- Uvc camera driver android
- Uvc camera driver android
- Building and Using the UVC Camera Driver Sample
- Overview
- Minimum Requirements
- Building the UVC Camera Driver
- Prerequisites
- Build the Dependencies
- Compile UVC Camera Driver
- Using UVC Camera Driver
- Using Android.mk
- CMakeLists.txt:
- Using Gradle
- Unity specifics
- Creating a New Camera Profile
- Calibration Information
Uvc camera driver android
FPViewer (Easycap & UVC Player)
версия: 1.3.3
Последнее обновление программы в шапке: 07.01.2019
Краткое описание:
Вывод изображения на экран Android устройства с подключенной камеры или FPV-приемника (UVC-камеры).
FPViewer — это приложение для отображения аналогового видео с помощью устройства захвата видео UVC (Easycap и т.п.), подключенного с помощью кабеля OTG к устройству Android (root-доступ не требуется).
Кроме того, FPViewer предлагает оптимизированную функцию, позволяющую использовать устройства Android в качестве монитора FPV.
Возможности:
Отображение аналогового видео с помощью устройства захвата видео Easycap на устройстве Android.
Поддерживается только версия Easycap для UTV007, HTV600, HTV800 и не поддерживается аудиовход.
Работа в качестве FPV монитора для приемников FPV (5.8 ГГц)
Работает с приемниками Eachine ROTG01 / ROTG02, ATX03, R051 и т.п.
Отображение аналогового видео с помощью устройства захвата видео (UVC) на устройстве Android.
(Функция аналогична Easycap).
Кроме того, если USB-камера имеет тип UVC, вы можете использовать камеру с этим приложением (поддерживается только разрешение 640×480).
Запись видео
Сохранение отображаемого видео в формате MP4. (Android 4.3 или выше)
Разделение изображения для работы с очками VR
Поддержка режима Side by Side (VR), так что вы можете использовать Android-устройство в качестве очков FPV.
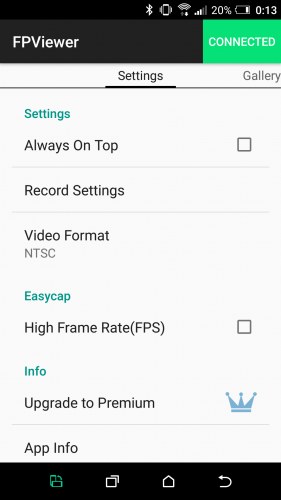
Always on Top
Возможно установить видеоокно на передний план. При этом экран просмотра никогда не исчезнет, даже если вы получите телефонный звонок или текстовое уведомление.
Требуется Android: 4.1 и выше
Русский интерфейс: Нет
Скачать: версия: 1.3.3

Источник
Uvc camera driver android
Still under development.
This is a Android Studio Project. It connects to a usb camera from your Android Device. (OTG cabel or OTG Hub needed) (It works with Micro Usb and Usb Type C devices)
This Project was built to perform an Isochronous Video Stream from all Android Devices (Above 4.0.4 Ice Cream Sandwich)(Mediathek Devices too).
The app connects to USB Cameras via variable, different input values for the camera driver creation. In most cases you won’t need to set up your own camera driver, because other apps may do this for you automatically, but for some Android devices it could help to watch videos from Usb Cameras.
- LibUsb Support Added: LibUsb raises the performance of the standard Usb Device Driver.
(Some OTG cabels doesn’t work —> I’ll found one which is an extern powered more Port USB-C OTG cable and doesn’t work . ) (An non working OTG cable doesn’t show the right interfaces and endpoints of you camera: —> When you click on ‘List Up The Camera’ Button)
Since Android 9 Google made a mistake granting the Usb Permissions for Usb Cameras, so this app may not works on Android 9 + Devices —> https://issuetracker.google.com/issues/145082934
Explaination: Before you start with entering the Camera values, your Android device have to detect the Camera: So you click the Button and then the Button . The app will ask you for granting the permissions.
