- 6 Best Android OS for PC (32, 64-bit download)
- Android OS for PC list in 2021
- 1. Phoenix OS – for everyone
- 2. Prime OS – the newcomer
- 3. Android-x86 project
- 4. Bliss OS – latest x86 fork
- 5. FydeOS – Chrome OS + Android
- 6. OpenThos – ahh IDK
- Try Android Emulator; LDPlayer
- Other Options
- Windows Subsystem for Androidв„ўпёЏ
- Set up your development environment
- Prerequisites
- Install the Amazon Appstore
- Settings app
- Input compatibility considerations for Windows devices
- Keyboard input
- Mouse input
- Window management and resizing
- Minimum screen requirement
- Letter & pillar boxing
- Additional resizing considerations
- Test and debug
- Enable developer mode in Windows Settings
- Connect to the Windows Subsystem for Android for debugging
- Connect to a test device
- Debug your app
- VM lifecycle considerations
- VM Properties
- Security
- Amazon Appstore
- Troubleshooting issues with Amazon Appstore
- Building Universal APKs
- Uninstalling Windows Subsystem for Android
6 Best Android OS for PC (32, 64-bit download)
Get to know the best Android OS for PC available on the internet and learn how to install them. In this guide, we reviewed the popular Android Operating system available to download and use for free. After the drill-down list of the best android OS forks, we discuss other options to install or simulate the Android environment on your computer. All these operating systems can be downloaded in ISO system image which allows one to easily create a bootable USB (with Rufus) read the instruction at the end.
There are multiple reasons for using Android on a computer.
- Testing Android apps and games on computers.
- Android OS boots faster compared to Windows on old machines.
- You can WhatsApp your friends, or did I tell you setting up a VPN in Android is way easier.
Android OS for PC list in 2021
You can use these Android OS to bring all your favorite Android games and apps to your computer. You’ve many options to run Android OS on your PC, starting with Phoenix OS. Android is popular with millions of mobile users worldwide, installing and using Android on a computer is also possible, how?
Natively installing android on your computer allows games and apps to run butter smooth and without any fuss. You can run the Android operating system for both 32-bit and 64-bit machines. We understand that by now you should have received enough information about the Android operating system on computers. You can now you can easily decide which Android operating system you can install on your computer. If you know of any Android device for PC we are looking forward to hearing from you as well.
| AndroidOS fork | latest version | Release date |
|---|---|---|
| Androidx86 | 9 | March 2020 |
| Bliss OS | 10 | 2020 |
| FydeOS | – | 2021 |
| OpenThos | – | nil |
| Phoenix OS | 7 and 5 | Mid 2020 |
| Prime OS | Android 7 | Sept 2021 |
Android OS for pc table for overview.
1. Phoenix OS – for everyone
Phoenix OS was released shortly after the publication of the Remix OS. At the time it went popular, especially because it was the only Android operating system to work on 32-bit machines. PhoenixOS is a great Android operating system, which is probably because of features and interface similarities to the remix operating system.
Both 32-bit and 64-bit computers are supported, new Phoenix OS only supports x64 architecture. It is based on the Android x86 project. It has many good features if you want to play games like PUBG Mobile. The Phoenix OS installer makes it easier to install the operating system on your hard drive/USB drive. This is the only android x-86 fork that currently offering updates and hopefully, they will continue to do so in the future. This is one Android operating system for the computer which is based on Android 7. The downside is annoying ads and built-in apps.
2. Prime OS – the newcomer
Download PrimeOS (external link) | Dual boot PrimeOS (Quickfever article) Android 7, DecaPro Keymapping.
Prime OS is an operating system that gives a full desktop experience just like Mac and Windows. Combines the best of Android and computer features and the output is incredible. You are seeking a gaming Android operating system you should check this out. The special thing about it is deca-key mapping for gamers. Read our in-depth review on PrimeOS Sure, PUBG Mobile is on-trend and players have been using Android Emulators which doesn’t do justice to the game performance, the lag problem goes away when you use Android as an operating system on your computer. Also, It does not change aspects and aesthetics which is a good thing, we don’t require something heavily modded like MIUI.
