- Правильная работа с БД в Android
- How to Create and Add Data to SQLite Database in Android?
- What is SQLite Database?
- How Data is Being Stored in the SQLite Database?
- Important Methods in SQLite Database
- What we are going to build in this article?
- Step by Step Implementation
- Mastering Database Storage and Retrieval in Android
- SQLite
- Creating a Database in Android
- onCreate
- onUpgrade
- Adding Values within the Database
- Running Raw Queries on a Database
- To Run Queries on Database
- The Database Cursor
- Deleting Values from the Database
- Using Cursor Adapter to Display Data Values.
- Conclusion
Правильная работа с БД в Android
Приветствую всех дроидеров в эти непростые для нас времена.
Честно говоря, заколебала эта шумиха о патентах, войнах и т.д., но в данной статье речь пойдет не об этом.
Я не собирался писать статью на данную тему, так как везде всего полно о работе с базой данных в Android и вроде бы все просто, но уж очень надоело получать репорты об ошибках, ошибках специфичных и связанных с БД.
Поэтому, я рассматрю пару моментов с которыми я столкнулся на практике, чтобы предостеречь людей, которым только предстоит с этим разбираться, а дальше жду ваших комментариев на тему решения указанных проблем после чего внесу изменения в пост и мы сделаем отличный туториал, который будет образцом работы с SQLite в Android не только для начинающих, но и для тех, кто уже знаком с основами и написал простые приложения.
Способы работы с БД
Существует три способа работы с данными в БД, которые сразу бросаются на ум:
1) Вы создаете пустую структуру базы данных. Пользователь работает с приложением(создает заметки, удаляет их) и база данных наполняется. Примером может служить приложение NotePad в демо-примерах developer.android.com или на вашем дроид-девайсе.
2) Вы уже имеете готовую БД, наполненную данными, которую нужно распространять с приложением, либо парсите данные из файла в assets.
3) Получать данные из сети, по мере необходимости.
Если есть какой-то еще один или два способа, то с радостью дополню данный список с вашей помощью.
Все основные туториалы расчитаны как раз на первый случай. Вы пишите запрос на создание структуры БД и выполняете этот запрос в методе onCreate() класса SQLiteOpenHelper, например так:
Примерно так. Более полный вариант класса и других составляющих можно посмотреть по ссылке внизу статьи.
Дополнительно можно переопределить методы onOpen(), getReadableDatabase()/getWritableDatаbase(), но обычно хватает того, что выше и методов выборки данных.
Далее, экземпляр этого класса создаем в нашем приложении при его запуске и выполняем запросы, то бишь проблемная часть пройдена. Почему она проблемная? Потому что, когда пользователь качает приложения с маркета, то не задумывается о вашей базе данных и может произойти что угодно. Скажем сеть пропала или процесс другой запустился, или вы написали уязвимый к ошибкам код.
Кстати, есть еще один момент, на который стоит обратить внимание. Переменную экземпляра нашего класса можно создать и хранить в объекте Application и обращаться по мере необходимости, но нужно не забывать вызывать метод close(), так как постоянный коннект к базе — это тяжелый ресурс. Кроме того могут быть коллизии при работе с базой из нескольких потоков.
Но есть и другой способ, например, создавать наш объект по мере необходимости обращения к БД. Думаю это вопрос предпочтения, но который также необходимо обсудить.
А теперь самое главное. Что, если нам понадобилось использовать уже сушествующую БД с данными в приложении?
Немного погуглив, Вы сразу наткнетесь на такую «замечательную статью» — www.reigndesign.com/blog/using-your-own-sqlite-database-in-android-applications в которой, как покажется, есть нужная панацея. Но не тут то было. В ней еще и ошибок несколько.
Вот они:
1) В методе createDataBase() строка:
SQLiteDatabase dbRead = getReadableDatabase();
и далее код… содержит crash приложения на НТС Desire, потому что получаем БД для чтения(она создается), но не закрывается.
