- Implement In-app Update In Android
- Make sure every user of your app is on the new version.
- What is In-App Update:
- Flexible Update:
- Benefits:
- In-App Updates: ускоряем процесс обновления приложения на Android
- Интеграция IAUs Flexible Flow
- Варианты использования
- Основные требования к тестированию
- Пример кода
- Ошибка «Update is Not Available»
- IAUs Flexible Flow в приложении Pandao
- Android Application In-App Update Using Android Studio
- Introduction
- Immediate
- Flexible
- Prerequisites
- Requirements
- Implementation
- Background
- Implementing flexible update flow
- An instance of AppUpdateManager
- Check for the update
- Handling the update flow
- Handling user actions
- Monitoring the update flow
- Complete the update flow
- Unregister the listener
- Implementing immediate updates
- Create an instance of appUpdateManager
- Check for the update
- Handling the update flow
- Handling user action
- Testing
- How to test
- Code setup and output
- Flexible
- Immediate
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Want to learn more about the EngEd Program?
Implement In-app Update In Android
Make sure every user of your app is on the new version.
Apr 6, 2020 · 8 min read
In this article, we will learn about the In-app update feature in Android what is all about In-app update, what are the benefits of using the In-app update in your android application. Recently I’ve been working on a product in which I need to Implement an In-app update Why we need to Implement this?.
As a Developer we always want our users to have the updated version of their application but there are a lot of people who actually turned off their auto update from google play store and he/she doesn’t know about any update available or not.
To overcome the problem Google Introduced this feature called In-app update from this feature you can easily prompt the user to update the application and with the user permission you can update the application also while updating the app user can be able to interact with the application. Now the user doesn’t need to go to google play store to check there is any update available or not.
What is In-App Update:
An In-app update was Introduced as a part of the Play Core Library, which actually allows you to prompts the user to update the application when there is any update available on the Google Play Store.
There are two modes of an In-app update.
- Flexible Update
- Immediate Update
Flexible Update:
In Flexible update, the dialog will appear and after the update, the user can interact with the application.
This mode is recommended to use when there is no major change In your application like some features that don’t affect the core functionality of your application.
The update of the application is downloading in the background in the flexible update and after the completion of the downloading, the user will see the dialog in which the user needs to restart the application. The dialog will not automatically show, we need to check and show to the user and we will learn how later.
Benefits:
The major benefit of the flexible update is the user can interact with the application.
Источник
In-App Updates: ускоряем процесс обновления приложения на Android
Среди многообразия инструментов, анонсированных на Android Dev Summit, особое внимание хочется уделить механизму обновления приложения In-App Updates (IAUs), который помогает разработчикам ускорить добавление новых фич, баг-фиксов и улучшений производительности. Поскольку эта функциональность была опубликована после Google I/O 2019, в этой статье я подробно расскажу об IAUs, опишу рекомендованные схемы реализации и приведу некоторые примеры кода. Также я расскажу о нашем опыте интеграции IAUs в Pandao, приложение для заказа товаров из Китая.
Новый API позволяет разработчикам инициировать обновление приложения до последней доступной в Google Play версии. Таким образом IAUs дополняет уже существующий механизм автоматического обновления Google Play. IAUs содержит несколько схем реализации, которые принципиально различаются с точки зрения взаимодействия с пользователем.
- Flexible Flow предлагает пользователям скачать обновление в фоновом режиме и установить в удобное для пользователя время. Он предназначен для случаев, когда пользователи всё ещё могут использовать старую версию, но уже доступна новая.
Immediate Flow требует от пользователей скачать и установить обновление, прежде чем продолжить использование приложения. Он предназначен для случаев, когда для разработчиков критически важно обновить приложение.
Поскольку второй вариант не так важен и меньше подходит для приложения Pandao, разберём подробнее сценарий Flexible Flow.
Интеграция IAUs Flexible Flow
Варианты использования
Процесс обновления с помощью IAUs состоит из нескольких шагов.
- Приложение с помощью библиотеки Play Core, которая проверяет в Google Play, есть ли доступные обновления.
