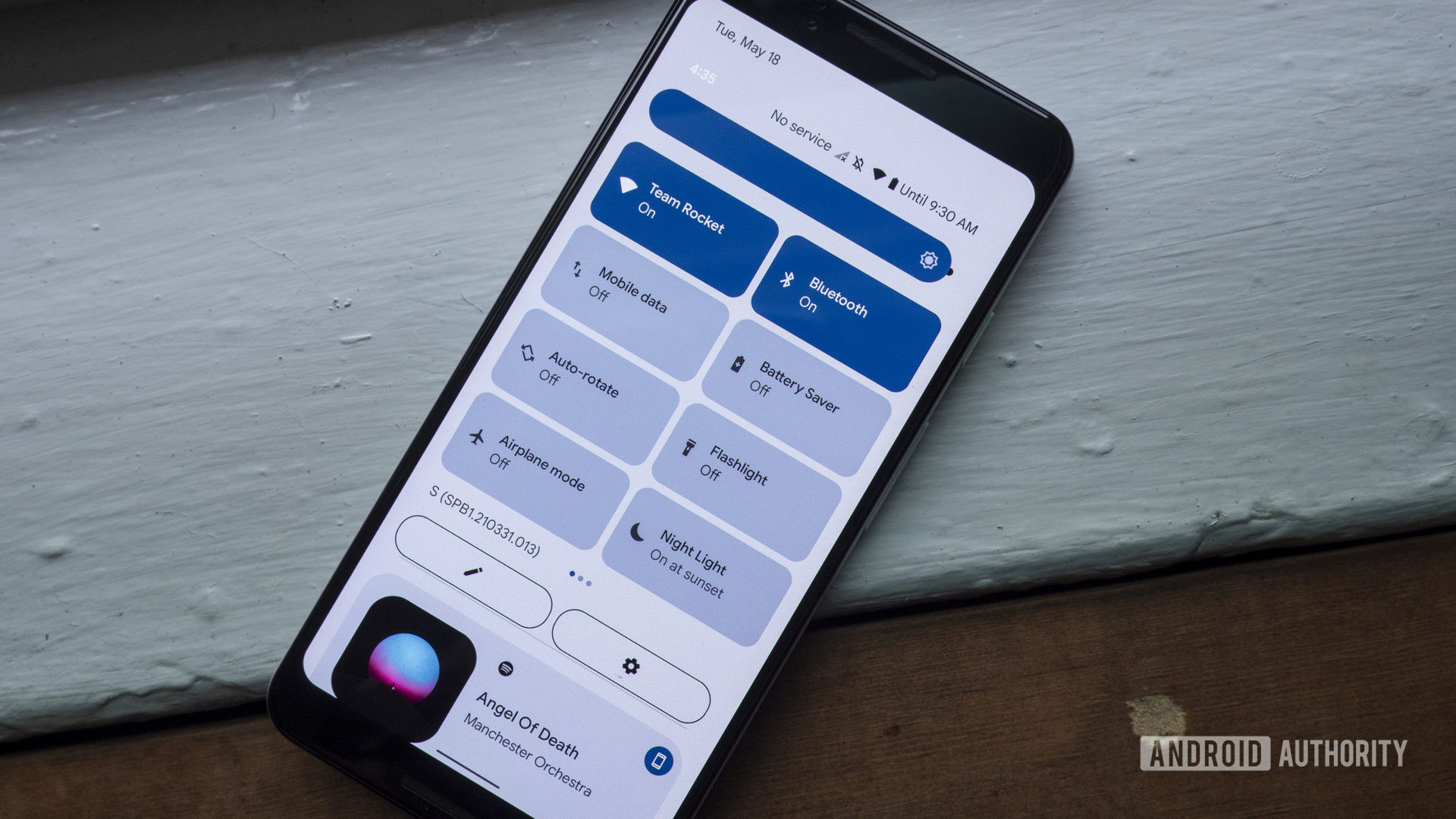
- 15 BEST Android Emulator in 2021 (Windows PC, Mac)
- Top Android Emulator for Windows PC, Mac
- 1) LDPlayer
- 2) Bluestacks
- 3) GameLoop
- 4) NoxPlayer
- 5)Memu
- 6) AndY
- 7)Genymotion
- 8)PrimeOS
- 9) Android-x86
- 10) ARChon
- 11) Ko Player
- 12) Droid4x
- 13)ARC Welder
- ❓ What is Android Emulator?
