- Хранение данных и файлов
- Внешняя карта памяти
- Состояние на текущий момент
- Что делать?
- Android 11
- What Is Cached Data? How to Clear Cache Android, Chrome, etc. [MiniTool Tips]
- Summary :
- Quick Navigation :
- What Is Cached Data?
- Is Cached Data Important?
- What Does Clear Cache Mean?
- How to Clear Cache?
- 1. How to Clear Cache Android
- 2. How to Clear Cache Chrome
- 3. How to Clear Cache Firefox
- 4. How to Clear Cache iPhone
- How to Access and View Google Chrome Cache
- Can You Recover the Deleted Cache Files in Browsers and Devices
- 1. Use a File Recovery Program
- 2. Run a System Restore
- Conclusion
- What Is Cached Data FAQ
- ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Хранение данных и файлов
В целом хранение файлов и данных можно условно разделить на две группы: во внутреннем или внешнем хранилище. Но разница между ними довольна тонка. В целом политика Гугла в отношение данных ужесточается с каждой версии системы.
Android поддерживает различные варианты хранения данных и файлов.
- Специфичные для приложения файлы. Доступ к файлам имеет только приложение, их создавшее. Файлы могут находиться во внутреннем и внешнем хранилище. У других приложений нет доступа (кроме случаев, когда файлы хранятся на внешнем хранилище). Методы getFilesDir(), getCacheDir(), getExternalFilesDir(), getExternalCacheDir(). Разрешений на доступ не требуется. Файлы удаляются, когда приложение удаляется пользователем.
- Разделяемое хранилище. Приложение может создавать файлы, которыми готово поделиться с другими приложениями — медиафайлы (картинки, видео, аудио), документы. Для медифайлов требуется разрешение READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE или WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE.
- Настройки. Хранение простых данных по принципу ключ-значение. Доступно внутри приложения. Реализовано через Jetpack Preferences. Настройки удаляются, когда приложение удаляется пользователем.
- Базы данных. Хранение данных в SQLite. На данный момент реализовано через библиотеку Room. Доступ только у родного приложения.
В зависимости от ваших потребностей, нужно выбрать нужный вариант хранения данных.
Следует быть осторожным при работе с внутренним и внешним хранилищем. Внутренне хранилище всегда есть в системе, но оно может быть не слишком большим по объёму. Вдобавок к внутреннему хранилищу, устройство может иметь внешнее хранилище. В старых моделях таким хранилищем выступала съёмная SD-карта. Сейчас чаще используют встроенную и недоступную для извлечения флеш-память. Если ваше приложение слишком большое, можно попросить систему устанавливать программу во внешнее хранилище, указав просьбу в манифесте.
В разных версиях Android требования к разрешению для работы с внешним хранилищем постоянно менялись. На данный момент (Android 10, API 29) требования выглядят следующим образом.
Приложение может иметь доступ к собственным файлам, которые находятся во внешнем хранилище. Также может получить доступ к определённым общим файлам на внешнем хранилище.
Доступ к общим файлам достигается через FileProvider API или контент-провайдеры.
Для просмотра файлов через студию используйте инструмент Device File Explorer.
Внешняя карта памяти
Когда появились первые устройства на Android, то практически у всех были внешние карточки памяти, которые вставлялись в телефон. Обычно там хранили фотки, видео и свои файлы. Всё было понятно — были различные методы для доступа к файловой системе. А потом началась чехарда. В телефонах также была и собственная «внешняя» память. Она вроде как и внешняя, но вставлена на заводе и вытащить её пользователь не мог, т.е. практически внутренняя. Затем пошла мода на телефоны, у которых была только такая внутреннее-внешняя карта. Пользователи поворчали, но привыкли. Сейчас встречаются оба варианта. Как правило, у телефонов с спрятанной картой больше памяти и выше степень водонепроницаемости.
Подобные фокусы с картой породили и другую проблему — Гугл озаботился безопасностью файлов и стала думать, как осложнить жизнь разработчику. С выходом каждой новой версии системы компания то давала добро на полный доступ к карточке, то ограничивала, то давала права с ограничениями, то откатывала свои решения назад. Короче, запутались сами и запутали всех.
Попробуем немного разобраться с этим зоопарком. Но помните, что процесс путаницы продолжается.
