout для вида элемента списка, опишем его простейшим образом (файл находится в res/layout/record.xml)
xml version =»1.0″ encoding =»utf-8″ ? >
TextView
android:id =»@+id/text1″
xmlns:android =»http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android:layout_width =»wrap_content»
android:layout_height =»wrap_content»
/>
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
Также, не забываем про файл ресурсов, где хранятся наши строки (файл в res/values/strings.xml)
xml version =»1.0″ encoding =»utf-8″ ? >
resources >
string name =»app_name» > SearchExample string >
string name =»add» > Add string >
string name =»text» > Enter text string >
string name =»no_records» > There are no records in the table string >
string name =»search_hint» > Search the records string >
string name =»search» > Search string >
resources >
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
xml version =»1.0″ encoding =»utf-8″ ? >
manifest xmlns:android =»http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
package =»com.example.search»
android:versionCode =»1″
android:versionName =»1.0″ >
application android:icon =»@drawable/icon» android:label =»@string/app_name» >
activity android:name =».Main»
android:label =»@string/app_name» >
intent-filter >
action android:name =»android.intent.action.MAIN»/>
category android:name =»android.intent.category.LAUNCHER»/>
intent-filter >
intent-filter >
action android:name =»android.intent.action.SEARCH»/>
intent-filter >
meta-data
android:name =»android.app.searchable»
android:resource =»@xml/searchable»
/>
activity >
application >
uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion =»5″/>
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
Сейчас, вы уже можете проверить, все ли вы сделали правильно. Вызвать диалог на эмуляторе можно, например, нажав кнопку поиска. Ну или если вы проверяете на девайсе, то зажав «Меню». Выглядеть должно примерно так:
Выполнение поиска
Получение запроса
Так как SearchManager посылает Intent типа Search нашему Activity, то всё что нужно сделать это проверить на Intent этого типа при старте Activity. Тогда, если мы получаем нужный Intent, то можно извлекать из него экстру и выполнять поиск.
Поиск данных
Так как тип структуры хранения данных для разных приложений может различаться, то и методы для них свои. В нашем случае, проще всего выполнить запрос по таблице БД SQLite запросом LIKE. Конечно, лучше использовать FTS3, он значительно быстрее, подробнее о FTS3 можно прочесть на сайте SQLite.org. В идеале, также нужно всегда рассчитывать, что поиск может занять продолжительное время, поэтому можно создать какой-нибудь ProgressDialog, чтобы у нас не завис интерфейс, и чтобы пользователь знал, что приложение работает.
Вывод результатов
Вообще вывод результатов — это проблема UI, но так как мы используем ListView, то для нас проблема решается простым обновлением адаптера.
Исходный код
Наконец, привожу полный исходный код двух классов с комментариями. Первый — Main, наследник ListActivity, он используется для наполнения БД и вывода результатов. Второй класс — RecordsDbHelper, он реализует интерфейс для взаимодействия с БД. Самые важные методы — добавление записей и поиск совпадений, с помощью запроса LIKE.
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.app.SearchManager;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuInflater;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class Main extends ListActivity <
private EditText text;
private Button add;
private RecordsDbHelper mDbHelper;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//Создаем экземпляр БД
mDbHelper = new RecordsDbHelper( this );
//Открываем БД для записи
mDbHelper.open();
//Получаем Intent
Intent intent = getIntent();
//Проверяем тип Intent
if (Intent.ACTION_SEARCH.equals(intent.getAction())) <
//Берем строку запроса из экстры
String query = intent.getStringExtra(SearchManager.QUERY);
//Выполняем поиск
showResults(query);
>
add = (Button) findViewById(R.id.add);
text = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.text);
add.setOnClickListener( new View.OnClickListener() <
public void onClick(View view) <
String data = text.getText().toString();
if (!data.equals( «» )) <
saveTask(data);
text.setText( «» );
>
>
>);
>
private void saveTask( String data) <
mDbHelper.createRecord(data);
>
private void showResults( String query) <
//Ищем совпадения
Cursor cursor = mDbHelper.fetchRecordsByQuery(query);
startManagingCursor(cursor);
String [] from = new String [] < RecordsDbHelper.KEY_DATA >;
int [] to = new int [] < R.id.text1 >;
SimpleCursorAdapter records = new SimpleCursorAdapter( this ,
R.layout.record, cursor, from , to);
//Обновляем адаптер
setListAdapter(records);
>
//Создаем меню для вызова поиска (интерфейс в res/menu/main_menu.xml)