- ⚡ What are the benefits of using Android Emulator software?
- 💻 How do Android Emulators Work?
- 🏅 Which are the Best Android Emulators for PC?
- What is Android? Here’s everything you need to know
- What is Android? Here are the basics
- What is an operating system?
- Where you’ll find Android — from phones to smartwatches
- The early beginnings of Android
- Android is open source, but what does that mean?
- What is Android’s Google Play Service?
- Who maintains Android?
- Android versions: A brief history
- Android apps: How you can get them
- Android vs iOS: The mobile OS battle
15 BEST Android Emulator in 2021 (Windows PC, Mac)
Updated November 23, 2021
Following is a handpicked list of Top Android Emulator, with their popular features and website links. The list contains both open source(free) and commercial(paid) software.
LDPlayer offers an ideal Android emulation system. It provides plenty of comprehensive features to fulfill every which is performed by any Android device. You can download Android Games and apps from pre-installed LD Store or Google Play.
Top Android Emulator for Windows PC, Mac
1) LDPlayer
LDPlayer offers an ideal Android emulation system. It provides plenty of comprehensive features to fulfill every which is performed by any Android device.
Features:
- You can download Android Games and apps from pre-installed LD Store or Google Play.
- It helps you to manage your gaming automatically.
- Offers custom control with keyboard and mouse
- It allows you to open several games simultaneously.
- Supported Platform: Windows PC
2) Bluestacks
Bluestacks is a very popular Android emulator. It is one of the best Android emulator for PC that offers custom key mapping for keyboard configurations. It helps you to improve your target and reaction time while playing a game with the keyboard and mouse.
- You can play multiple games simultaneously.
- Record and replay any action in real-time.
- It allows you to do video recording and screen recordings.
- Supported Platform: Microsoft Windows, and Apple macOS.
3) GameLoop
GameLoop is an Android emulator that is used as a gaming platform. It is an ideal emulator if you want to play games on your desktop. GamLoop emulator includes many popular games like Call of Duty: Mobile and PUBG Mobile.
Features:
- It supports android PUBG mobile games and allows them to play on PC.
- This Android Emulator for Mac offers configured controls for playing PUBG games on PC.
- Users can customize PUBG mobile’s control overlay.
- This Emulator doesn’t ask for any type of account creation, so no need to register on it.
- This simulator works in a low configuration computer tool.
- Supported Platform: Windows, Mac
4) NoxPlayer
Nox Player is another Android Emulator which is recognized by gaming lovers around the world. You can run this Emulator on various devices that allows running multiple functions.
Features:
- It is one of the best emulator for PC that offers open keyboard mapping running with a single click, all gaming controls on the mouse, and keyboard.
- Nox player comes with a default macro recorder to record the complex operations.
- It offers the best user experience and superior performance.
- Supported Platform: Windows, Mac
5)Memu
Memu is easy to install an Android emulator app. It is one of the best Android emulator for PC which offers support for Intel and AMD chips, as well as integrated and dedicated graphics.
Features:
- Range of keyboard mapping options to enhance your gaming experience.
- Provide an option for virtualization.
- It offers various dedicated keyboard settings for the fast gaming experience.
- Supported Platform: Android and Microsoft Windows.
6) AndY
AndY is another popular Android emulator. It breaks down the main barrier between mobile and desktop computing by keeping the customer updated with the latest Android upgrades.
Features:
- It offers storage capacity to users and the freedom to play any games available on the Android platform with ease.
- It provides the feature of the phone as a joystick so that the user never has to leave multi-touch or amazing gaming elements.
- AndY offers smooth interaction between mobile and desktop devices.