При подготовке материала я опирался на письма некоторых читателей сайта, которые присылали свои мысли по этому поводу. Спасибо им за структуризацию материала.
Вот что я (кажется) понял, попытавшись загрузить картинку с внешней SD карточки.
External это не External
«EXTERNAL_STORAGE» называется так не потому, что это внешняя память по отношению к устройству, а потому что она выглядит как внешняя память для компьютера, если устройство подключить кабелем к компьютеру. Причём именно выглядит, потому что обмен идёт по протоколу MTP – устройство только показывает компьютеру список папок и файлов, а при необходимости открыть или скопировать файл он специально загружается на компьютер, в отличие от настоящей флешки, файлы которой становятся файлами в файловой системе самого компьютера. Обмен по MTP позволяет устройству продолжать работать, когда оно подключено к компьютеру.
Emulated это не Emulated
Сначала я пытался прочесть файл с карточки на эмуляторе (из этого так ничего и не вышло). Функция getExternalStorageDirectory() давала мне /storage/emulated/0, и я думал, что «emulated» – это потому что на эмуляторе. Но когда я подцепил реальный планшет, слово «emulated» никуда не исчезло. Я стал рыться в интернете и обнаружил, что «Emulated storage is provided by exposing a portion of internal storage through an emulation layer and has been available since Android 3.0.» – то есть это просто кусок внутренней памяти, которая путём какой-то эмуляции делается доступной для пользователя, в отличие от собственно внутренней памяти.
При этом с точки зрения системы доступная для пользователя папка называется /storage/emulated/0, а при подключении к компьютеру по USB это просто одна из двух главных папок устройства – у меня в Windows Explorer она называется Tablet. Вторая папка у меня называется Card, и это и есть настоящая внешняя карточка.
Нет стандартных средств добраться из приложения до файлов на внешней карточке. Все попытки добраться до настоящей внешней карточки делаются с помощью неких трюков. Самое интересное, что я нашел, это статья на http://futurewithdreams.blogspot.com/2014/01/get-external-sdcard-location-in-android.html — парень читает таблицу смонтированных устройств /proc/mounts, таблицу volume daemons /system/etc/vold.fstab, сравнивает их и выбирает те тома, которые оказываются съёмными (с помощью Environment.isExternalStorageRemovable()).
Оказалось, что несистемным приложениям в принципе запрещено напрямую обращаться к съёмной карточке! Похоже, что это было так всегда, но вот начиная с версии Android 6 Marshmallow написано: внешняя карточка может быть определена как Portable либо Adoptable. Adoptable – это как бы «усыновляемая» память которая может быть «adopted», то есть взята в систему (примерно как кот с улицы в дом – это тоже называется to adopt) и использована как внутренняя. Для этого ее надо особым образом отформатировать и не вынимать, иначе не факт, что система продолжит нормально работать.
Portable – это нормальная съёмная карточка, но несистемным приложениям запрещено обращаться из программ к файлам на ней! Вот что написано в https://source.android.com/devices/storage/traditional.html:
Android 6.0 supports portable storage devices which are only connected to the device for a short period of time, like USB flash drives. When a user inserts a new portable device, the platform shows a notification to let them copy or manage the contents of that device. In Android 6.0, any device that is not adopted is considered portable. Because portable storage is connected for only a short time, the platform avoids heavy operations such as media scanning. Third-party apps must go through the Storage Access Framework to interact with files on portable storage; direct access is explicitly blocked for privacy and security reasons.
Если я правильно понял, этот самый Storage Access Framework позволяет работать с документом на карточке через диалог (открыть файл/сохранить файл), а вот прочитать или записать файл на карточке непосредственно из программы невозможно.
Общий вывод – реально из программы можно работать только с файлами на предоставляемой пользователю части встроенной памяти устройства, а на съёмной карточке – нет.
Это напоминает войну Microsoft с пользователями и разработчиками по поводу диска C:, компания уговаривала не устраивать беспорядок в корне этого диска, а ещё лучше — перенести свои файлы на другой диск. Но явных запретов не было.
Состояние на текущий момент
Гугл утверждает, что с версии Android 10 Q стандартный доступ к файлам будет прекращён. Ещё в Android 4.4 появился Storage Access Framework, который и должен стать заменой для работы с файлами.
Методы Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() и Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory() признаны устаревшими и будут недоступны. Даже если они будут возвращать корректные значения, ими вы не сможете воспользоваться.