- Если они есть, то приложение просит Google Play показать диалог IAUs. Google Play показывает пользователю диалог с предложением обновиться.
- Если пользователь соглашается, Google Play в фоновом режиме скачивает обновление, показывая пользователю в статус-баре прогресс скачивания.
- Если скачивание завершилось, когда приложение работает в фоновом режиме, Google Play автоматически завершает установку. Если же приложение в этот момент активно, то для таких случаев нужно определять собственную логику завершения установки. Рассмотрим следующие сценарии.
- Приложение запускает процесс установки, показав пользователю диалог Google Play с индикатором прогресса. После завершения установки запускается обновленная версия приложения. В этом случае рекомендуется отобразить дополнительный диалог, который позволит пользователю подтвердить, что он готов сейчас перезапустить приложение. Это рекомендуемая схема реализации.
- Приложение ждёт, пока оно окажется в фоновом режиме, и после этого завершает обновление. С одной стороны, это менее навязчивое поведение с точки зрения UX, так как взаимодействие пользователя с приложением не прерывается. Но с другой — оно требует от разработчика реализовать логику для определения того, находится ли приложение в фоновом режиме.
Если установка скачанного обновления не была завершена, то Google Play может завершить установку в фоновом режиме. Данный вариант лучше не использовать явно, потому что он не гарантирует установки обновления.
Основные требования к тестированию
Чтобы вручную выполнить весь процесс обновления на тестовом устройстве, нужно иметь как минимум две версии приложения с разными номерами сборок: исходная и целевая.
- Исходная версия с более высоким номером должна быть опубликована в Google Play, она будет идентифицирована Google Play как доступное обновление. Целевая версия с более низким номером сборки и интегрированным IAUs должна быть установлена на устройстве, её мы будем обновлять. Суть в том, что когда приложение попросит Google Play проверить наличие обновления, он сравнит номера сборок у установленной и доступной версии. Так что IAUs будет запущено только в том случае, если номер сборки в Google Play выше, чем у текущей версии на устройстве.
- Исходная и целевая версии должны иметь одинаковые имена пакета и должны быть подписаны одинаковым релизным сертификатом.
- Android 5.0 (API level 21) или выше.
- Библиотека Play Core 1.5.0 или выше.
Пример кода
Здесь мы рассмотрим пример кода для использования IAUs Flexible Flow, который также можно найти в официальной документации. Для начала необходимо добавить библиотеку Play Core в build.gradle файл на уровне модуля.
Затем создадим экземпляр AppUpdateManager и добавим функцию обратного вызова к AppUpdateInfo , в которой будет возвращаться информация о доступности обновления, объект для запуска обновления (если оно доступно) и текущий прогресс скачивания, если оно уже началось.
Чтобы показать диалог для запроса обновления из Google Play, необходимо передать полученный объект AppUpdateInfo в метод startIntentSenderForResult .
Для отслеживания состояния обновления можно добавить в менеджер IAUs слушатель событий InstallStateUpdatedListener .
Как только обновление будет скачано (статус DOWNLOADED ), нужно перезапустить приложение, чтобы завершить обновление. Перезапуск можно инициировать с помощью вызова appUpdateManager.completeUpdate() , но перед этим рекомендуется показать диалоговое окно, чтобы пользователь явно подтвердил свою готовность к перезапуску приложения.
Ошибка «Update is Not Available»
Во-первых, перепроверьте соответствие требованиям, перечисленным в разделе «Basic Implementation Requirements». Если вы все выполнили, однако обновление согласно вызову onSuccess , всё же недоступно, то проблема может быть в кэшировании. Вполне вероятно, что приложение Google Play не знает о доступном обновлении из-за внутреннего механизма кэширования. Чтобы избежать этого при ручном тестировании, вы можете принудительно сбросить кэш, зайдя на страницу «Мои приложения и игры» в Google Play. Или можете просто очистить кэш в настройках приложения Google Play. Обратите внимание, что эта проблема возникает только в ходе тестирования, она не должна влиять на конечных пользователей, поскольку у них кэш всё равно обновляется ежедневно.