- This Android Emulator for Mac allows users to download any app from any desktop browser to AndY OS.
- Supported Platform: Android, macOS, and Microsoft Windows.
7)Genymotion
Genymotion is a multi-support Android emulator. The software helps you to speeds up testing, share live demos. You can also monitor performance across all devices.
Features:
- It offers high definition pixel compatibility, which provides better clarity on your PC.
- It is one of the best Android emulator for Linux that allows you to test the products in a secure virtual environment.
- It allows you to use a desktop webcam as the video source to record screencasts.
- This Android emulator for Ubuntu is capable of emulating more than 3000 Android device configurations like the Android version and screen size.
- This Android emulator for Mac has strong sensors, like GPS and multi-touch.
- Supported Platform: Android, Mac OS, Microsoft Windows, and Linux
8)PrimeOS
PrimeOS emulator provides a complete desktop experience the same as Mac OS or Windows with access to many Android applications. This Android Emulator is designed to bring you both worlds – a complete fusion of Android and PC.
Features:
- Support for dual boot with a single click with a PrimeOS installer.
- It combines the Android ecosystem with the system interface to provide a great gaming experience.
- It offers high performance when compared to the Windows budget system.
- Supported Platform: Android, Mac OS, and Microsoft Windows.
9) Android-x86
Android X86 is an open-source platform. This is an open-source Android emulator which is licensed under Apache Public License 2.0.
Features:
- Provide WiFi support with GUI.
- Power Suspend/resume (S3 mode)
- Offer Battery Status.
- V4l2 Camera support.
- It offers support for netbook native resolution.
- Allows mirror mode on external monitors.
- External storage automount support.
- Support external keyboard
- Supported Platform: Windows PC
10) ARChon
ArChone is Google’s official App Runtime for Chrome package. This streamlined Emulator has the ability to run any Android app as a ChromeOS app.
Features:
- Very lightweight because it is integrated with Google Chrome.
- You can use it with all operating systems.
- It is one of the best Linux Android emulators that provide support for the latest Android system.
- This Android emulator Linux can be used for all applications and Android games.
- Supported Platform: Windows, Mac, Linux
11) Ko Player
Ko player is an Android emulator tool that helps users gain the quality Android playing experience on their Windows PC or Mac. The main focus of this Emulator is to provide a lag-free gaming experience to its users.
Features:
- It allows you to take advantage of all the features and functions of Android without owning any device.
- Ko player has simple, easy to use, and interactive user interface.
- The built-in video recording allows you to record your favorite videos and enjoy them at your convenient time.
- This Android app emulator also allows you to record videos.
- Enhance gaming performance.
- You can record and share your gameplay with your friends or anyone you want.
- It comes with an inbuilt Google Play Store, thus giving you access to any app you want.
- Supported Platform: Windows, Mac
12) Droid4x
Droid4X is an Android emulator developed for Windows PC that allows you to user-run mobile applications and games using on a desktop. This Emulator supports most of the games available in the play store.
Features:
- It helps you to complete user experience on PC and supports the touch screen computer to work across devices.
- This Emulator allows you to customize controls as per their needs and can directly download the app to the Emulator.
- This Android emulator for Windows 10 provides supports for keyboard and gamepad for the quick configuration of games.
- Supported Platform: Windows PC
13)ARC Welder
ARC Welder is another Android emulator tool that allows Android applications to run on Google Chrome for Windows systems.
Features:
- It is one of the best Android emulators for Windows that allows you to test and run Android applications within Chrome OS to overcomes any runtime errors or bugs.
- You can test applications in the Google Chrome web browser.
- Supported Platform: Windows PC
❓ What is Android Emulator?
An Android emulator is a software application that allows your mobile to imitate Android OS features into your PC. It allows you to install Android Apps on your computer or laptop and use them natively. It is mainly used for debugging purposes.
⚡ What are the benefits of using Android Emulator software?
Here are some other reasons for using Android Emulator:
- It will have a larger display thus also offers better controls to use applications in computers.
- You don’t need to care about the battery life of your Android devices.
