- Android — Session Management
- Shared Preferences
- Session Management through Shared Preferences
- Example
- Session Management in Android with Example
- Example
- Step by Step Implementation
- Android — Управление сессиями
- Общие настройки
- Управление сессиями через общие настройки
- пример
- Android Session Management with Examples
- Android Session Management Example
- activity_main.xml
- details.xml
- MainActivity.java
- DetailsActivity.java
- AndroidManifest.xml
- Output of Android Session Management Example
Android — Session Management
Session help you when want to store user data outside your application, so that when the next time user use your application, you can easily get back his details and perform accordingly.
This can be done in many ways. But the most easiest and nicest way of doing this is through Shared Preferences.
Shared Preferences
Shared Preferences allow you to save and retrieve data in the form of key,value pair. In order to use shared preferences, you have to call a method getSharedPreferences() that returns a SharedPreference instance pointing to the file that contains the values of preferences.
You can save something in the sharedpreferences by using SharedPreferences.Editor class. You will call the edit method of SharedPreference instance and will receive it in an editor object. Its syntax is −
Apart from the putString method, there are methods available in the editor class that allows manipulation of data inside shared preferences. They are listed as follows −
| Sr.No | Mode & description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| Steps | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | You will use android studio IDE to create an Android application under a package com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication. |
| 2 | Modify src/MainActivity.java file to add progress code to add session code. |
| 3 | Create New Activity and it name as second.java.Edit this file to add progress code to add session code. |
| 4 | Modify res/layout/activity_main.xml file to add respective XML code. |
| 5 | Modify res/layout/second_main.xml file to add respective XML code. |
| 7 | Run the application and choose a running android device and install the application on it and verify the results. |
Here is the content of MainActivity.java.
Here is the content of second_main.java.
Here is the content of activity_main.xml.
Here is the content of second_main.xml.
Here is the content of Strings.xml.
Here is the content of AndroidManifest.xml.
Let’s try to run your application. I assume you had created your AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project’s activity files and click Run 
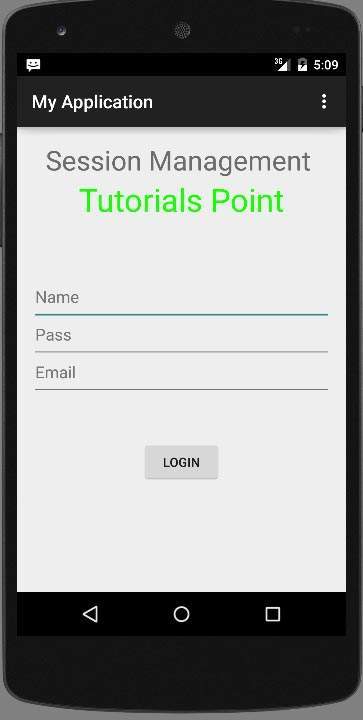
Type in your username and password (type anything you like, but remember what you type), and click on login button. It is shown in the image below −
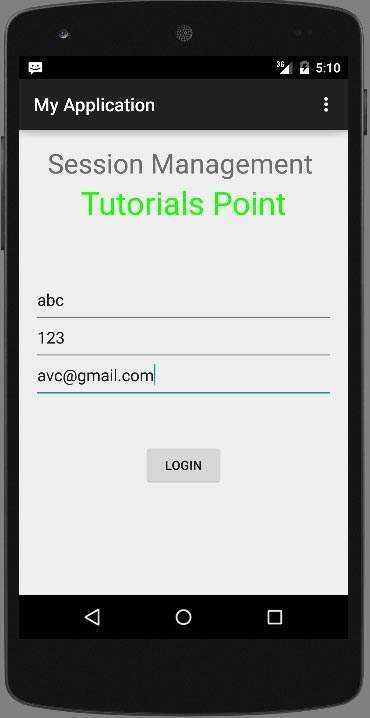
As soon as you click on login button, you will be brought to this Welcome screen. Now your login information is stored in shared preferences.