3. Android-x86 project
Android x86 is the project to port AOSP-Android for x86 machines. The project plays a very significant role in all the mentioned Android operating systems. If you want a lightweight android operating system without customization, install the android OS build from here. You’ll get the same key features and interface seen on a real Android smartphone. If you lack good computer hardware you can test the KitKat/Marshmallow x86 build which is a 350+MB image file you can burn into a USB to create bootable media. After, simply boot and use the Android OS. Also android-x86 ports of Android Lollipop and Marshmallow you can use in computers with moderate hardware.
Note: For most users, the 64-bit version should just work fine, people with a single onboard processor can use the x86_64 build.
4. Bliss OS – latest x86 fork
Download Bliss OS | Android 11
Blisspop is pure Android x86 ports but with few modifications like the taskbar and system stability. You can also launch apps in Windowed mode rather than the full-screen which helps open two or more apps side by side. A note about Openthos and Bliss OS: When testing both OS failed to boot over UEFI firmware, they run successfully when Legacy mode was turned on from the BIOS settings. So if you have a computer with only UEFI firmware you maybe not be able to boot both of the Android Operating systems from a bootable media device.
But if you insist and like to test them you can use virtual machine software to run them on the operating system you are using. Some of the modern computers might have support for Legacy mode, but you need to enable it from the BIOS settings. So technically if you are running on Windows 8 or newer your computer probably has support for UEFI firmware in you might face problems booting these two so check in your BIOS settings if you can find Legacy mode and enable it.
- Latest Android version
- Compatibility with ARM and x86/x86_64 apps.
- 3 User Interface (Desktop, tablet, and stock) to choose from
People who care less about highly modified Android OS under a Windows look-alike skin but still want some usability features should try this.
5. FydeOS – Chrome OS + Android
Download FydeOS | Chromium OS with Android App support, 64-bit only. Use Eicher tool to make bootable USB.
FydeOS is based on a chromium fork to run on Intel computers. Version 10.x runs on running on Chromium r83 (I tested) and supports Android Apps. Despite you won’t find the play store as it was mainly focused on the Chinese market where Google services are banned. Still, you can sideload Android apps or even install the Google Play Store.
Since the last time we checked, it made lots of progress and booted quickly. Sadly 32-bit machine owners won’t be able to boot this operating system. You can choose a Google Account to log in to sync your Chrome Browser data. To install Android Apps, open “Android App” from the shelf (app drawer) it’ll ask for an agreement after that you can just download .apk file and open them to install.
Update 09/2021: Windows 11 will eventually support Android apps in near future.
6. OpenThos – ahh IDK
Project abandoned and unknown status | Download OpenThos
Openthos is new, and it supports Android apps and Linux apps in multi-windows. For this to run your computer’s CPU should be 64-bit architecture. Getting the ISO file of this operating was a task itself. First, you have to go through the link and enter the password, and later you need Baidu client software where you need to create an account (which is also problematic because everything will be in Chinese) then you can download the operating system image. Moreover, tested in the Legacy mode as it failed to boot in UEFI mode. If you really want to test put android OS on your computer, you may probably want Phoenix OS or something near stock-like Android x86. OpenThos vision is good on paper but still, it has not achieved a great user experience just yet.
Remix OS (Dead)
[Marshmallow, discontinued] Remix OS — the first best Android operating system is released in 2016 by Jide. It was the discussion topic because of its similarities to Windows 10: the taskbar, notification system, etc. Remix OS supports both 32-bit and 64-bit computer architecture and can be easily installed whether PC is UEFI-based or Legacy. If you want a great Android operating system, then Remix OS will work best. For starters, you have to make a bootable USB remix OS so you can directly boot and run on a computer. Then if you wish to keep running it from USB, you can do so by creating a persistence USB that will allow running this Android operating system from a USB drive. Otherwise installing it on the hard disk is a better option when you solely want to have this as your primary operating system.
Remix OS was probably the greatest Android OS until it was pulled off and discontinued. You can still use this operating system by downloading its system image, but you need to know that you will be using a system released back in 2016 with no future updates.
Bonus: Android 5 and 6 (android x86)
Android 5.1 for x86 fork: download and Android 6 download
If you have limited resources try the Android lollipop or marshmallow forks of the Android-x86 project. Android Lollipop is known to be the best fork available for x86 machines and popular Android emulators like LDPlayer run on version 5.1. To boot Android version 5 Android OS fork on your computer, download the appropriate ISO file using the links below and use Rufus to create bootable media.