IAUs Flexible Flow в приложении Pandao
Мы участвовали в программе раннего доступа и интегрировали IAUs Flexible Flow (рекомендованная реализация) в приложение Pandao — платформу, на которой производители и вендоры могут торговать китайскими товарами. Диалог IAUs отображался на главном экране, так что с ним могло взаимодействовать максимальное количество пользователей. Изначально мы хотели показывать диалог не чаще раза в день, чтобы не отвлекать людей от взаимодействия с приложением.
Поскольку A/B-тестирование играет ключевую роль в жизненном цикле любой новой фичи, мы решили оценить эффект от IAUs в нашем приложении. Мы случайным образом разделили пользователей на две непересекающиеся группы. Первая была контрольной, без использования IAUs, а вторая группа была тестовой, этим пользователям мы показывали диалог IAUs.

A/B-тест IAUs Flexible Flow в приложении Pandao.
В течение последних нескольких релизов мы измерили долю активных пользователей каждой версии приложения. Оказалось, что среди активных пользователей с последней доступной на тот момент версией основную часть составляли участники из группы B, то есть с функцией IAU. Фиолетовая линия на графике показывает, что в первые дни после публикации версии 1.29.1 количество активных пользователей с IAUs превысило количество пользователей без этой функции. Поэтому можно утверждать, что пользователи с IAUs быстрее обновляют приложение.
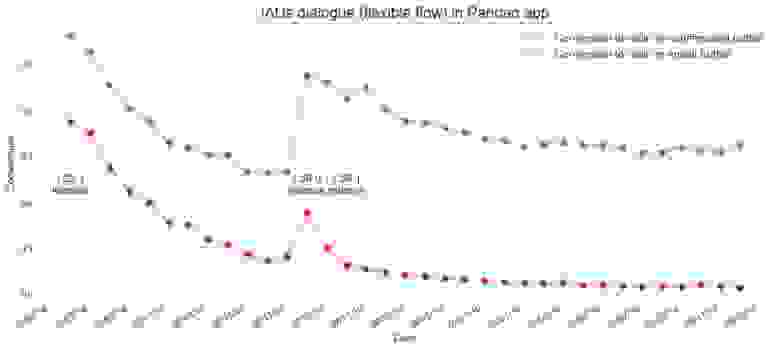
Диалог IAUs Flexible Flow в приложении Pandao.
Согласно нашим данным (см. график выше), пользователи больше всего кликают на кнопку подтверждения в диалоге IAUs в первые дни после релиза, а затем конверсия постоянно снижается вплоть до публикации следующей версии приложения. То же самое наблюдается с кнопкой установки в диалоговом окне, которая инициирует установку скачанного обновления. Следовательно, можно сказать, что среднее значение конверсии в обоих случаях прямо пропорционально частоте релизов. В Pandao средняя конверсия в течение одного месяца достигает 35 % для клика на кнопку подтверждения и 7 % для клика на кнопку установки.
Мы предполагаем, что уменьшение доли подтверждений с течением времени — лишь проблема пользовательского опыта, потому что люди, которым интересна новая версия, будут обновляться довольно быстро, а те, кто не интересуются обновлением, так и не станут интересоваться. Исходя из этого предположения, мы решили не беспокоить тех, кому не интересно обновление, и не спрашивать их каждый день. Хорошей практикой будет использование другой логики запросов, которая основывается на «устаревании», то есть чтобы не беспокоить пользователей, мы оцениваем, насколько старые версии стоят у них и как часто мы уже предлагали им обновиться.
В целом IAUs продемонстрировала хорошие результаты в ходе A/B-тестирования, так что мы раскатили IAUs для всех пользователей.
Источник
Android Application In-App Update Using Android Studio
December 30, 2020
As developers, we always want users to update their applications to the latest version quickly. We want everyone to use the latest features included in the updates. Google notifies Android users whenever updates are available for certain applications. However, this is mainly for users who have enabled the auto-update feature. It is, therefore, important for users to know when your application has a new update available.