В Android 7.0 добавили исключение FileUriExposedException, чтобы разработчики перестали использовать схему file://Uri.
Можно создавать файлы в корневой папке карточки при помощи Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), а также папки с вложенными файлами. Если папка уже существует, то у вас не будет доступа на запись (если это не ваша папка).
Если вы что-то записали, то сможете и прочитать. Чужое читать нельзя.
Кстати, разрешения на чтение и запись файлов не требуются, а READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE и WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE объявлены устаревшими.
Другие приложения не могут получить доступ к файлам вашего приложения. Файлы, которые вы создали через getExternalFilesDir(), доступны через Storage Access Framework, кроме файлов, созданных в корне карточки (что-то я совсем запутался). Ещё можно дать доступ через FileProvider.
При подключении USB-кабеля через getExternalFilesDir(), вы можете увидеть свои файлы и папки, а также файлы и папки пользователя. При этом файлы и папки пользователя на корневой папке вы не увидите. Вам не поможет даже adb или Device File Explorer студии.
Что делать?
Пользуйтесь методами класса Context, типа getExternalFilesDir(), getExternalCacheDir(), getExternalMediaDirs(), getObbDir() и им подобными, чтобы найти место для записи.
Используйте Storage Access Framework.
Используйте MediaStore для мультимедийных файлов.
Используйте FileProvider, чтобы файлы были видимы другим приложениям через ACTION_VIEW/ACTION_SEND.
Android 10: Появился новый флаг android:allowExternalStorageSandbox=»false» и метод Environment.isExternalStorageSandboxed() для работы с песочницей. Флаг android:requestLegacyExternalStorage=»true» для приложений, которые ещё используют старую модель доступа к файлам.
Как временное решение можно добавить в блок манифеста application атрибут android:requestLegacyExternalStorage=»true», чтобы доступ к файлам был как раньше в Android 4.4-9.0.
Android 11
Если вы создаёте файловый менеджер, то ему нужны возможности для просмотра файлов. Для этого следует установить разрешение MANAGE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE или использовать атрибут android:requestLegacyExternalStorage=»true» (см. выше).
Источник
What Is Cached Data? How to Clear Cache Android, Chrome, etc. [MiniTool Tips]
By Alisa | Follow | Last Updated May 31, 2021
Summary :
What is cached data? This post offers an answer. You can also learn the advantages and disadvantages of cached data, what does clear cache mean, and how to clear cache in different browsers and devices. For deleted or lost data recovery, you can try the free data recovery software – MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
Quick Navigation :
What Is Cached Data?
According to Wikipedia, Cache is a component on your device that is used to store related data when you browse online or use an app. Cached data is usually composed of files, images, scripts, or other multimedia. It is stored on your device when you visit a website or open a program for the first time. When you revisit the same website or reopen the same app, it can quickly load that data.
Cache can be divided into hardware cache and software cache. Hardware caches include CPU cache, GPU cache, DSPs, etc. Software caches include disk cache, web cache, app cache, memorization, etc.
Browsers like Chrome and Firefox, streaming services like YouTube and Spotify, most games, and many other apps save related information as cached data and make use of these cache files to offer a faster browsing experience. For instance, you frequently visit a website that has many pictures in Google Chrome browser, it doesn’t need to download the images next time you open the web page. Therefore, you may also think of Cache as temporary storage as for what is cached data.
Is Cached Data Important?
The advantages of cached data: Reduce the loading time of pages, websites, or apps. Speed up the internet browsing process or app usage. Clearing the cached data may cause the thing to be slower since it needs to reload everything of a web page or app.
The disadvantages of cached data: If you never clear cache, then the cached data will be more and more, and occupy much space. This may make the device or app usage slow. Some problems of browser or apps may be owing to the corrupted cached data. Clearing cache may be a good way to fix a problematic app or browser.
Detailed guides for how to clear cache for one specific site in Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Safari, Opera browser, etc.
What Does Clear Cache Mean?
Clearing cache means deleting all the cached data. When you visit the webpage next time, everything on this page has to be downloaded again.
In general, clearing cache and clearing data mean the same thing. However, there are some differences between clearing cache and clearing data on Android. When you use an app on Android, the app stores the user settings, databases, and login information as data, whereas, it stores some other information like browsing history as cache. If you clear data on Android, it will clear both data and cache. If you only clear cache on Android, then the vital information like user settings won’t be deleted.