- PCs are highly powerful than Android devices so that it can handle HD games and videos at a decent speed.
💻 How do Android Emulators Work?
Android Emulators work on the principle of platform virtualization for both hardware and software. The AVD manager (Android Virtual Device) helps you to set up and do the configurations for virtual Android devices.
🏅 Which are the Best Android Emulators for PC?
Here are some of the best Android emulators for PC:
Источник
What is Android? Here’s everything you need to know
By now, most people know there are two prominent mobile operating systems: Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS. There used to be a lot more, but now pretty much every major mobile device runs one or the other. Being that this is a site with “Android” in its name, we might have visitors who wonder: “What is Android?” That’s actually a huge question, and we aim to answer it as thoroughly as possible here!
Even if you’re a smartphone pro, there could be a lot to learn about Android in the sections below. But if you’re new to the world of smartphones — or just the world of Android — this is the perfect place to get up-to-speed on the world’s most popular operating system.
What is Android? Here are the basics
Android is a mobile operating system that has been around for nearly 15 years. You’ll primarily find it as the base operating system of phones and tablets around the world. Additionally, there are other operating systems that natively support Android applications, including Chrome OS and Windows 11.
Search giant Google owns Android. However, the system is open source, which makes it freely accessible to anyone, even for commercial use. This makes Android very different from Apple’s iOS, macOS, and Microsoft’s Windows, which are all closed-source platforms.
Android is by far the world’s most popular operating system. Estimates suggest it runs on 2.5 billion active devices across the globe, with over three billion users — or roughly 39% of the entire global population. This dwarfs Apple’s iOS by a significant margin and even tops Microsoft’s Windows, which is the second-most-popular operating system globally.
There are over three million applications that work on Android. Most of these apps can be found on the official Google Play Store, but you can also sideload apps from the web. This variety makes Android phones very powerful and customizable — but also susceptible to viruses and other types of malware.
If you don’t know what some of these terms mean, don’t worry: we’re going to explain everything in more detail!
What is an operating system?
If you ask “What is Android?” you’re likely to hear back, “It’s an operating system.” That answer is only useful if you know what an operating system is!
In brief, an operating system is computer software that works to integrate hardware and software resources. It allows for different types of hardware to work together while simultaneously providing a platform for various bits of software to work with that hardware and, consequently, other pieces of software.
If that’s still confusing, think of the analogy of a stage play. To put on a play, you’ll need a stage, lights, microphones, and other pieces of hardware. You’ll also need actors, stage crew, ushers, and other workers, which would be analogous to software. In this analogy, the director of the play would be similar to an operating system, as they would act as a conduit that instructs everything on how to work together. Without the director, you’d just have a ton of unused hardware with a bunch of people running around with no idea what to do.
In the case of smartphones, Android acts as the “director” for the unique hardware in your phone and the apps you’ve chosen to install.
Where you’ll find Android — from phones to smartwatches
When most people think of Android, they think of phones. While it’s true that most Android devices are smartphones, there are plenty of other devices out there with Android on board.
Tablets are the most obvious secondary Android device. After all, they are just big phones, in many respects.
Android also appears on smartwatches. If you own a watch that runs on Wear OS, that is an Android-based operating system. What is an Android-based operating system? That’s when someone takes Android and tweaks it to make it something different but still based on the same core code.
There is also a TV platform, appropriately called Android TV. We also can’t forget about Android Automotive, which is Android-based software that powers vehicles. However, don’t confuse this with Android Auto, which is a way for smartphones to integrate with dash systems in cars.
Finally, there are other operating systems out there that are not based on Android but do support running Android apps. Recent versions of Chrome OS allow for this. That means pretty much all Chromebooks on the market also support Android apps. Starting in late 2021, Windows 11 will also support Android apps.
The early beginnings of Android
Believe it or not, Android started out as software for cameras. Andy Rubin and his team developed Android starting in 2003 by using core code from Linux, another open-source operating system. The idea was to make a universal operating system that all camera companies could use.