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) <
MenuInflater inflater = getMenuInflater();
inflater.inflate(R.menu.main_menu, menu);
return true ;
>
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) <
switch (item.getItemId()) <
case R.id.search_record:
onSearchRequested();
return true ;
default :
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
>
>
>
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.SQLException;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.util.Log;
public class RecordsDbHelper <
public static final String KEY_DATA = «data» ;
public static final String KEY_ROWID = «_id» ;
private static final String TAG = «RecordsDbHelper» ;
private DatabaseHelper mDbHelper;
private SQLiteDatabase mDb;
private static final String DATABASE_CREATE = «CREATE TABLE records(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, »
+ «data TEXT NOT NULL);» ;
private static final String DATABASE_NAME = «data» ;
private static final String DATABASE_TABLE = «records» ;
private static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
private final Context mCtx;
private static class DatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper <
DatabaseHelper(Context context) <
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null , DATABASE_VERSION);
>
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) <
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) <
Log.w(TAG, «Upgrading database from version » + oldVersion + » to »
+ newVersion + «, which will destroy all old data» );
db.execSQL( «DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tasks» );
onCreate(db);
>
>
public RecordsDbHelper(Context ctx) <
this .mCtx = ctx;
>
public RecordsDbHelper open() throws SQLException <
mDbHelper = new DatabaseHelper(mCtx);
mDb = mDbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
return this ;
>
public void close() <
mDbHelper.close();
>
//Добавляем запись в таблицу
public long createRecord( String data) <
ContentValues initialValues = new ContentValues();
initialValues.put(KEY_DATA, data);
return mDb.insert(DATABASE_TABLE, null , initialValues);
>
//Поиск запросом LIKE
public Cursor fetchRecordsByQuery( String query) <
return mDb.query( true , DATABASE_TABLE, new String [] < KEY_ROWID,
KEY_DATA >, KEY_DATA + » LIKE» + «‘%» + query + «%'» , null ,
null , null , null , null );
>
>
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter .
Источник
How to scan QR Codes with Android phones without an app
Sneh Ratna Choudhary
Last Updated:  December 3, 2021
Confused whether Android phones can scan QR Codes without QR Code reader apps? Read this guide to find out!
The 2017’s iOS 11 update added the native capability to all iPhones allowing them to scan QR Codes without an app and just in time because 2022 is the year of QR Codes. From delivering discounts to allowing consumers to listen to their favorite Spotify playlist while they shop, QR Codes are ubiquitous and businesses and marketers alike have begun to run entire campaigns based on this cost-effective QR Code technology.
Table of Contents
What are QR Codes? – Quick Recap
QR Codes are 2-dimensional barcodes that when scanned open up a link, add contacts, send SMSes, make calls among other things.
Need to know how to scan QR Code menus? Pull up the native camera and point it at the QR Code. The menu will pop up instantly as a notification.
Does Android have an in-built QR Code reader?
Yes. Just like iPhones, Android 9 (Android Pie) and Android 10 have an in-built QR Code reader. Even the Android 8 or Oreo does not need an app to scan QR Codes.
How do I scan a QR Code without an app on Android?
Scan QR Codes with Android 9 (PIE) and Android 10
Android 9 and Android 10 have an in-built QR code reader courtesy of Google Lens. Consumers have to open their camera app and point it at the QR Code and see a URL pop-up.
Activating Google Lens
To activate Google Lens to scan QR Codes suggestions, open the camera app and click on more. Open Settings and activate Google Lens suggestions to scan QR Codes.
Scan QR Codes with Android 8 (Android OREO)
1. Google Screen Search : Google Screen Search allows consumers to scan QR Codes without an app instantly. All one has to do is point their camera at the QR Code, long-press the Home button and click on ‘What’s on my screen?’ The QR Code link will be available for consumers to open.
Activating Screen Search
If the smartphone’s screen search is not on, open the Google app and tap Navigation. From the settings, enable Screen Search.
2. Google Lens: An AI interface by Google, Google Lens recognizes everything in the camera including QR Codes. It is available on both the camera app as well as Google Assistant.
Simply download Google Lens and start scanning QR Codes or use Google Lens from Google Assistant.