This post tells how to delete app usage history, delete all browsing history on Google, Firefox, Edge, IE, etc. in Windows 10/8/7 with step-by-step guide.
How to Clear Cache?
After analyzing what is cached data, you may find that Cached data isn’t that important. You can choose to keep it or clear it. You don’t need to clear it every day but you can clear cache regularly to prevent it from taking up more space on your computer or phone.
You can check the guides below for how to clear cache on Android, Chrome, Firefox, iPhone, etc.
1. How to Clear Cache Android
To clear cache for one app
For some older Android versions:
- You can tap Settings app, and tap Storage in Settings window.
- Tap Apps, and it will list all apps on your Android phone along with how much storage each app uses.
- Tap the target app that you want to clear cache.
- Tap Clear data or Clear cache button based on your own needs to clear data or cache of this application on Android. If you choose Clear cache option, then it will not delete the app data like account information.
For newer Android versions:
- Tap Settings -> Apps & notifications -> App management.
- Tap the target app you’d like to clear cache or data, and tap Storage.
- Then tap Clear cache to remove app caches, or tap Clear data to delete app data. Please be noted that the clearing cache or data action cannot be undone.
To delete caches for all apps on Android
- Some older Android versions let you delete all caches on Android. You can tap Settings -> Storage -> Cached data.
- In the pop-up Clear caches window, tap OK to clear caches for all apps.
2. How to Clear Cache Chrome
- Open Google Chrome browser on your computer.
- Click the three-dot Chrome menu icon at the top-right corner. Click More tools -> Clear browsing data.
- Select the time range. Check the “Cookies and other site data” and “Cached images and files” options. And click Clear data button to clear cached data of Chrome.
3. How to Clear Cache Firefox
- Open Firefox browser, and click the three-line icon at the top-right corner. Click Library -> History -> Clear Recent History.
- In the pop-up window, you can then choose a time range, and check Cache and Cookies options.
- Click Clear Now button to clear caches in Firefox.
4. How to Clear Cache iPhone
Unfortunately, iPhone doesn’t allow you to remove all cached files or delete caches for one app. But you can go to Settings app on your iPhone, and click General -> iPhone Storage. Check the list of apps and tap one app. Tap Documents & Data to check how much space this app occupies. If it uses much storage, you can click Delete App to uninstall this app and delete cached data, then download and reinstall this application.
How to Access and View Google Chrome Cache
What is cached data and how to clear cache? You should know now. You might also wonder how to access cache files, check below.
1. Chrome cache location in Windows: Google Chrome caches are stored in the folder: C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache.
You may go to the directory above to find Chrome cached data, but if you don’t find it, then the files may be hidden. You may need to show hidden files in Windows 10 before you can see the Chrome cache in Windows. To show hidden files, you can open a File Explorer window, click View -> Options, find and click “Show hidden files, folders and drives”, and click Apply and OK.
2. Alternatively, you can also use some third-party software like ChromeCacheView to read the cache folder of Google Chrome browser and list all cache files. This tool will display the cache file name, URL, content type, file size, last access time, etc. It lets you choose one or more cache files and extract them to another folder or copy them to the clipboard.
3. Some information online says that you can type About:cache in Google Chrome address bar to view the list of cache files and their paths, but this feature has been removed since Chrome version 66.
Can You Recover the Deleted Cache Files in Browsers and Devices
If you cleared the cache in Chrome, it’s not easy to recover it. But you may try the two ways below to see if it can help you get back deleted cache files or recover Google Chrome history.
1. Use a File Recovery Program
MiniTool Power Data Recovery is a smart free data recovery program for Windows. You can use this utility to recover any deleted or lost files from computer, SD card, memory card, USB, external hard drive, etc.
Download and install this clean and free data recovery software – MiniTool Power Data Recovery -on your Windows computer, and check how to use it to recover cached data below.