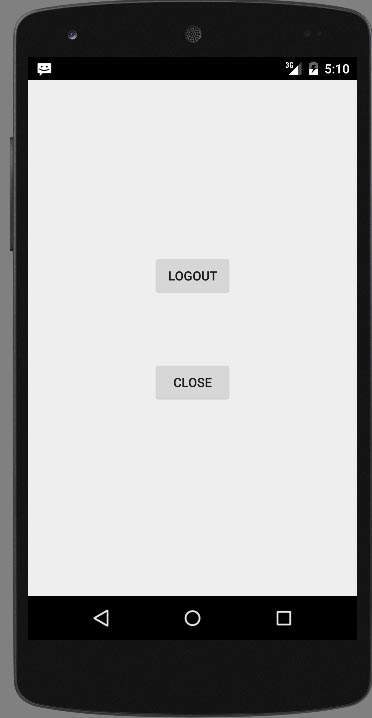
Now click on Exit without logout button and you will be brought back to the home screen and in preference file out put would be as shown below image
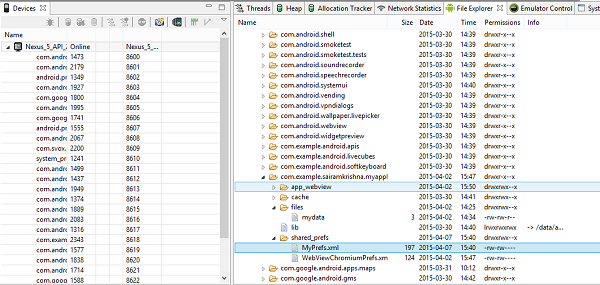
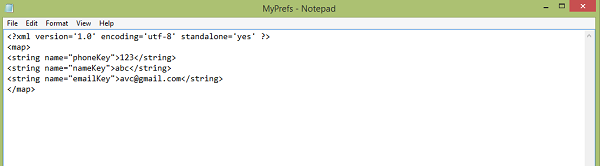
If you open myPref.xml file as note file, it would be as follows
If you click on logout button, it will erase preference values. and if you entered different values as inputs,it will enter those values as preference in XML.
Источник
Session Management in Android with Example
Session Management is one of the most important features that are to be used in the Android App when you are integrating the login feature in Android. In your android app if you are using a feature of Login then you should have to save the state if the user has signed the first time. Then when the user closes his app and reopens it then he should redirect to our Home screen, rather than opening a login screen. So in this article, we will implement Session Management functionality in our Android app. For implementing this functionality we are creating a simple login form and a home screen. In our login form, the user has to enter his credentials and login into the app. After login, the user’s credentials will be saved inside the app, and whenever he reopens the app the user will be redirected to the home screen. For session management inside our app, we will be using Shared Preferences to store users’ credentials. Now we will move towards the implementation part.
Example
We will be creating a simple Login app as mentioned above for storing user session. A sample GIF is given below in which we will get to see what we will be building in our app. Note that we will be implementing this project using Java language.
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important Java Foundation and Collections concepts with the Fundamentals of Java and Java Collections Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.
Step by Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a New Project
To create a new project in Android Studio please refer to How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio. Note that select Java as the programming language.
Источник
Android — Управление сессиями
Сеанс поможет вам, когда вы захотите сохранить пользовательские данные за пределами вашего приложения, чтобы при следующем использовании пользователем вашего приложения вы могли легко вернуть его данные и выполнить соответствующие действия.
Это можно сделать разными способами. Но самый простой и приятный способ сделать это — через Shared Preferences .
Общие настройки
Общие настройки позволяют сохранять и извлекать данные в виде пары ключ-значение. Чтобы использовать общие предпочтения, вы должны вызвать метод getSharedPreferences (), который возвращает экземпляр SharedPreference, указывающий на файл, который содержит значения предпочтений.
Вы можете сохранить что-то в общих настройках с помощью класса SharedPreferences.Editor. Вы вызовете метод edit экземпляра SharedPreference и получите его в объекте редактора. Его синтаксис —
Помимо метода putString в классе редактора есть методы, которые позволяют манипулировать данными внутри общих настроек. Они перечислены следующим образом —
| Sr.No | Режим и описание | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| меры | Описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | Вы будете использовать Android Studio IDE для создания приложения Android в пакете com.example.sairamkrishna.myapplication. |
| 2 | Измените файл src / MainActivity.java, чтобы добавить код прогресса для добавления кода сеанса. |
| 3 | Создайте новую активность и назовите ее second.java. Измените этот файл, чтобы добавить код прогресса для добавления кода сеанса. |
| 4 | Измените файл res / layout / activity_main.xml, чтобы добавить соответствующий код XML. |
| 5 | Измените файл res / layout / second_main.xml, чтобы добавить соответствующий код XML. |
| 7 | Запустите приложение и выберите работающее устройство Android, установите на него приложение и проверьте результаты. |
Вот содержание MainActivity.java .
