- What Is a Root Folder or Root Directory?
- Definition & examples of root folders and root directories
- Examples of Root Folders
- Accessing a Root Folder
- More About Root Folders & Directories
- Assets Folder in Android Studio
- How the asset folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
- But when to use which folder?
- How to Create Assets Folder in Android Studio?
What Is a Root Folder or Root Directory?
Definition & examples of root folders and root directories
The root folder, also called the root directory or sometimes just the root, of any partition or folder is the «highest» directory in the hierarchy. You can also think of it in general as the start or beginning of a particular folder structure.
The root directory contains all other folders in the drive or folder, and can, of course, also contain files. You can visualize this with an upside-down tree where the roots (the root folder) are at the top and the branches (subfolders) fall below; the root is what holds together all of its lower items.
For example, the root directory of the main partition on your computer is probably C:\. The root folder of your DVD or CD drive might be D:\. The root of the Windows Registry is where hives like HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT are stored.
ROOT is also an acronym for ROOT’s Object Oriented Technologies, but it has nothing to do with root folders.
Examples of Root Folders
The term root may also be relative to whatever location you’re talking about. For example, a program that installs to C:\Programs\Example uses that particular folder as its root, with potentially a series of subfolders beneath it.
This same thing applies to any other folder. Do you need to go to the root of the user folder for User1 in Windows? That’s the C:\Users\Name1\ folder. This, of course, changes depending on what user you’re talking about—the root folder of User2 would be C:\Users\User2\.
Accessing a Root Folder
A quick way to get to the root folder of the hard drive when you’re in a Windows Command Prompt is to execute the change directory—cd—command like this:
After executing, you’ll immediately be moved from the current working directory all the way up to the root folder. So, for example, if you’re in the C:\Windows\System32 folder and then enter the cd command with the backslash (as shown above), you’ll immediately be moved from where you’re at to C:\.
Similarly, executing the cd command like this:
. will move the directory up one position, which is helpful if you need to get to the root of a folder but not the root of the entire drive. For example, executing cd .. while in the C:\Users\User1\Downloads\ folder changes the current directory to C:\Users\User1\. Doing it again takes you to C:\Users\, and so on.
Below is an example where we start in a folder called Germany on the C:\ drive. As you can see, executing that same command in Command Prompt moves the working directory to the folder just before/above it, all the way to the root of the hard drive.
You may try to access a root folder only to find that you can’t see it when you’re browsing through Explorer. This is because some folders are hidden in Windows by default. See our article How Do I Show Hidden Files and Folders in Windows? if you need help unhiding them.
More About Root Folders & Directories
The term web root folder may sometimes be used to describe the directory that holds all of the files that make up a website. The same concept applies here as on your local computer—the files and folders in this root folder contain the main web page files, such as HTML files, that should be displayed when someone accesses the main URL of the website.
The term root used here shouldn’t be confused with the /root folder found on some Unix operating systems, where it’s instead of the home directory of a specific user account (which is sometimes called the root account). In a sense, though, since it’s the main folder for that specific user, you could refer to it as the root folder.
In some operating systems, files can be stored in the root directory, like the C:/ drive in Windows, but some OSs don’t support that.
The term root directory is used in the VMS operating system to define where all the user’s files are stored.
The root folder is the lowest level directory on your SD card. It’s the first folder you see when you open your SD card. You may see folders named DCIM and MISC, or you may see nothing at all if you recently formatted your memory card.
The /root directory in Linux is the user folder for the system administrator or root user. Like the Windows C:\Users folder, it has sub-directories for each user containing all the account’s data.
The /html folder is the root directory for your WordPress files. You can access the root folder via SFTP, SSH, or the File Manager.
Источник
Assets Folder in Android Studio
It can be noticed that unlike Eclipse ADT (App Development Tools), Android Studio doesn’t contain an Assets folder in which we usually use to keep the web files like HTML. Assets provide a way to add arbitrary files like text, XML, HTML, fonts, music, and video in the application. If one tries to add these files as “resources“, Android will treat them into its resource system and you will be unable to get the raw data. If one wants to access data untouched, Assets are one way to do it. But the question arises is why in the asset folder? We can do the same things by creating a Resource Raw Folder. So let discuss how the assets folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
How the asset folder is different from the Resource Raw folder?