Try Android Emulator; LDPlayer
LDplayer is an emulator to play online android games like PUBG Mobile and Call of duty. You would love to emulate the Android environment on your Windows computer when you have good hardware. It is possibly an amazing Emulator for playing PUBG mobile. Tested on an i5 (Gtx 1060) computer, it was able to run the game at 60fps, HDR extreme graphics, and 2K resolution. This is the best you can get from this game. Because it is a royale battle game, you may notice frame drops at certain times.
Other Options
Virtual Machines are much like emulators as they help you test any Android operating system in a simulated environment. You control resources like CPU and RAM to allow. For instance, you can select how much RAM and disk space to assign along with the CPU cores. VirtualBox and VMWare are some favorite free Virtual Machines. It is always good to test, and operate systems for you to use on your computer too quickly to know if you’re good to go with it.
Starting with a virtual machine is quite easy, first, download any of the Android OS ISO and save it from your on your computer. Open up your favorite Virtual Machine software and create a new environment and select the ISO image as a boot image. Please understand that installing an Android operating system on a virtual machine is not the best idea if plan to do intense tasks including Gaming.
Also, PUBG mobile players with emulators deal with game lag, screen tearing so it’ll be super awesome if you play these games on the Android operating system. Emulators only take a percentage of computer resources and won’t be able to give you a smooth Android experience.
Источник
Windows Subsystem for Androidв„ўпёЏ
Windows Subsystem for Androidв„ўпёЏ enables your Windows 11 device to run Android applications that are available in the Amazon Appstore.
If you’re a developer interested in targeting Windows desktop devices and optimizing for the Windows operating system, this guide is for you. Learn how to:
- Set up your development environment, including prerequisites, installing the Amazon Appstore, and using the Settings app.