However, during the later development of Android, Rubin realized that smartphones were the future. He decided to revamp Android as a smartphone operating system instead. The idea didn’t attract much investment since Windows Phone, Symbian, and other phone operating systems were already dominating the market. Rubin and his team almost stopped development when they ran out of money.
In the end, a generous monetary gift from a friend kept the team going and Google swept in and bought Android for about $50 million in 2005. The Android team worked under Google to develop an operating system that worked well on mobile phones with physical buttons and full QWERTY keyboards.
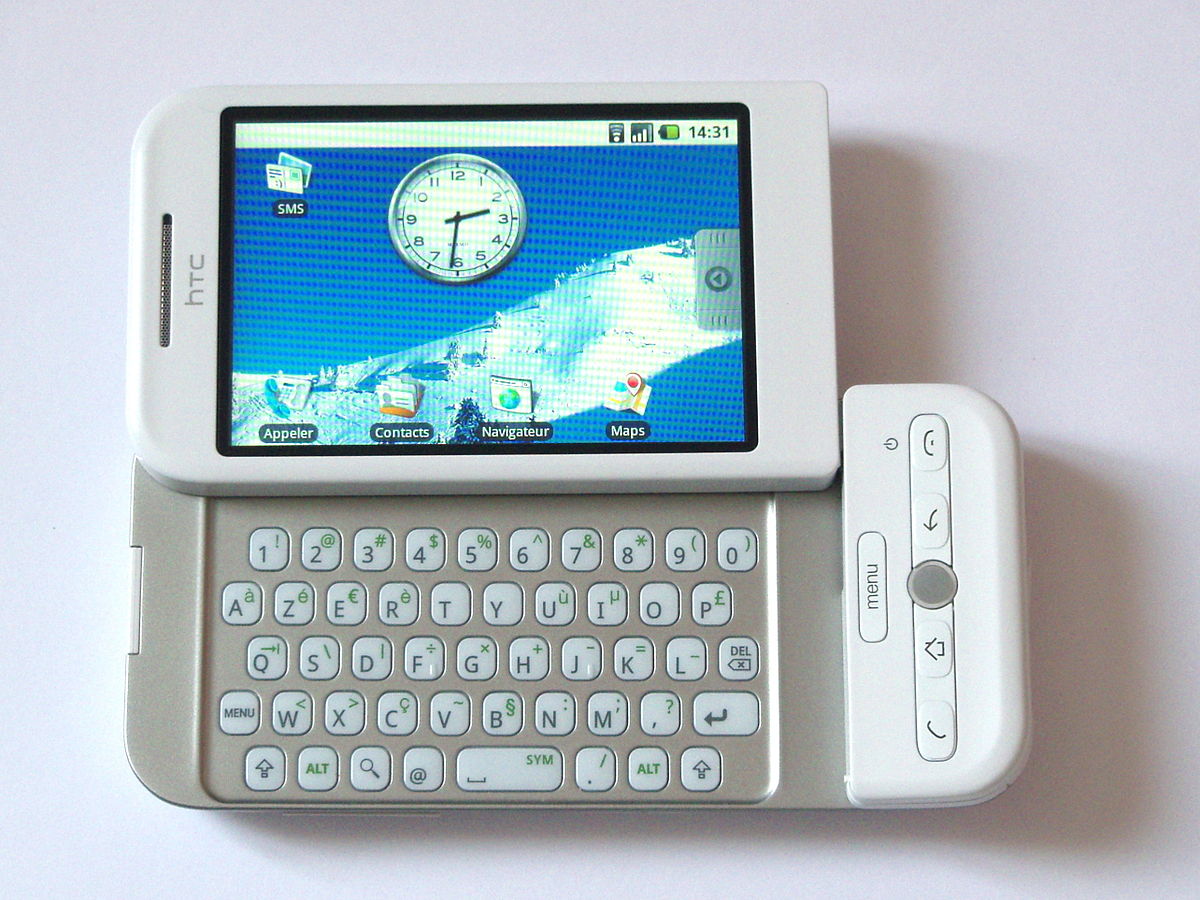
However, the arrival of the iPhone in 2007 forced the team to go back to the drawing board. They revamped Android again to also work with touchscreens. This resulted in the HTC Dream, also known as the T-Mobile G1, the very first commercial Android phone. It had a touch screen and a QWERTY keyboard, as seen above.