Добавляем строкой ниже dbRead.close() и фикс готов, но момент спорный.
Вот что говорит дока на тему метода getReadableDatabase():
Create and/or open a database. This will be the same object returned by getWritableDatabase() unless some problem, such as a full disk, requires the database to be opened read-only. In that case, a read-only database object will be returned. If the problem is fixed, a future call to getWritableDatabase() may succeed, in which case the read-only database object will be closed and the read/write object will be returned in the future.
Like getWritableDatabase(), this method may take a long time to return, so you should not call it from the application main thread, including from ContentProvider.onCreate().
И так. Данный метод не стоит вызывать в главном потоке приложения. В остальном все понятно.
2) Ошибка: No such table android_metadata. Автор поста выкрутился, создав данную таблицу заранее в БД. Не знаю на сколько это правильный способ, но данная таблица создается в каждой sqlite-бд системой и содержит текущую локаль.
3) Ошибка: Unable to open database file. Здесь много мнений, разных мнений, которые Вы можете прочесть по ссылкам ниже.
Возможно, что проблемы связаны с тем, что один поток блокирует БД и второй не может к ней обратиться, возможно проблема в правах доступа к приложению(было замечено, что чаще проблемы с БД проявляются на телефонах марки НТС именно на тех моделях, которые нельзя рутануть, хотя не только на них, например на планшетах Асер), но как бы то ни было проблемы эти есть.
Я склоняюсь к варианту, что проблема в потоках, не зря ведь нам не рекомендуют вызывать методы создания базы в главном потоке.
Возможно выходом из этого будет следующее решение(рассматривается вариант №2). Используя первый вариант работы с базой, наполнить ее данными после создания, например:
Данный подход еще нужно проверить на практике, но так как этот пост нацелен на выработку верного коллективного решения по данной тематике, то комментарии и пробы на даннную тему только приветствуются.
Мораль истории такова: если вы нашли какой-то хороший кусок кода для вашего решения, то проверьте его, не поленитесь, прежде чем копипастить в свой проект.
Вцелом, данный пост показывает(касательно способа №2) как делать не надо, но и также содержит пару любопытных мыслей.
Метод getReadableDatabase() можно переопределить например так:
Кстати: следуя практике самой платформы, поле первичного ключа стоит называть «_id».
Пишите в комментарии свои используемые практики. Мы сделаем данный пост лучше для всех, а может и мир станет чуточку добрее.
UPD Только что проверил свой подход. Все работает в эмуляторе, но будьте осторожны.
Файлик data.txt лежит в assets такой:
Zametka #1
Zametka #2
Zametka #3
Zametka #4
И класс приложения:
Отмечу, что данный класс используется только для демонстрации и проверки того, что произойдет при вызове методов getReadableDatabase()/getWritableDatabase() и создании базы. В реальных проектах код нужно адаптировать.
Кроме того в базе появилась табличка android_metadata(без моего участия), поэтому указанная выше ошибка решена.
Надеюсь кому-то пригодится.
Любопытные дополнения №1(от хабраюзера Kalobok)
Источник
How to Create and Add Data to SQLite Database in Android?
SQLiteis another data storage available in Android where we can store data in the user’s device and can use it any time when required. In this article, we will take a look at creating an SQLite database in the Android app and adding data to that database in the Android app. This is a series of 4 articles in which we are going to perform the basic CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operation with SQLite Database in Android. We are going to cover the following 4 articles in this series:
- How to Create and Add Data to SQLite Database in Android?
- How to Read Data from SQLite Database in Android?
- How to Update Data to SQLite Database in Android?
- How to Delete Data in SQLite Database in Android?
What is SQLite Database?
SQLite Database is an open-source database provided in Android which is used to store data inside the user’s device in the form of a Text file. We can perform so many operations on this data such as adding new data, updating, reading, and deleting this data. SQLite is an offline database that is locally stored in the user’s device and we do not have to create any connection to connect to this database.