- Handle input compatibility considerations for Windows devices, such as: keyboard input, mouse input, and window management and resizing.
- Test and debug your app on a Windows 11 device.
- Submit apps to the Amazon Appstore: Your app must be available in the Amazon Appstore to run on Windows 11 devices.
Set up your development environment
To test your Android app in the Windows desktop environment, a bit of set up will be required.
Prerequisites
Windows Subsystem for Android is currently only available through preview via the Beta and Dev Channels of the Windows Insiders Program (Windows 11 Build 22000.xxx series) in the U.S. only.
Your device also must meet specific Windows 11 requirements. Check the «Windows Subsystem for Android» section under «Feature-specific requirements» on the page: Find Windows 11 specs, features, and computer requirements.
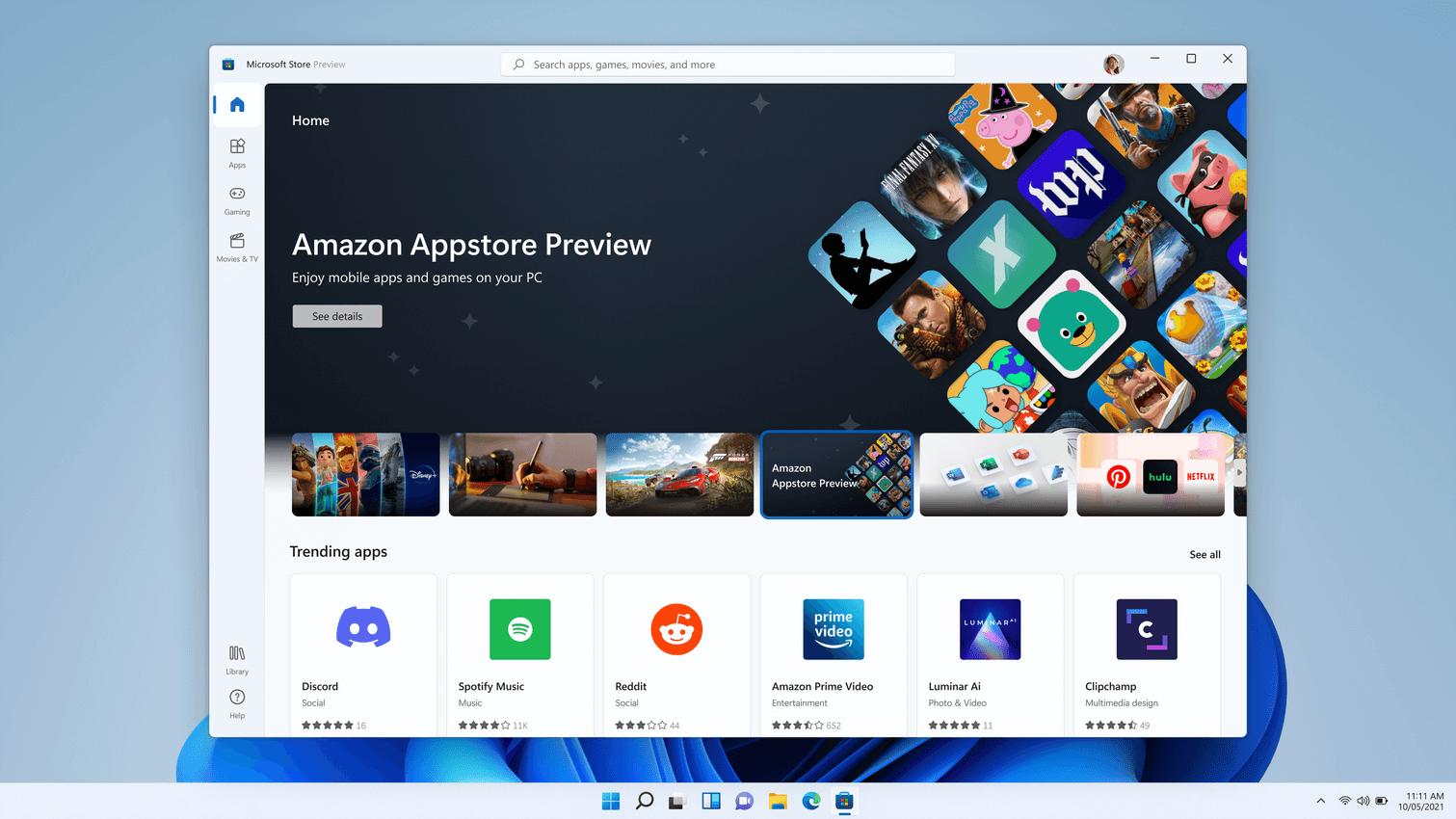
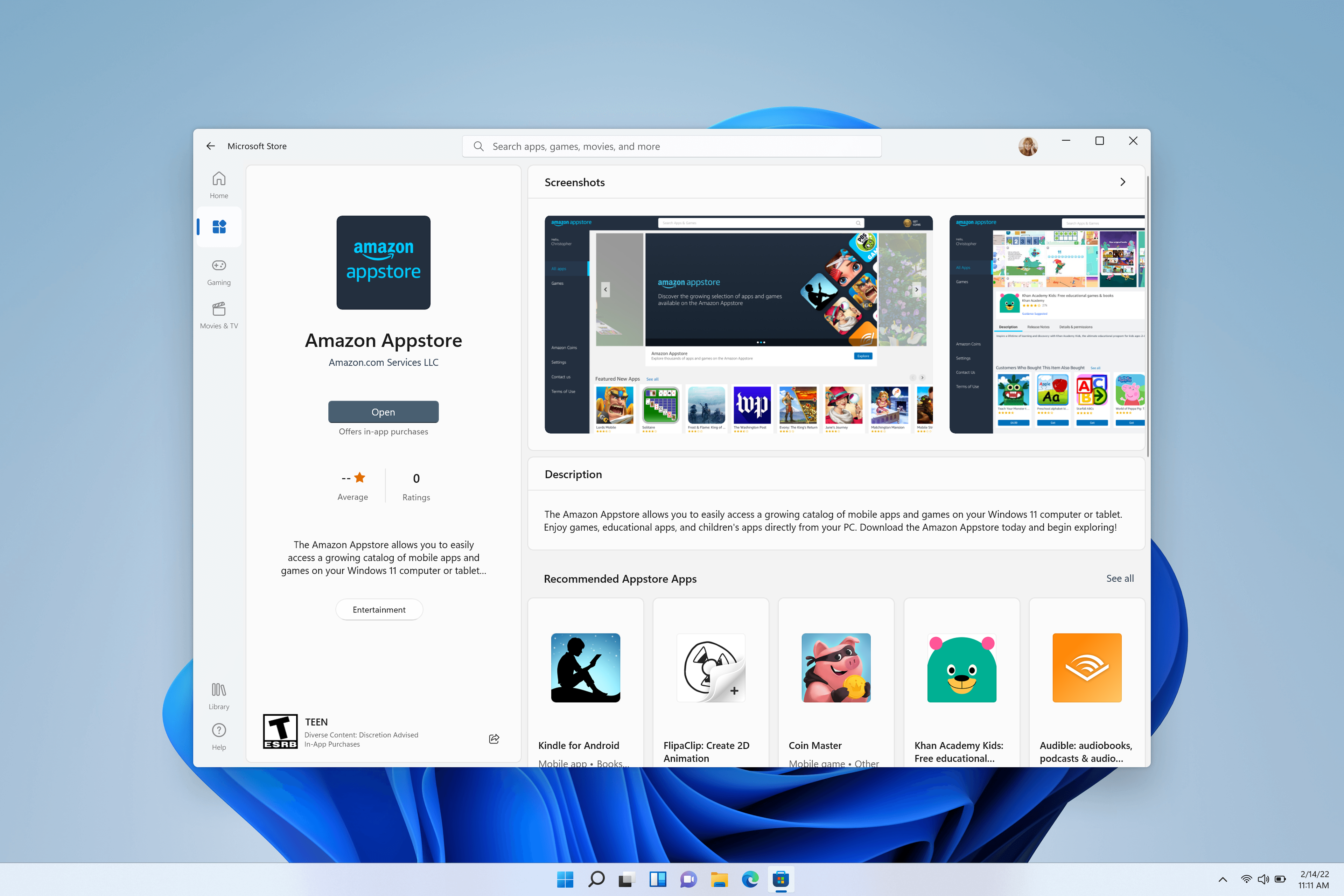
Install the Amazon Appstore
The Microsoft Store will automatically install Windows Subsystem for Android (running Android 11) silently in the background when either of the two following user actions are taken:
- Install the Amazon Appstore from the Microsoft Store.
- Install an Android or Amazon app from the Microsoft Store for the first time, which will also install the Amazon Appstore.
The Amazon Appstore will then appear in the Windows 11 Start menu and be available on search, offering a curated catalogue of Android apps.
Selecting Get will begin the installation of the app. The app will also appear in Windows Start, Search and in the Windows Programs list.
Settings app
To access the Windows Subsystem for Android Settings app, go to: Start > All Apps > Windows Subsystem for Androidв„ўпёЏ. The Settings app can be used to adjust the following settings:
Subsystem Screen Reader
If touch input isn’t working, make sure the Subsystem Screen Reader is turned off. For more info, see Microsoft Support: Accessibility on Windows Subsystem for Android.
Subsystem resources
As needed: When this is selected, the subsystem will open when a mobile app is opened. Since the subsystem needs to open first, the mobile app might take a little longer to open. Mobile apps opened after the first one might not be affected.