Introduction
Suppose a user has your application installed on their mobile phone. Yet, you have added new critical features or fixed a bug to the app. The only way the user can access these functionalities is by updating the application. Some users lack the interest or time to open the Google Play store and update their applications. This means that they will take time before switching to the latest version.
To solve this problem, Google I/O introduced an in-app update API. This API alerts users whenever you have a new version on the Google Play store. The API introduces an update UI within your application to notify users to update to the newly available application version. Users do not have to open the Google Play store to initiate the update.
In this guide, we will learn about Google’s in-app updates and implement them in our applications. We will discuss the two methods to implement in-app updates: immediate and flexible.
Immediate
The immediate update introduces a blocking full-screen UI . When a user starts the update, he/she can’t use the application until the update is installed. The app will automatically restart when the update is completed. This method is preferred when the update introduces critical functionalities.
Flexible
A flexible update allows users to interact with the application while the update occurs in the background. Once the update is downloaded, the app will prompt the user to restart the application. The application will then install the update and open the app to the foreground. It is preferred when the update has minor changes that do not affect the application’s critical functionalities.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes you have prior knowledge of Android application development using Android Studio and Java.
To carry out testing, you will need:
- A Google Play Console account.
- An application already published in the Google Play store.
Requirements
- A device running Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher.
- Google Play Core Library version 1.5.0 or higher.
Implementation
Add the following library on your app.gradle file.
Sync to download the library.
At the time of writing this guide, the Google Play Core version was 1.8.3 . It is recommended to have the latest version. Check for the latest version here.
Background
Setting the in-app update is simple. The Google Core API implements all major functionalities. A user does not have to activate auto-updates in the Google Play store. The API will handle the update flow in any application that has implemented this in-app update concept.
Before handling the update type, either flexible or immediate, you should understand how the API works. Let’s discuss some of the key classes and functions that help us to trigger an update flow.
To check if there is an update available in the Google Play store, we have to create an instance of appUpdateManager. It communicates with the AppUpdateInfo object. The object triggers a remote communication with the Google Play store. It holds the property results and status of any available update. The result is a collection of data for the update availability, such as the available app version. The data will then be used to determine whether the API should initiate the update flow.
AppUpdateInfo has the following methods:
updateAvailability() processes the following:
UPDATE_AVAILABLE : This checks whether an application has a new version available in the Google Play store.
DEVELOPER_TRIGGERED_UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS : This handles a case where a user-initiated the update process but closed the application while the update was in progress. updateAvailability() will return the state of the update progress.
installStatus() returns the value of the update milestone. installStatus() is an instance of installStateUpdatedListener hooked to the appUpdateManager . It returns the values of the update status, such as:
DOWNLOADED : When the user hits the update, the application will first download the APK. installStatus() sets the action that should be done when the APK has been downloaded.
INSTALLED — installStatus() sets the action when the newly available update has been installed.
To trigger the update flow, we first check the updateAvailability() to determine if there is an update available. The returned value should be UPDATE_AVAILABLE if the developer has pushed new features.
Next, we will validate whether the update type is allowed with the function isUpdateTypeAllowed() and pass AppUpdateType , which can be IMMEDIATE or FLEXIBLE .
We have determined whether an update is available or not (the state of the available update). If the update type is allowed, appUpdateManager will return the update status from the AppUpdateInfo values and trigger the update flow with startUpdateFlowForResult .
We pass the following parameters to startUpdateFlowForResult to start the update flow UI:
- The appUpdateInfo that we previously fetched from the Google Play store.
- The updated flow that we want to trigger. Previously passed to isUpdateTypeAllowed as AppUpdateType that can be IMMEDIATE or FLEXIBLE .
- The execution context in the current activity.
- A request code to catch Onactivity results such as: — If a user canceled the update. — If the update is OK. — If the update flow failed.
With that, we are ready to complete the update with completeUpdate() .