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important Java Foundation and Collections concepts with the Fundamentals of Java and Java Collections Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.
How Data is Being Stored in the SQLite Database?
Data is stored in the SQLite database in the form of tables. When we stored this data in our SQLite database it is arranged in the form of tables that are similar to that of an excel sheet. Below is the representation of our SQLite database which we are storing in our SQLite database.
Important Methods in SQLite Database
Below is the several important methods that we will be using in this SQLite database integration in Android.
| getColumnNames() | This method is used to get the Array of column names of our SQLite table. |
| getCount() | This method will return the number of rows in the cursor. |
| isClosed() | This method returns a Boolean value when our cursor is closed. |
| getColumnCount() | This method returns the total number of columns present in our table. |
| getColumnName(int columnIndex) | This method will return the name of the column when we passed the index of our column in it. |
| getColumnIndex(String columnName) | This method will return the index of our column from the name of the column. |
| getPosition() | This method will return the current position of our cursor in our table. |
What we are going to build in this article?
We will be building a simple application in which we will be adding data to the SQLite database. We will be creating a database for adding course name, course description, course duration, and course tracks. We will be saving all this data in our SQLite database. A sample video is given below to get an idea about what we are going to do in this article. Note that we are going to implement this project using the Java language.
Step by Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a New Project
To create a new project in Android Studio please refer to How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio. Note that select Java as the programming language.
Источник
Mastering Database Storage and Retrieval in Android
Data has always been the most important part of any mobile application. Developers need to store substantial amounts of data in an organized fashion in order for their apps to be truly valuable to their users. In Android, you can store your data using quite a few different methods, both in active memory and in written files. Many apps also have a remote web service that provide the data for the app in question. Android also supports data storage in a local database, and the operating system provides a good infrastructure for storing and retrieving data. In most cases, the most simple and straightforward way to acquire and preserve user data is via SQLite databases.
SQLite
SQLite is a relational database technology that’s used most often when the developer requires an embedded database in a small system. SQLite is included with the Android system and can be easily used in your Android app. For more details on SQLite, you can visit http://www.sqlite.org and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SQLite
Creating a Database in Android
In order to write data to a database, we need to create our database first. To create a database in SQLite in Android, you need to create a subclass of the class SQLiteOpenHelper. This class provides the functionality to create a database and calls a function that can be overridden by the derived class. The SQLiteOpenHelper constructor accepts four arguments, which are
- Context – This is the context that will be used to create the database. (Here you can pass the Activity object.)
- Name – The name of the new database file.
- Factory – A cursor factory (you can usually pass this as null)
- Version – The version of the database. This number is used to identify if there is an upgrade or downgrade of the database.
Below, we I’ve created a class (MyDatabaseHelper) that is going to derive from SQLiteOpenHelper:
In the constructor above, we pass the name of the database that we want to create called as “MyFriendsDatabase.” We also override the following methods:
onCreate
This method is called when we create the database. It is passed the SQLiteDatabase reference, which we can use to perform various operations on the database. In this method, we use the function execSQL to execute an SQL query to create a table called “friends,” which has three columns. The first column, (_id) is required to generate a unique id for each column. This is necessary in case you are going to use classes like SimpleCursorAdapter (more on this later in the article). The second and third columns (name and phone number) are the data fields that we actually want to store.
onUpgrade
This method is called whenever the database is upgraded. In this method, SQLiteDatabase and the oldVersion number and newVersion number are passed.
In this function, we simply drop the “friends” table if it exists and create a new one, but there could be more complex logic based on the tables you are creating in the database and what you would want to happen on an upgrade.
Adding Values within the Database
Once the database is created, now let’s examine how we can add values to the database. We are going to use the insert function on the SQLiteDatabase class. The insert function takes three arguments: the name of the table in which to insert values, the name of one of the column of the table, and a reference to a ContentValues
In class MyDatabaseHelper below, we will write a function to insert values into the database.