Вот содержание second_main.java .
Вот содержание activity_main.xml .
Вот содержание second_main.xml .
Вот содержимое Strings.xml .
Вот содержимое AndroidManifest.xml .
Давайте попробуем запустить ваше приложение. Я предполагаю, что вы создали свой AVD во время настройки среды. Чтобы запустить приложение из студии Android, откройте один из файлов деятельности вашего проекта и нажмите «Выполнить». 
Введите свое имя пользователя и пароль (введите все, что вам нравится, но помните, что вы вводите) , и нажмите кнопку входа. Это показано на рисунке ниже —
Как только вы нажмете кнопку входа, вы попадете на этот экран приветствия. Теперь ваша информация для входа хранится в общих настройках.
Теперь нажмите кнопку « Выход без выхода» , и вы вернетесь на главный экран, а в файле настроек будет показано, как показано на рисунке ниже.
Если вы откроете файл myPref.xml как файл заметок, это будет выглядеть следующим образом
Если вы нажмете кнопку выхода, это приведет к удалению значений предпочтений. и если вы ввели разные значения в качестве входных данных, они будут вводиться как предпочтения в XML.
Источник
Android Session Management with Examples
In android, Session Management is a process that is used to maintain the required values in a session to use it in the application.
Generally, in android, we can manage the logged in user details in session either by storing it in global variables or in Shared Preferences. In case, if we store the values in global variables, those will be lost whenever the user closes the application but if we store the values in Shared Preferences, those will be persisted even if the application closed by the user.
In android, Shared Preferences are used to save and retrieve the primitive data types (integer, float, boolean, string, long) data in the form of key-value pairs from a file within an apps file structure.
To know more about Shared Preferences, check this Android Shared Preferences with Examples.
Now we will see how to store and retrieve logged in user details from shared preferences file using SharedPreferences object and clear or delete the stored session values from Shared Preferences file whenever the user clicks on the logout button in android application with examples.
Android Session Management Example
Following is the example of storing and retrieving the logged-in user details from shared preferences file using SharedPreferences and clear the stored session values on the logout button click.
Create a new android application using android studio and give names as SharedPreferencesExample. In case if you are not aware of creating an app in android studio check this article Android Hello World App.
Once we create an application, open activity_main.xml file from \res\layout folder path and write the code like as shown below.
activity_main.xml
xml version= «1.0» encoding= «utf-8» ?>
LinearLayout xmlns: android = «http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android :orientation= «vertical» android :layout_width= «match_parent»
android :layout_height= «match_parent» >
TextView
android :id= «@+id/fstTxt»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :layout_marginTop= «150dp»
android :text= «UserName»/>
EditText
android :id= «@+id/txtName»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :ems= «10»/>
TextView
android :id= «@+id/secTxt»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :text= «Password»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»/>
EditText
android :id= «@+id/txtPwd»
android :inputType= «textPassword»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :ems= «10»/>
Button
android :id= «@+id/btnLogin»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_marginLeft= «100dp»
android :text= «Login»/>
LinearLayout >
Now we will create another layout resource file details.xml in \res\layout path to get the first activity (activity_main.xml) details in second activity file for that right click on your layout folder à Go to New à select Layout Resource File and give name as details.xml.