In the Picture above a camera was found and the Permissions to the Camera are granted. If no Camera is detected, you can nott use this app. (except of the WebRTC function). Next you have read out the camera Interfaces, to see if your camera is UVC complient. So you click the Button: :
Here you can see a sucessful return of an UVC compliant camera. The first Interface is always the ControlInterface and the second is always the Stream Interface. This Controlinterface (1st) has only 1 Endpoint. The StreamInterface could have more than one Endpoints (depends on the supported resolution of the camera). Here the Endpoint of the StreamInterface has a maxPacketSize of 3072 bytes (You need such a value later). (It could be, that your camera has an audio output, or Sd-Card output too, than see more than 2 Interfaces for your device). If those two Buttons work correctly, you can start to set up the UVC values: Click the Button to start the camera setup. You have two pissibilies: The and the Method. The method is in beta stadium for now, so if this button fails, you choose the method next time! The automatic method should find working camera values for its own, but this values may not be optimal for video transmission. To choose the right values for your own, you click on the Button.
Manual Method Explained: First you choose you Maximal Packet Size: You Camera may supports more Values for the MaxPacketSize, so you can test out each of them, which works best. If your phone uses a Mediathek Chipset you may choose the smallest value, but normaly you choose the highest value! Click on and proceed to the Packets Per Request selection: The Values you select builds the size of the Stream. This means if you select higher Values (such as 32 or more ..) you stream gets bigger, but there may could result error from your device or the camera because of a too large amount of data. For the start you select 1 for this Value. (This would be definitly to less, but you can raise it later) .. Next Sceen shows the ActiveUrbs (actice Usb Request Blocks) —> This is also a value which represents the size of the camera stream. One Block of the activeUrbs is exactly the maxPacketSize x packetsPerRequest. You can select 1 for the start (You will have to raise it later ..) Then the Setup Method will ask you for the Camera Format, which your camera supports. If there is only one format, you click on , if there were more, you select one (does not matter which one) (eventually MJpeg if present) and click on . Next you have to select you Camera Resolution, which you camera supports with the Format (perhaps your camera supports other resolutions, with the other Format . ). Select something . and click on Then you have to select the Frame Interval, which your camera supports. You can click on a Value (maybe the lowest on displayed on the screen, because it is better for the setup. You can save your Entries now: Click on to save this values (you do not need to run the method again, if you have finished the setup and found some working values . If you click on in the next screen —> an automatic name will be taken from the camera to save the file. You can also enter a unique name or enter the value, which is displayed on the bottom, to choose an existing file.
The picture shows the output of the sucessful setup: Now you want to know, if your Camera works with your selected Values. So you start the comunication with your camera by clicking on the Button and then you select the first entry
If you output is the same like on the Picture above, you have sucessfuly initialized your camera with your selected values. If you do not get a sucessful output of this Button (Video Probe-Commit Control) you can not use the app with your phone / camera. If this output fails, you may contact the developer or try to run the manual Uvc setup method again. If you were sucessful, then you can proceed with reading out the camera frames (first only over the Text View, because your frames may be corrupted or too short or .. To receive some data from your camera, your press the Button again and then on and then on . You then should receive the first frame data from your camera.
The first data which was received on the picture above, were 39950 byte in this case. This means that the camera communicats with the android device and trys to submit the frame data. But the data received above is much to less for a frame Image of a sample size of 640 x 480. So tbe Values «ActiveUrbs» and «PacketsPerRequest» should be raised to get a better output: in my case to 16 Packets and 16 Urbs. If you were not able to get the frame data from your camera, then re-run the manual setup method and change same values. (lower the maxPacketSize, raise activeUrbs, raise packetsPerRequest). To raise the vales for (packetsPerRequest and activeUrbs) you can re-run the setup method or you click on the Button There you should only change the values for these two values (packetsPerRequest and activeUrbs). If you re-run the manual method, you can keep your values by clicking on done, or type in new values to change em.