In this function, we take the input arguments as the name and the phonenumber. Then, we create a new object of ContentValues, we put the values for name and phonenumber within that new object. Once we have done that, we get the SQLiteDatabase reference for writing using the function getWritableDatabase, which is a member of SQLiteOpenHelper. Once we have the reference of the SQLiteDatabase, we call the insert function, which takes the arguments as the table name, one of the columns of the table, and the ContentValues. This will enter a new row in your friends database table.
If I want to use MyDatabaseHelper to create a database and add some data values, the code would be as follows:
Here in our activity, we create a new object (MyDatabaseHelper) and then add some values in the table by calling the function addFriend.
Running Raw Queries on a Database
Once we have added the data into the database, we will now see how the data can be retrieved. To retrieve the data, there are two possible methods.
Runing a raw SQL query
We can directly run an SQL query likeВ SELECTto retrieve the records from the database.
To run a raw SQL query, you have the function rawQuery, which takes the SQL statement as a string as its first parameter and the selection arguments as its second parameter. So, if we have to write a function in MyDatabaseHelper to retrieve all records from table friends, it would be as follows:
To Run Queries on Database
We can also run queries on the database using the function query on the SQLiteDatabase. The query function lets you query on one table and also specify some selection and ordering criteria. The query function takes several arguments: the name of the table, the name of the columns of the table to retrieve, the selection criteria, the arguments for selection criteria, the group by clause, the having clause, the order by clause, and the limit.
If we have to write the same function above to retrieve all friends using query, it would be as follows:
The Database Cursor
The result of a query is returned in form of a Cursor object, which basically helps by caching the result of the query in an efficient way and providing functions to access the data.
If we want to fetch the data of all friends from the Cursor returned by the getFriends function, we would write the following code:
The cursor has functions such as moveToFirst, which moves the cursor to the first record, moveToNext, which moves the cursor to the next record, and isAfterLast, which checks if the Cursor has moved passed the last record.
The cursor also has functions like getInt, getString, etc., which take the index of the column and return the value.
Deleting Values from the Database
To delete values from the database, you can either run raw query or use the delete function on SQLiteDatabase. The delete function takes three arguments: the table name, the where clause, and the where clause arguments. The function to delete all values from the database is as follows:
Using Cursor Adapter to Display Data Values.
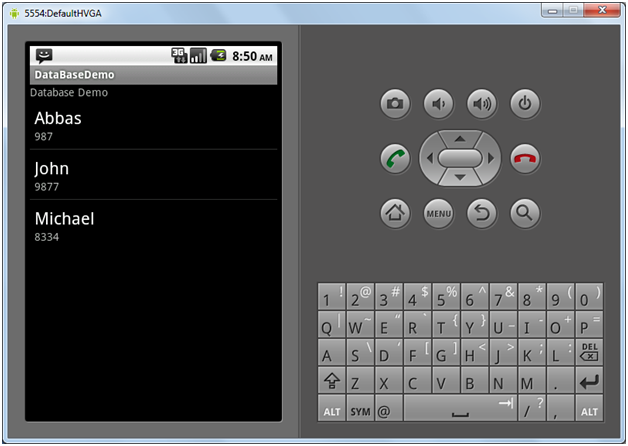
Android provides us with Cursor adapters, which let us attach a cursor with a ListView. The class SimpleCursorAdapter is one of these adapters, and it’s quite useful. If we want to show the list of friends in a list view, the code would be as follows:
Once we do this, the list of friends will appear on the Android device as shown below.
Conclusion
Data is the most important part of today’s competitive apps. A well-built app must store and retrieve data efficiently and with ease, so that it can function smoothly and please users. Android provides several forms of good support to store data in databases for your Android apps. It provides all the functionality to create and update SQLite databases and database tables. Make sure to make the most of it when designing your next Android app!
Источник