Once we create a new layout resource file details.xml, open it and write the code like as shown below
details.xml
xml version= «1.0» encoding= «utf-8» ?>
LinearLayout xmlns: android = «http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
android :orientation= «vertical» android :layout_width= «match_parent»
android :layout_height= «match_parent» >
TextView
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :id= «@+id/resultView»
android :layout_gravity= «center»
android :layout_marginTop= «170dp»
android :textSize= «20dp»/>
Button
android :id= «@+id/btnLogOut»
android :layout_width= «wrap_content»
android :layout_height= «wrap_content»
android :layout_gravity= «center»
android :layout_marginTop= «20dp»
android :text= «Log Out»/>
LinearLayout >
Now open your main activity file MainActivity.java from \java\com.tutlane.sharedpreferencesexample path and write the code like as shown below
MainActivity.java
package com.tutlane.sharedpreferencesexample;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity <
EditText uname , pwd ;
Button loginBtn ;
SharedPreferences pref ;
Intent intent ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout. activity_main );
uname = (EditText)findViewById(R.id. txtName );
pwd = (EditText)findViewById(R.id. txtPwd );
loginBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id. btnLogin );
pref = getSharedPreferences( «user_details» , MODE_PRIVATE );
intent = new Intent(MainActivity. this ,DetailsActivity. class );
if ( pref .contains( «username» ) && pref .contains( «password» )) <
startActivity( intent );
>
loginBtn .setOnClickListener( new View.OnClickListener() <
@Override
public void onClick(View v) <
String username = uname .getText().toString();
String password = pwd .getText().toString();
if (username.equals( «suresh» ) && password.equals( «dasari» )) <
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = pref .edit();
editor.putString( «username» ,username);
editor.putString( «password» ,password);
editor.commit();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), «Login Successful» ,Toast. LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
startActivity( intent );
>
else
<
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), «Credentials are not valid» ,Toast. LENGTH_SHORT ).show();
>
>
>);
>
>
If you observe above code, we are checking whether the entered username and password details matching or not based on that we are saving the details in shared preferences file and redirecting the user to another activity.
Now we will create another activity file DetailsActivity.java in \java\com.tutlane.sharedpreferencesexample path to show the details from shared preference file for that right-click on your application folder à Go to New à select Java Class and give name as DetailsActivity.java.
Once we create a new activity file DetailsActivity.java, open it and write the code like as shown below
DetailsActivity.java
package com.tutlane.sharedpreferencesexample;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
* Created by tutlane on 03-01-2018.
*/
public class DetailsActivity extends AppCompatActivity <
SharedPreferences prf ;
Intent intent ;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) <
super .onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout. details );
TextView result = (TextView)findViewById(R.id. resultView );
Button btnLogOut = (Button)findViewById(R.id. btnLogOut );
prf = getSharedPreferences( «user_details» , MODE_PRIVATE );
intent = new Intent(DetailsActivity. this ,MainActivity. class );
result.setText( «Hello, » + prf .getString( «username» , null ));
btnLogOut.setOnClickListener( new View.OnClickListener() <
@Override
public void onClick(View v) <
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = prf .edit();
editor.clear();
editor.commit();
startActivity( intent );
>
>);
>
>
Now we need to add this newly created activity in AndroidManifest.xml file in like as shown below.
AndroidManifest.xml
xml version= «1.0» encoding= «utf-8» ?>
manifest xmlns: android = «http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android»
package= «com.tutlane.sharedpreferencesexample» >
application
android :allowBackup= «true»
android :icon= «@mipmap/ic_launcher»
android :label= «@string/app_name»
android :roundIcon= «@mipmap/ic_launcher_round»
android :supportsRtl= «true»
android :theme= «@style/AppTheme» >
activity android :name= «.MainActivity» >
intent-filter >
action android :name= «android.intent.action.MAIN»/>
category android :name= «android.intent.category.LAUNCHER»/>
intent-filter >
activity >
activity android :name= «.DetailsActivity» android :label= «Shared Preferences — Details» > activity >
application >
manifest >
If you observe above example, we are checking whether the entered user details matching or not based on that we are saving the user details in shared preferences file and redirecting the user to another activity file (DetailsActivity.java) to show the users details and added all the activities in AndroidManifest.xml file.
Output of Android Session Management Example
When we run above example in the android emulator we will get a result like as shown below
If you observe above result, the entered username and password matches then we are redirecting the user to another activity file to show the user details from the shared preferences file. After that, if we click on Logout button, it will clear all the values in shared preferences file and it will redirect the user to the login page.
This is how we can use session management in android applications with Shared Preferences to store and retrieve session values based on our requirements.
Источник