Continuous: The subsystem is always ready to open apps. Since it’s always open in the background, it will use more of your PC’s memory and processing power.
Enable developer mode
To test and debug your app on a Windows 11 device, you will need set Developer Mode to On.
Input compatibility considerations for Windows devices
There are a few unique input behaviors to consider that will likely require updates to your Android app code, designed for handheld devices, to be compatible when running on a Windows desktop device via the Amazon Appstore.
Keyboard input
For text input fields handled by an on-screen virtual keyboard input method (or IME), such as EditText , apps should behave as expected. (EditText class in the Android docs).
For keystrokes that cannot be anticipated by the framework, apps will need to handle the behavior themselves. If this is already implemented in-app, no extra work is required.
As an example, some games may already support movement facilitated via keyboard, through w a s d keys, alongside touch input.
The following are keyboard inputs that developers should consider code updates for when building for Windows 11 devices:
- Enter Key
- Arrow-key and Tab-key Navigation
- Change Selected Item Highlight Color
- Ctrl-based Shortcuts
Learn more about how to optimize for these keyboard input scenarios on desktop devices by following the Android documentation:
Mouse input
Developers should consider updating code for the following mouse inputs when building for Windows devices:
- Right Click
- Tooltips / Hover Text
- Hover Effects
- Mouse Scroll Wheel Action
- Drag and Drop
Mouse input, similar to keyboard input, must follow the official Android app guidelines. This means using the InputDevice class paired with the SOURCE_MOUSE constant. Learn more about how to optimize for these mouse input scenarios on desktop devices by following the Android documentation:
Window management and resizing
Unlike traditional mobile form factors, Android apps running on Windows 11 can be freely resized, should be responsive in their resizing, and can be snapped using Windows actions/gestures.