Since then, there have been thousands of Android phones and it is now the most popular operating system in the world.
Android is open source, but what does that mean?
When something is open source it means the copyright owner allows its use for any purpose, without any need for financial remuneration. As mentioned earlier, the core code of Android is based on open-source software called Linux. This means that Android, by definition, must also be open source.
To better understand this, let’s look at the opposite: closed-source software. Apple’s iOS is closed source, which means that no one can use it unless the copyright holder — in this case Apple — gives permission. If you were to obtain the source code of iOS and release it on any device, Apple could sue you for infringement on its ownership.
With open-source software, this limitation is gone. Instead, the person or company using the software simply needs to abide by a set of rules related to the licensing of that software. Our own Gary Sims explains these rules in the video above. In brief, this means that their “new” software must also be open source and they must make the code easily available to anyone who would like to use it.
The open-source nature of Android is one of the main reasons it is the most popular operating system in the world. Since anyone can use it for free, it’s incredibly easy for companies of all sizes to create terrific products without needing to invest in creating their own operating system. This is why you find Android in all manners of electronics from all sorts of different brands.
You might be wondering why Google is OK with giving away this product for free. The explanation is actually pretty simple, some aspects of Android you use on your phone are not open source. As you’d imagine, these are some of the most vital apps and services made for Android.
What is Android’s Google Play Service?
The core of Android is open source, which we call “stock” Android. This software lands as part of the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). This is Android in its purest, most basic form.
However, the Android you get with almost all smartphones has tons of other software incorporated that is not open source. Most of this software falls under a system called Google Play Services. This brings Google-branded products to Android, including the Google Play Store, Gmail, YouTube, etc.
In other words, you can use AOSP software all you like for free, but you can’t use Google all you like. Just like with Apple’s tight control of iOS, Google tightly controls Google Play Services. To use it, you need a license and to agree to let Google earn money from your products.
Even though most of the world closely associates Google and Android, there are plenty of Android-based devices out there without Google Play Services. For example, Google does not allow most of its products in China. If you go there, you can easily find Android phones without Google. There will be app stores, apps, and all sorts of familiar features, but not from Google. A more US-centric example would be Amazon’s Fire tablets, which utilize a custom version of Android called Fire OS that substitutes Google apps for Amazon’s own in-house options.
Throughout most of the world, though, Google is inseparable from Android. This is by design. Android’s dependence on Google earns the company billions.
Who maintains Android?
The answer to this question has a few facets. In brief, Google employees maintain the core Android experience. They are responsible for adding new features, updating old ones, and making sure Android follows open-source principles.
However, there’s more to it than that. Most manufacturers also “skin” Android, which means they create their own software that lives on top of Android. This is why the Android you find on a Samsung phone and the Android you find on a OnePlus phone function similarly but look very different. Each manufacturer maintains its own Android skin.
There’s also the question of distributing Android. Obviously, your phone comes with a version of Android when you first take it out of the box. But how does it get updates? Depending on how you bought the phone, an update could need to pass through multiple rungs. First, it needs to come from Google. Then, it needs to get tweaked by your phone’s manufacturer to make sure the skin still works well. Then, it may need to go through your carrier, because it also usually customizes phones it sells.
This long chain of events is one of the big reasons why Android phones don’t see updates as often or for as long as iOS devices. For iPhones, Apple controls everything. There are no skins and carriers have little ability to interfere with how iOS looks and works. In essence, Apple can push an update to every iPhone around the world quickly and easily with little influence from carriers or other companies. Android phones don’t have this luxury.
Android versions: A brief history
As of today, there have been 18 versions of Android, with 11 major releases. The most recent stable version of the operating system is Android 11. We expect Android 12 to land later in 2021, at the end of August or the beginning of September, which will make it the 19th version and 12th major release.
