Среда выполнения Android — Android Runtime
| Разработчики) | |
|---|---|
| Репозиторий | android .googlesource .com / платформа / искусство / |
| Написано в | C , C ++ |
| Операционная система | Android |
| Тип | Среда выполнения |
| Лицензия | Лицензия Apache 2.0 |
| Веб-сайт | источник .android .com / devices / tech / dalvik / art .html |
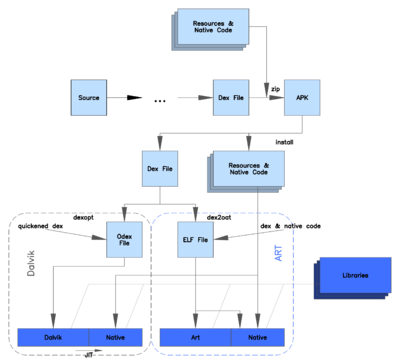
Android Runtime ( ART ) — это среда выполнения приложений, используемая операционной системой Android . Заменяя Dalvik , виртуальную машину процесса, изначально используемую Android, ART выполняет преобразование байт-кода приложения в собственные инструкции , которые позже выполняются средой выполнения устройства.
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
Обзор
Android 2.2 «Froyo» привнес в Dalvik JIT-компиляцию на основе трассировки , оптимизируя выполнение приложений за счет постоянного профилирования приложений каждый раз, когда они запускаются, и динамической компиляции часто выполняемых коротких сегментов их байт-кода в собственный машинный код . В то время как Dalvik интерпретирует остальную часть байт-кода приложения, собственное выполнение этих коротких сегментов байт-кода, называемых «трассировками», обеспечивает значительное улучшение производительности.
В отличие от Dalvik, ART вводит использование предварительной компиляции (AOT) путем компиляции целых приложений в собственный машинный код после их установки. Исключая интерпретацию Dalvik и JIT-компиляцию на основе трассировки, ART повышает общую эффективность выполнения и снижает энергопотребление, что приводит к повышению автономности работы от батареи на мобильных устройствах . В то же время ART обеспечивает более быстрое выполнение приложений, улучшенные механизмы выделения памяти и сборки мусора (GC), новые функции отладки приложений и более точное высокоуровневое профилирование приложений.
Для обеспечения обратной совместимости ART использует тот же входной байт-код, что и Dalvik, предоставляемый через стандартные файлы .dex как часть файлов APK , в то время как файлы .odex заменяются исполняемыми файлами в формате ELF. Как только приложение скомпилировано с помощью установленной на устройстве утилиты dex2oat ART , оно запускается исключительно из скомпилированного исполняемого файла ELF; в результате ART устраняет различные накладные расходы на выполнение приложений, связанные с интерпретацией Dalvik и JIT-компиляцией на основе трассировки. Недостатком ART является то, что при установке приложения для компиляции требуется дополнительное время, а приложения занимают немного больше вторичного хранилища (обычно флэш-памяти ) для хранения скомпилированного кода.
Android 4.4 «KitKat» предоставляет предварительную версию технологии ART, включая его в качестве альтернативной среды выполнения и сохраняя Dalvik в качестве виртуальной машины по умолчанию. В последующем крупном выпуске Android, Android 5.0 «Lollipop» , Dalvik был полностью заменен на ART.
Android 7.0 «Nougat» переключил свою среду выполнения Java с прекращенной Apache Harmony на OpenJDK , представив JIT-компилятор с профилированием кода для ART, что позволяет постоянно улучшать производительность приложений Android при их запуске. Компилятор JIT дополняет текущий опережающий компилятор ART и помогает повысить производительность во время выполнения и сэкономить место для хранения за счет компиляции только некоторых частей приложений.
Источник
Android Runtime Improvements
Android Runtime (ART) is an application runtime environment used by the Android operating system. Replacing Dalvik, the process virtual machine originally used by Android, ART performs the translation of the application’s bytecode into native instructions that are later executed by the device’s runtime environment.(ART introduced in Android L).
Every year google make changes in Android Run time to improve user experience and device performance.Before going to further on improvements let’s first discuss about ART in brief.
What is ART- ART is software layer between applications and operating system.It provide mechanism for executing java language.ART perform two major things to achieve this
1.Runs Android framework and Applications using hybrid model of Interpreter, JIT and profile based Ahead of time compilation(AOT).
2.Memory Management using Memory allocator and Concurrent compacting Garbage collector.
Changes Already happened in the previous years
1.Profile guided ahead of time compilation to improve app startup time,reduce memory usage and reduce storage requirements. Previously in Dalvik whenever app is launched app bytecode is decompiled every time.
2. Android 7.0 Nougat introduced JIT again to remove the need for optimizing apps during system upgrades and reboot. The JIT compiler complements ART’s current Ahead of Time compiler and helps improve runtime performance.
3. Improved Concurrent compacting garbage collector to reduce RAM requirements
What’s New in ART in Android P
- Kotlin optimizations-New Compiler optimization to help accelerate the performance in Kotlin code.Changes are made in Kotlinc compiler and D8/R8 bytecode converters to improve kotlin code performance rather than direct changes in ART.Improved Auto vectorization of loops.
2. Memory and storage optimization-This will be more helpful to entry level devices(i.e.Android Go devices with less memory and storage) to perform smoothly.
CompactDex(new dex format)-To reduce the amount of space and memory consumption by app we have to reduce dex files size by shrinking dex codes. Major part of Dex files consist code item instructions and StringData, so by reducing these sections we can optimize dex size.
When 64k Class methods crossed in android code multiple dex file is created that have duplication of some data(i.e.StringData) so in Android P Runtime “Shared data section ” is introduced inside Vdex Container.
Dex layout optimizations are also done to improve locality in code.Because During application usage only required parts is loaded into memory so improved locality provide startup time benefits and reduction in memory usage.
3. Cloud profiles-In Android P Cloud profiling is introduced to increase advantage of profile guided optimisations. Profiles are first introduced in Android N,it is the metadata Android run time captures about the application execution .This profile data will be used to profile guided optimization process.
How Profiling works-After we install app from playstore ART((JIT and interpreter)) decompile app and perform some optimization on the code. JIT system records this information in profile files..When device comes in idle mode these profiles are used for profile guided optimization and original app code is replaced with this optimized app code.Now this code is already and interpreted ,just in time compiled and pre-optimized. So app startup performance improved over the time user uses that app.
Advantage of Profile Guided Optimization-
- Faster startup
- Reduced memory footprint
- Less jank
- Less disk space used
- Increased Battery life
How Cloud profiling works— Profiles data from all the devices are uploaded on play console and a aggregate core profiles will be generated and whenever a new user install app, this core profile will be delivered alongside of app.So for new user profile guided optimisation will be performed right from first time install that will deliver improved cold startup and steady state performance.
Core profile data can also be used by developers to tune application code.
Profile aggregated using cloud profiling will provide a stable core profile by only 20–40 profiles from user. so if we release our app in alpha, beta channels then our productions user will get this core profile from start.
So that’s all about the changes in Android run time in Android P. For better understanding you can see full video here.
Источник