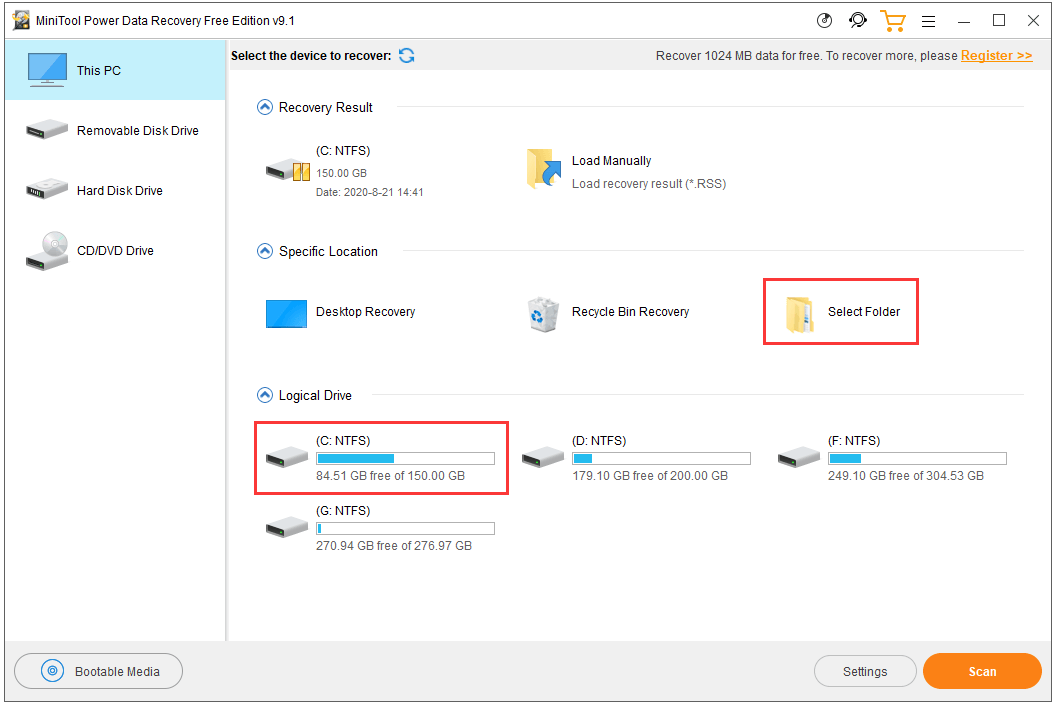
Select the location to scan:
- Run MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
- Double-click Specific Folder under Specific Location on the main interface.
- Select the folder that may contain the Chrome cache files. Based on the Chrome cache location, you can choose one of the directories in this path C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache, and click Open. MiniTool Power Data Recovery will start scanning the chosen folder.
- After the scan process finishes, you can check the recovery result to find if there are the cache files you deleted. Check the needed files and click Save button to save them to a preferred folder.
Select the whole C drive to scan:
If the specific folder scan doesn’t help you recover the deleted Chrome cache files, you may choose the whole C drive to scan.
- Launch MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
- Click This PC in the left column and click C drive in the right window. Click Scan button to scan the whole C drive.
- After the scan, check the scan result to find the cache files. You may follow the Google Chrome cached data folder path to find the cache files. Check wanted files and click Save button to store the recovered files to a new destination.
For Mac users, you can use the stellar Mac data recovery software to recover deleted/lost files.
Free pen drive data recovery. Easy 3 steps to recover data/files from pen drive for free (incl. corrupted, formatted, not recognized, not showing pen drive).
2. Run a System Restore
Another way to restore the deleted cache files of Google Chrome is to perform a System Restore for your computer. If you’ve ever created a system restore point for your computer, you may restore your computer to a previous state when you want. But be careful, you may lose some current data on your computer. If recovering cached data is not that important, it’s advised you do not take this risk, or at least, make a backup of your Windows OS and data at first with MiniTool ShadowMaker.
Conclusion
What is cached data? From this article, you can learn everything about cache, should you keep it or clear it, what does clear cache mean, how to clear cache on Android phone, Chrome, Firefox, iPhone, and how to recover cache files of Google Chrome, etc.
If you are interested in MiniTool Software products, go to its official website.
What Is Cached Data FAQ
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Position: Columnist
Alisa is a professional English editor with 4-year experience. She loves writing and focuses on sharing detailed solutions and thoughts for computer problems, data recovery & backup, digital gadgets, tech news, etc. Through her articles, users can always easily get related problems solved and find what they want. In spare time, she likes basketball, badminton, tennis, cycling, running, and singing. She is very funny and energetic in life, and always brings friends lots of laughs.
Источник