Originally, Google named Android after “sweet treats.” Each treat name happened in alphabetical order, starting with the letter “C” in 2009. However, Google abandoned this trend in 2019 with the launch of Android 10.
Here are all the major Android releases:
- 2009 — Cupcake (v. 1.5)
- 2009 — Donut (v. 1.6)
- 2009 — Eclair (vs. 2.0, 2.0.1, and 2.1)
- 2010 — Froyo (vs. 2.2 through 2.2.3)
- 2010 — Gingerbread (vs. 2.3 through 2.3.7)
- 2011 — Honeycomb (vs. 3.0 through 3.2.6)
- 2011 — Ice Cream Sandwich (vs. 4.0 through 4.0.4)
- 2012 — Jelly Bean (vs. 4.1 through 4.3.1)
- 2013 — KitKat (vs. 4.4 through 4.4W.2)
- 2014 — Lollipop (vs. 5.0 through 5.1.1)
- 2015 — Marshmallow (vs. 6.0 through 6.0.1)
- 2016 — Nougat (vs. 7.0 through 7.1.2)
- 2017 — Oreo (vs. 8.0 and 8.1)
- 2018 — Pie (v. 9.0)
- 2019 — Android 10
- 2020 — Android 11
Android 11 introduced several new features related to messaging, privacy, security, and accessibility. However, it looked mostly the same as Android 10 and Android 9 Pie before it.
With Android 12, we expect Google to revamp the way the operating system looks and feels. There will also be even more features and controls related to privacy and security.
If you are curious which version of Android you have on your device, head to Settings > About > Software Information.
Android apps: How you can get them
Assuming you have a device with Google Play Services on board, the easiest and safest way to get Android apps is to use the Google Play Store. This comes pre-installed on all Google-supported phones, tablets, and other devices. Just open the app and search for whatever game, program, media, or other product you’re looking for. Many of them are free, but some will require payment.
If you don’t have a device with Google Play Services, you likely have access to a different app store. The most common example of this is Amazon devices, which come with the Amazon App Store pre-installed. Another example is modern Huawei devices, which will have App Gallery. Consult your device’s manufacturer if you are unsure as to which app store you should be using.
Regardless of your device’s particular app store, you can also manually install Android apps by downloading them from the open web. This is called “sideloading.” Generally, this practice is safe. However, there is an inherent security risk to sideloading apps as they do not need to meet the safety requirements enacted by app stores. As such, you should only sideload apps from trustworthy sources.
If you are looking for some suggestions of apps you should install, we have plenty of articles to help with that:
Android vs iOS: The mobile OS battle
We’ve already touched a few times on what makes Android different from Apple’s iOS. However, we want to point out that the two operating systems have become much more similar than different over the years.
In the early days of the smartphone industry, Android and iOS were wildly different. Each OS offered features the other didn’t. They also didn’t look at all similar. This dichotomy created an “Android vs iOS” culture that still pervades today.
Really, though, there are only a handful of things Android can do that iOS can’t (and vice versa). Google and Apple have been cribbing from each other so much over the years that the two operating systems are closer than ever.
The only distinct difference between the two is how much control Apple has over iOS — and how Google doesn’t have that same level of control over Android. It is impossible to sideload apps on an out-of-the-box iPhone, for example, and there’s only one app store (the Apple App Store). Apple also tightly controls the kinds of apps developers can make for iPhones.
By contrast, we’ve already discussed how easy it is for you to install Android apps from other stores or even from the open web. Additionally, Google allows you to choose which apps you use for pretty much every smartphone function, from your browser to your messaging apps to your keyboard.
The advantage to Apple’s model is that iOS is more uniform, safer, and allows devices to see updates for long periods of time. The downside, of course, is that the user doesn’t have as much say as to what they can do with their device.
If you are moving from an iPhone to Android, we also have a guide to help with that transition, as you can see here.
If you came to this article asking yourself, “What is Android?”, we hope you’ve found your answer! Be sure to bookmark this page, as we will update it with new information regarding Android versions as they launch.
Источник