Here you see, that the frame now gots larger —> 614400 —> this is exact the size of imageWidth x ImageHight x 2 —> 640 x 480 x 2. So in the shown case, the correct setting was found and now the camera setup is finished! Sometimes cameras compresses the frames they send to the devices, so in some cases you have to receive frames with a nearly same size too each other (use the 2nd method from the testrun menu —> «Frames for 5 seconds») When all frames are identically (or nearly) and also all methods above were sucessful, you have sucessfuly finish the setup. You will sure have to spend more time to figure out the right values, but if you have found them, save them and later you can easy restore them any time. If you want to delete some savefiles you will have to manually do this with a file explorer (but only this one you do not need any more) To the Button «Frames for 5 secound»: Have a look at your frames: If they are all identically and big enougth, than you can proceed to start the camera stream with the button from the main screen. Otherwise you have to edit some values for your camera: Perhaps -PacketsPerRequest- or -ActiveUrbs-, or something else. Click the —> Button to start the transmission. If everything works, you can watch the video of your camera.
Descripton of the Camera Values:
Alt-Setting: The Alt-Setting is a camera specific setting which defines which interface of your camera shall be used for the isochronous data transfer.
Maximal-Packet-Size: Each Alt-Setting has its own Maximal-Packet-Size. The Maximal-Packet-Size is byte Number which defines how many bytes each Packet of the iso transfer maximal contains.
Format-Index: Your Camera can support different Format Indexs. This could be MJPEG, or uncompressed (YUV) or .
Videoformat: This is a helper value, which has to be set to your selected Format-Index. You have to enter YUV, or MJPEG, or .
Frame-Index: Each Format-Index of your camera can have different Frame Indexs. This is a number which represents the camera resolution (1920×1020, or 640×480)
Image-Width, Image-Hight: This are helper values, which have to be set to your selected Frame-Index. For Example: Image-Width = 640 and Image-Hight = 480
Frame-Interval: The Frame-Interval is a number which defines, on how much nano secounds each new frame will be sent from the camera to your device.For example: 666666 means each 0,066 Secounds a frame is sent. 666666 = 15 frames per secound.333333 are 30 Frames per secound
Packets-Per-Request: This is a value wich defines how many Packet will be sent from your camera to your device in one cycle of the transfer.
Active-Urbs: And this value defines have many cycles are running paralell to each other in the data steam between camera and Android device.
Источник
Building and Using the UVC Camera Driver Sample
The UVC (USB Video Class) Camera Driver Sample demonstrates how to access a USB camera from within Android.
Overview
The UVC Camera Driver Sample is an implementation of an External Camera using the Vuforia Engine Driver Framework and has been designed to work on both handheld devices and Qualcomm’s Dragonboard 410C . You can download the UVC Camera Driver Sample from the Vuforia Developer Portal.
The sample plugin uses an open source UVCCamera library to access camera frame data from USB-cameras. This library uses modified versions of libusb and libuvc to handle the USB-cameras. Unmodified versions of libuvc and libub do not work directly on Android because the USB-device handles can’t be obtained in the same way as on a standard desktop Linux-system. So Android’s USBManager is needed to obtain a device handle and then inject it into libusb through libuvc . The UVCCamera library that this sample uses have implemented the device handle injection.
The current supported cameras profiles are:
- Logitech HD Webcam c310 / c910
- Microsoft LifeCam Studio
The UVC Camera Driver uses the Java-based Android USBManager API to access camera data. As the Driver needs to be implemented in C++, a pointer to the current JVM-instance needs to be injected through the Vuforia Engine stack into the Driver using the userData pointer passed in with the Vuforia::setExternalProviderLibrary() call. Then inside the Driver a JNI (Java Native Interface) is used to call the USBManager using the injected JVM-pointer. The Android USBManager is used to obtain a device handle for the attached webcam, which is then passed to libuvc and libusb .