Implementing flexible update flow
This flow does not block a user from interacting with the application. When the update is available, the user downloads the update APK, which occurs in the background. When the download is complete, the user will be prompted to install the newly downloaded application to bring the new updates on board.
Let’s handle the flow.
Before we check this, make sure you implement the update flow on your main launch application page—for example, a log-in activity. This will make sure that a user is alerted as soon they open the application.
An instance of AppUpdateManager
Create an instance of AppUpdateManager . Go ahead and declare AppUpdateManager right above onCreate .
Below onCreate , create the instance.
Check for the update
To implement the update flow, you need to check whether there is an updated application version in the Google Play store.
Create a function checkUpdate() and call it in the onCreate .
Here is what the function does:
It communicates with the Play store to check if an update is available.
- The update availability for the current application,
- An intent to start an update flow,
- And, if applicable, the state of updates currently in progress.
Register a listener to communicate with the appUpdateInfoTask . If the conditions check that UPDATE_AVAILABLE is true , check whether the update is allowed and set the update mode to FLEXIBLE . If these conditions are met, we will start the update flow with startUpdateFlow(appUpdateInfo) (we will look into this later).
In this case, our update mode is set to Flexible. The update is downloaded in the background. We then need to check the install status. If the status shows that the app is DOWNLOADED , we need to notify the user that the download has been completed. You can choose to use a Snackbar or an AlertDialog . In this tutorial, we will use a Snackbar .
Create a function named popupSnackBarForCompleteUpdate(). This method will be called when the installStatus() is equal to DOWNLOADED . The UI will react by nudging the user to install the downloaded APK.
Remember to press alt + enter on a PC and option + enter on a Mac to import the classes after copying and pasting the code blocks into your IDE.
Handling the update flow
Now create the startUpdateFlow(appUpdateInfo) function we passed above.
We have checked whether the update is available or not. We have also confirmed that the updated platform is supported, and we are, therefore, ready to request the update.
startUpdateFlowForResult() will request the update from AppUpdateInfo that holds the update information. To ensure the update flow kick-off as expected, we pass some parameters to startUpdateFlowForResult . They include:
AppUpdateType — the mode of the update flow we want to perform. In this case, we have set that to FLEXIBLE .
this — the execution context of the current activity requesting the update.
FLEXIBLE_APP_UPDATE_REQ_CODE — a request code that handles user actions onActivityResult . Make sure you declare FLEXIBLE_APP_UPDATE_REQ_CODE right above onCreate , as shown below.
Handling user actions
We need to handle onActivityResult to check the user’s action, such as instances where the update is canceled or has failed. FLEXIBLE_APP_UPDATE_REQ_CODE monitors the update request as implemented in the code below.
From the above code, there are several results:
- If a user canceled the installation, you could call checkUpdate() to restart the update flow.
You can do many things here, such as:
- Popping up a dialog to inform the user that they need to update the application.
- Inform them of the new features or the bugs that the update will fix.
If the user agrees, you can call checkUpdate() to reinitiate the update flow. You can also decide to close the application with finish() . Otherwise, do nothing and continue with the normal application flow.
RESULT_OK — shows that the update was successful. We can’t assign any action to it, as our goal is met. But you can choose to show a message to the user to thank them for taking the time to update the application to the latest version.
If the update failed, this could be an error such as poor internet connection. Request the update again by calling checkUpdate() to restart the update process.
Monitoring the update flow
As mentioned earlier, a flexible update flow occurs in the background. We need to monitor the update flow to know when the application download is complete and initiate an install process.
To do this, we need to register a listener to get the status of the update. The listener informs the app of every step in the update process.
Declare the listener.
Add the following code just below the appUpdateManager instance created inside the onCreate method.
The above code tracks down the update status.
- If the status is equal to DOWNLOADED , launch a snack bar to instruct the user to install the downloaded update.
- If the status is equal to INSTALLED , unregister the listener. When the update is installed, there is no need to register a listener anymore.
Complete the update flow
Since we have the download ready, it’s time to set the snack bar’s action. Create a function popupSnackBarForCompleteUpdate() .