In Android one can store the raw asset file like JSON, Text, mp3, HTML, pdf, etc in two possible locations:
- assets
- res/raw folder
Both of them appears to be the same, as they can read the file and generate InputStream as below
But when to use which folder?
Below is some guidance that might be helpful to choose
1. Flexible File Name: (assets is better)
- assets: The developer can name the file name in any way, like having capital letters (fileName) or having space (file name).
- res/raw: In this case, the name of the file is restricted. File-based resource names must contain only lowercase a-z, 0-9, or underscore.
2. Store in subdirectory: (possible in assets)
- assets: If the developer wants to categories the files into subfolders, then he/she can do it in assets like below.
3. Compile-time checking: (possible in res/raw)
- assets: Here, the way to read it into InputStream is given below. If the filename doesn’t exist, then we need to catch it.
- res/raw folder: Here, the way to read it into InputStream is:
So putting a file in the res/raw folder will provide ensure the correct file-name during compile time check.
4. List filenames at runtime: (possible in assets)
- assets: If the developer wants to list all the files in the assets folder, he/she has used the list() function and provide the folder name or ” “ on the root folder as given below.
- res/raw: This is not possible in this folder. The developer has to know the filename during development, and not runtime.
So, in assets, one can read the filename during runtime, list them, and use them dynamically. In res/raw, one needs to code them ready, perhaps in the string resources file.
5. Filename accessible from XML: (possible in res/raw)
So if you need to access your file in any XML, put it in the res/raw folder. Let’s make a table to remember the whole scenario easily.
| Res/Raw Folder |
|---|
| Flexible File Name NO |
| Store in subdirectory NO |
| Compile-time checking YES |
| List filenames at runtime NO |
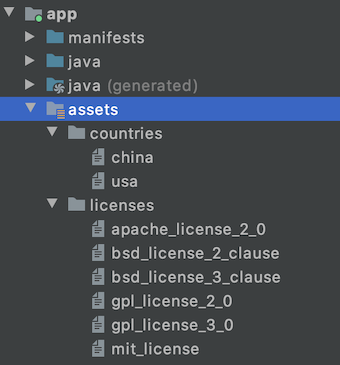
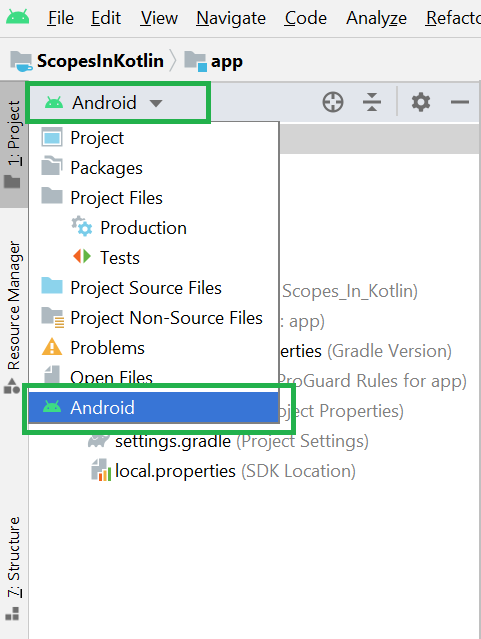
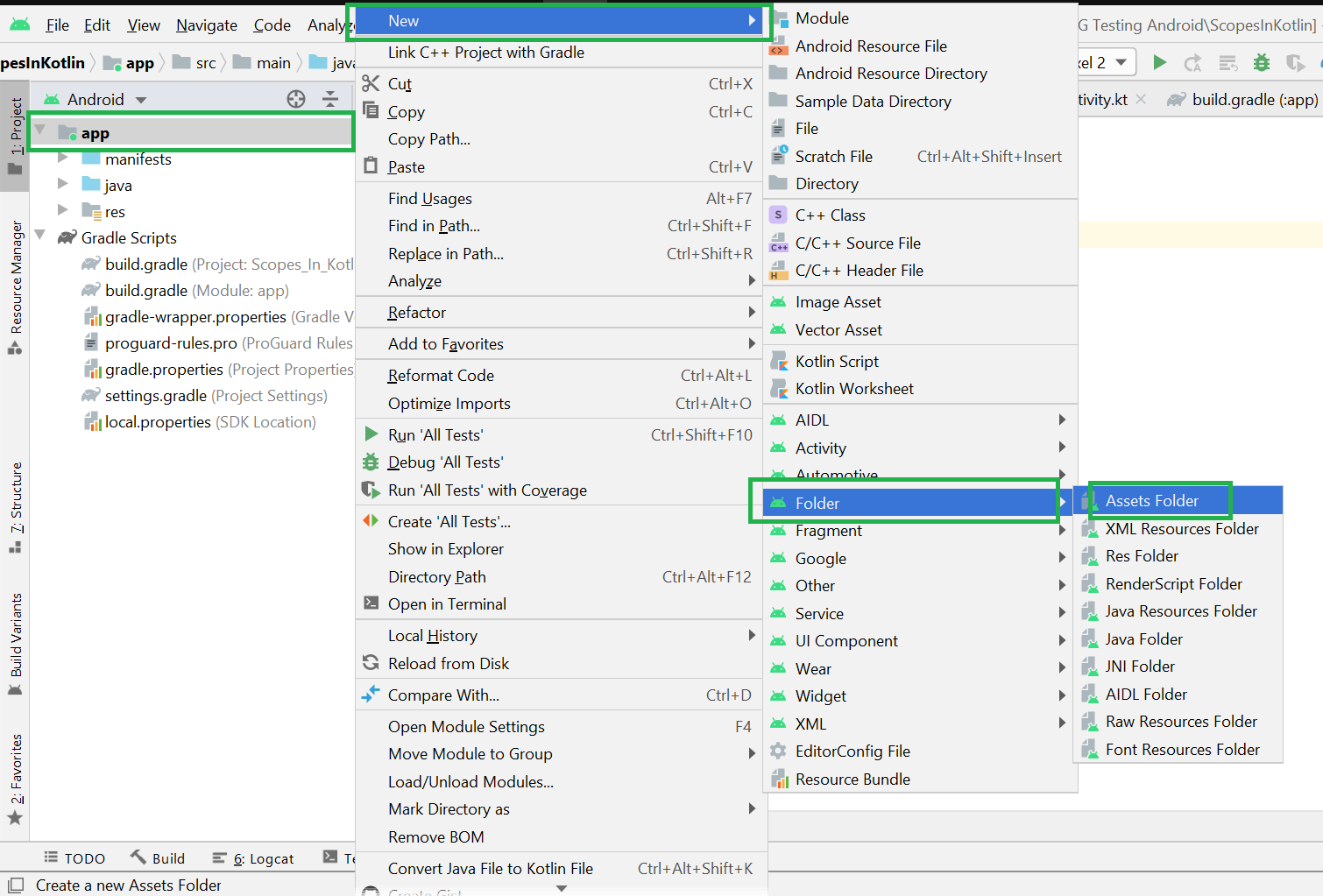
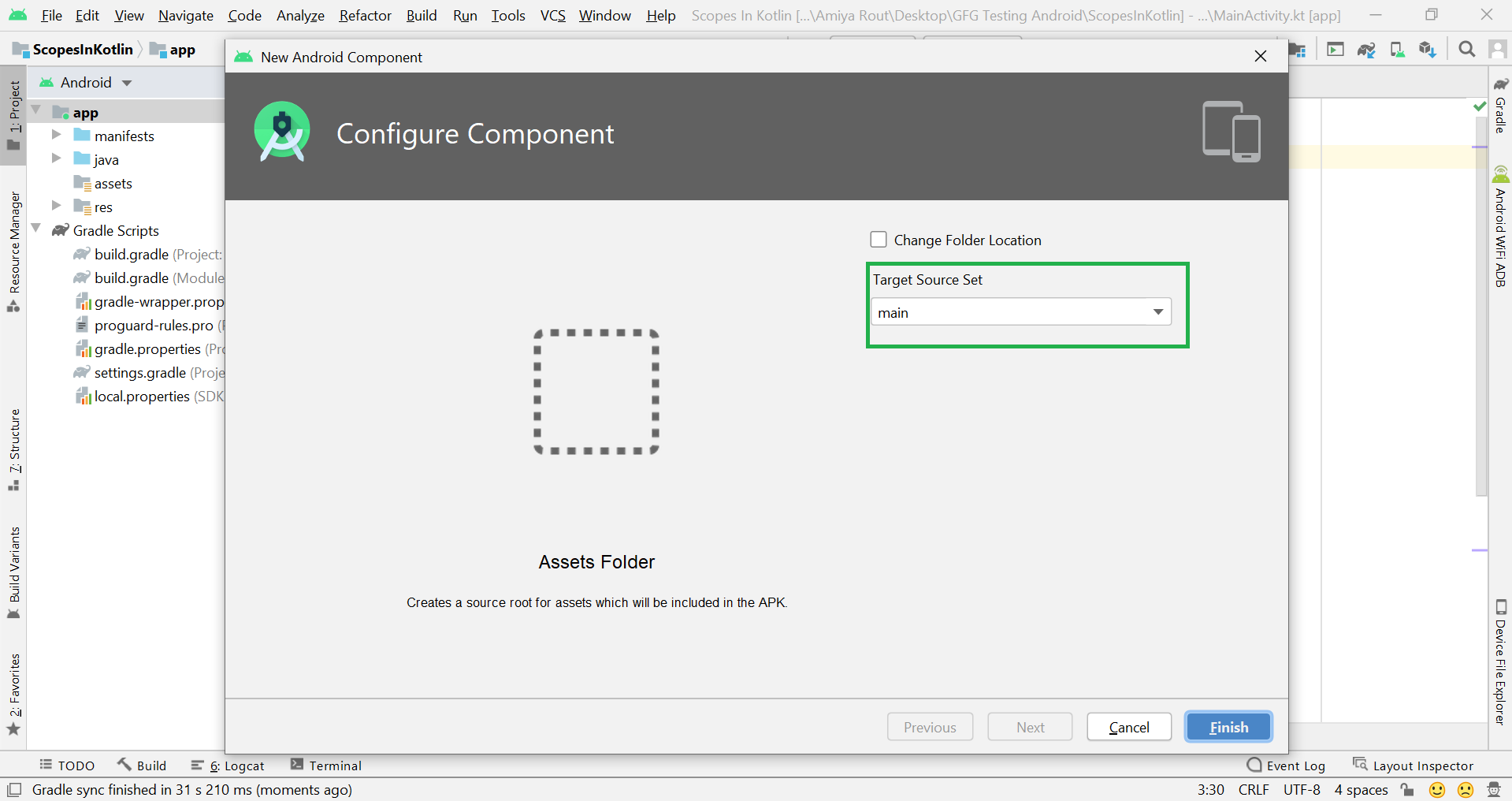
Filename accessible from XML How to Create Assets Folder in Android Studio?Now let’s discuss how to create an assets folder in the android studio. Below is the step-by-step process to create an assets folder in Android studio. Step 1: To create an asset folder in Android studio open your project in Android mode first as shown in the below image. Step 2: Go to the app > right-click > New > Folder > Asset Folder and create the asset folder. Step 3: Android Studio will open a dialog box. Keep all the settings default. Under the target source set, option main should be selected. and click on the finish button. Step 4: Now open the app folder and you will find the assets folder by the name of “assets” as shown in the below image. Источник |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tim-fisher-5820c8345f9b581c0b5a63cf.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WorkBadgePhoto-61c0b98ef5a74e4a85851a8f706dbd65.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/What-is-a-root-folder-or-root-directory-2625989-aafb8d25a54146879a236236ab8ea6c0.png)