Minimum Requirements
The UVC Camera Driver requires phones, tablets or the Dragonboard running Android 6 or later.
Building the UVC Camera Driver
Prerequisites
- Operating System: Refer to Vuforia Engine Supported Versions for supported systems
- Python 2 or later
- Bash (required on Windows https://git-scm.com/downloads)
- CMake 3.6 or greater
- Ninja build system (https://ninja-build.org)
- Android NDK 13b
- git
- Android SDK with API level 22 support
- libuvc, libusb, libjpg-turbo
Build the Dependencies
- Download Vuforia Engine for Android from the Vuforia Engine Developer Portal
- Download the UVCDriver Sample from the Vuforia Engine Developer Portal
- Extract the Vuforia Engine for Android package
- Extract the UVC Driver Sample package to the VuforiaSDK/Samples directory. The UVCDriver directory should be located in VuforiaSDK/samples/UVCDriver/
- Clone the https://github.com/ptc-shunt/UVCCamera repository to VuforiaSDK/Samples/UVCDriver directory. The UVCCamera directory should be located in VuforiaSDK/samples/UVCDriver/UVCCamera
- Open terminal and change directory to the jni-build directory: UVCCamera/libuvccamera/src/main/jni
- Run ndk-build from NDK 13b:
- [path-to-ndk-on-your-machine]/ndk-build ( ndk-build.cmd on Windows)
Compile UVC Camera Driver
These instructions assume that the “Compile Dependencies” section above was followed.
- Go to the VuforiaSDK/samples/UVCDriver directory
- Run python build.py (For more build options, use python build.py —help )
- This should compile the plugin and copy all the dependencies into UVCDriver/build/bin .
NOTE: It also creates an intermediate directory to ../../build_android .
Using UVC Camera Driver
- Add libUVCDriver.so , libuvc , libusb and libjpeg-turbo from build/bin into your Android-app project. The libraries can be added to an app depending on your build system: Using Android.mk or CMakeLists.txt or Gradle . Please note that you need to substitute ‘ [path-in-your-filesystem] ‘ with the correct path.
Using Android.mk
Add library definitions to your Android.mk :
When defining your local module in the same Android.mk add prebuilt libraries as dependencies to your LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES :
CMakeLists.txt:
When linking libraries in CMake, link libraries in the same CMakeLists.txt :
Using Gradle
This can be done in your app/build.gradle with the following:
Add UVCDriver.jar from build/bin into your Android-app project.
This can be done in your app/build.gradle with the following:
Add following call to your source code before calling vuEngineStart() :
- It is required to call requestUSBPermission to start the external USB camera.
- For Kotlin, after the driver is loaded, this code must be added to the applications Activity to request permission to access the camera.
Unity specifics
In Unity, after the driver is loaded, this code must be added to the application to request permission to access the camera.
Creating a New Camera Profile
Calibration Information
To add additional camera profiles to the UVC Camera Driver, please follow the steps outlined in External Camera Calibration Instructions. Once the calibration data has been produced, create a new CameraDevice-node in the ExternalCameraCalibration.xml file that is in the UVCDriver/src/main/assets directory. A sample node is shown below.
In addition to the calibration data, the following camera information must also be provided:
- VendoriID, integer in hexadecimal format
- ProductID, integer in hexadecimal format
Both of these values can be obtained from a desktop operating system such as Windows or Mac.
- Go to “Control panel” -> “Device manager”
- Find your webcam. It will be under “Cameras” or “Imaging Devices”
- Right click on your webcam and select “Properties”
- Go to the “Details”-page and select “Hardware Ids” from the dropdown menu
- Click the “Apple” Icon on top-left corner of the screen.
- Select “About this Mac” -> “System Report”
- From the Hardware-list select the Camera and find the correct camera.
Источник