This notifies the user that the update APK is downloaded and ready to be installed. When the user clicks Install , the appUpdateManager automatically installs the downloaded APK. This will bring the newly updated features onboard.
Unregister the listener
We have now achieved the update installation. We don’t need the installStateUpdatedListener anymore.
To unregister it, create a function removeInstallStateUpdateListener() and call it when installStatus() is equal to INSTALLED .
This prevents the callbacks from being triggered when they are no longer required. Unregistering the listener also helps to avoid memory leaks.
Implementing immediate updates
When the AppUpdateType is set to IMMEDIATE , appUpdateManager initiates a blocking UI . It blocks the user from interacting with the application until the update is complete.
Immediate updates are similar to the flow of events discussed while implementing the flexible mode. To avoid repeating the detailed explanation we have done above, we will state the update flow that implements an immediate update.
Create an instance of appUpdateManager
Check for the update
Create a checkUpdate() function and call it the onCreate .
The app will communicate with the play store and check whether the update is available.
If the update is available, check whether the update type is allowed. In this case, we are checking if the IMMEDIATE mode is allowed to start the update flow. If yes, we call startUpdateFlow(appUpdateInfo) .
If the user initiated the update and closed the app before the process was over, set the UpdateAvailability to DEVELOPER_TRIGGERED_UPDATE_IN_PROGRESS . The user can resume the update process by initiating startUpateFlow(appUpdateInfo) .
Handling the update flow
Initiate the update flow and set the AppUpdateType to IMMEDIATE in the current activity context. Again, remember to pass a result code that will track the user’s actions, such as canceling the update.
Handling user action
OnActivityResult handles the action a user takes when prompted to install an update. This is comprised of three main actions, including:
- RESULT_CANCELED — when a user cancels an update, you may choose an action that follows that decision. checkUpdate() to force the application to restart the update. Or call finish() to close the application whenever the user cancels an update.
- RESULT_OK — shows that a user has accepted the update to be installed.
- RESULT_IN_APP_UPDATE_FAILED — If an update fails with an error, you would want the app to reinitiate the update flow again. For that reason, call checkUpdate() , and the update flow will start again.
Testing
Testing an in-app update is not straightforward. It can be a little tricky to perform a test.
How to test
Generate a signed app bundle/APK. Note that the APK signing key and the applicationId should be the same as the already published application.
Share the generated APK with a tester. To do that, select the published application in the Google console, navigate to Internal App Sharing , and upload the generated APK there. Check how to use Google Internal App Sharing.
Copy the upload’s shareable link and share it with a tester. In this case, the tester should have an Android mobile phone.
Open the shared link on the phone’s browser. You will be redirected to the Play store.
Download the app and wait for the installation to complete.
Once done, generate another signed app bundle/APK. This time change versionCode and versionName in your app.gradle file to a higher version. If, for example, in the first generated APK, the values were:
Change these values to a higher version. For example:
To be sure that the update will take place, on your activity.xml replace android:text=»Hello World!» with android:text=»Congratulations, you now have the newest version of this app installed.» .
Once you have generated the app bundle/APK, head to App Internal Sharing and upload it.
Again, copy the shareable link generated by this upload and open it with the tester. When the link launches on the Google Play store, you will get an update button, do not click update.
Close the Google Play store and open the application we installed earlier. This will launch an update UI that will prompt you to update the application. The UI may differ depending on your update type (either flexible or immediate).
Code setup and output
Flexible
Immediate
Conclusion
I hope this guide helps you implement in-app updates, both immediate and flexible, within your application context.
Peer Review Contributions by: Michael Barasa
About the author
Joseph Chege is an undergraduate student taking a Bachelor in Business Information Technology, a 4th-year student at Dedan Kimathi University of Technology. Joseph is fluent in Android Mobile Application Development and has a lot of passion for back-end development.
Want to learn more about the EngEd Program?
Discover Section’s community-generated pool of resources from the next generation of engineers.
Источник