Scan QR Codes with ANDROID 7 and below (Requires a QR Code reader app)
Android smartphones with Android 7.0 and below require an app to scan QR Codes. After downloading the app, all QR Codes can be scanned instantaneously. Since a lot of apps use QR Codes within the app to perform a function like payments or scanning a product to get more information, consumers are already aware of how to operate a QR Code reader app. You can use Snapchat, Amazon, and Paytm to scan QR Codes on Android without having to download an additional app.
What are the best QR Code reader apps for Android in 2021?
According to our research, these 6 free QR Code reader apps are perfect for older Android versions that allow Android phones to scan QR Codes –
For more details on these apps, check out our best QR Code scanner apps for Android guide.
How to scan QR Codes with Samsung Galaxy S10e, S10 and S10+
An OTA update will allow users of Samsung Galaxy S10e, S10, and S10+ to start using their cameras to scan QR Codes. No third-party app is required anymore. Here’s how to start scanning QR Codes:
- Go to Camera Settings
- Toggle the feature “Scan QR Codes”
Source
How to scan QR Codes with Samsung Galaxy S9
A June 2019 security update has made it possible for Galaxy S9 users to scan QR Codes right from their camera by toggling a button that says ‘Scan QR Codes’. Now Samsung Galaxy S9 users can simply point the camera at a QR code and the associated link will pop up. There is no need for Bixby Vision or any other third-party apps. This update has not been rolled out to Samsung’s flagship phones. [Some phones have started receiving this update]
How to scan QR Codes with Vivo smartphones?
For Vivo smartphones with Android 8 and above, you can use the Google Lens on your camera. There is also an in-built scanner on some Vivo smartphones on the Notification Panel and Smart Launcher Screen.
Can Pixel scan QR Codes?
Google’s Pixel can scan QR Codes. You don’t even need Google Lens to do so. Open the camera app and point it to a QR Code and you will see the link appear just above the shutter button. Click on this link to open up the website, landing page, or URL.
How to scan QR Codes with Pixel 2 XL?
Simply open the camera and point it at a QR code. The Pixel 2 XL can natively scan QR Codes just like iPhones. The associated link pops up on the screen which acts as a prompt for the user.
Made with Easelly infographic templates. Start customizing your infographic here.
Scanning QR Codes with Android: FAQs
What happens when you scan QR Codes?
When consumers scan QR Codes, a number of things can occur. Businesses can use QR Codes to deliver coupons, product information, and deals or use it to ask shoppers to leave reviews, feedback and follow them on social media.
Are QR Codes free?
Yes, QR Codes can be generated for free online. Although these QR Codes are static codes and once downloaded cannot be changed. To change the content that a QR Code contains, you need dynamic QR Codes.
Create dynamic QR Codes with a dynamic QR Code generator in a flash
How far away can you scan a QR Code?
Typically, QR Codes found in magazines can be scanned from at least 10 inches away and the QR Codes found on billboards can be scanned from 2 meters away. The relationship between the scan distance and the minimum QR Code size should be 10:1. A 2.5 cm QR Code can be scanned from 250 mm or 10 inches away.
How do I keep a QR Code on my phone?
Once you create a free QR Code on the QR Code generator, you can save the QR Code on your phone. If you are using QR Codes on Facebook, Snapchat or LinkedIn, you can save it as an image on your phone or share it so that other people can add you to that particular network.
How do you use QR Codes?
Apart from useful information about a certain product, QR Codes are also used on GMO labeling in the US as well as for proximity marketing. Businesses can leverage QR Codes to attract new visitors by allowing them to scan and get navigation details or paste them on flyers and deliver rewards and discounts. Businesses can also automate the process of creating QR Codes with an API.
Are there any risks to scanning QR Codes?
Phishing or malicious software being downloaded through QR Codes is rare but it is a slim possibility. Only scan QR Codes that specify the action or what you can expect once you scan them or see that the URL slug is from a credible source like Beaconstac (tapnscan.me/).
Can a phone with Android versions 8 and 9 scan QR Codes?
Android versions 8 and 9 can automatically scan QR Codes without an app. Some older Android versions will also receive the latest update.
GOOD READS:
Interested in QR Codes? Talk to our expert or explore QR Code marketing examples and leverage the advanced analytics of the Beaconstac dashboard to improve your business’s ROI.
Источник