Minimum screen requirement
Windows 11 enforces a minimum screen requirement of 720p resolution (1280×720) with a >9” screen.
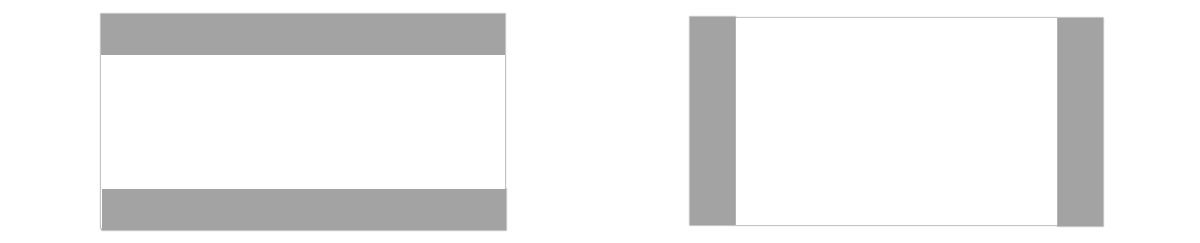
Letter & pillar boxing
When the aspect ratio of a window size does not align between the device screen sizes that window is being displayed on, the result may be Letterboxing (the window is wider than it is high, or horizontally longer) or Pillarboxing (the window is more narrow than it is wide, or vertically longer). The result is bars being placed on the sides of the window in order to center it. These bars may be light- or dark-themed depending on the system settings selected. This will only occur as necessary when the Android app is snapped or maximized, allowing Android apps to take advantage of the rich snapping features in Windows and integrate into the windowing model.
Additional resizing considerations
The following should also be considered when updating an Android app to run on a Windows 11 device with respect to window management and resizing:
- Initial launch size
- Window dimensions
- Content bounds
- Free form resizing
- Screen Orientation
Learn more about how to optimize for window resizing scenarios on desktop devices by following the Window Management guide in the Android docs.
Test and debug
To test and debug your app on a Windows 11 device using the Windows Subsystem for Android the following set up steps are required.
Enable developer mode in Windows Settings
You must first enable developer mode in Windows Settings. There are three ways to enable developer mode:
- Open the Windows Subsystem for Android Settings app. Once open, select Enable Developer Settings.
- Search for “Developer Settings” in Windows search.
- Navigate to Settings > Privacy and Security > For developers > Developer mode.
Connect to the Windows Subsystem for Android for debugging
To connect to the Windows Subsystem for Android VM for debugging, you have two options:
Recommended Method:
- Use localhost for connecting to debugging. The IP address of the localhost is: 127.0.0.1:58526 . Windows Subsystem for Android must be running in order to connect, the best way to launch Windows Subsystem for Android is by launching an Android app that was installed with the Amazon Appstore.
- To connect to the localhost address of Windows Subsystem for Android, enter: adb connect 127.0.0.1:58526
Alternative Method: Use the Windows Subsystem for Android Settings app to get the IP address.
- Launch the Settings app. (Use Windows Search to select and launch.)
- The IP address will be displayed under the IP address section. If there is no IP address being displayed, launch an Android app that was installed using the Amazon Appstore, then select Refresh on the IP address button in the Settings app.
Now that you have the IP address to connect to the Windows Subsystem for Android VM, connect using adb connect:
Connect to a test device
To connect to a test device (with Windows Subsystem for Android installed) on the same network from Windows/Mac:
On the test device (where Windows Subsystem for Android is installed) open a PowerShell window and identify the IP address of the test device by running the command:
Using the debugging device terminal where Android Studio and the Android SDK is installed (Mac/Windows), enter the command:
The can be found in the output of «ipconfig» from the test device. You can also deploy and debug apps from Android Studio.
To use Android Debug Bridge (ADB) to connect your development workstation directly to your Android device so you can install packages and evaluate changes, see Android Debug Bridge in the Android Open Source Project docs.
Debug your app
While apps should be installed using the Amazon Appstore, debugging an Android app on a Windows device is possible using an APK (Android application package) and adb (Android Debug Bridge).
To debug an APK using adb:
Follow the steps to connect to the Windows Subsystem for Android VM above.
Install the APK using the adb install command: adb install app-debug .apk
A successful “app installed” notification will appear in the Windows notification menu and the app will launch once selected.
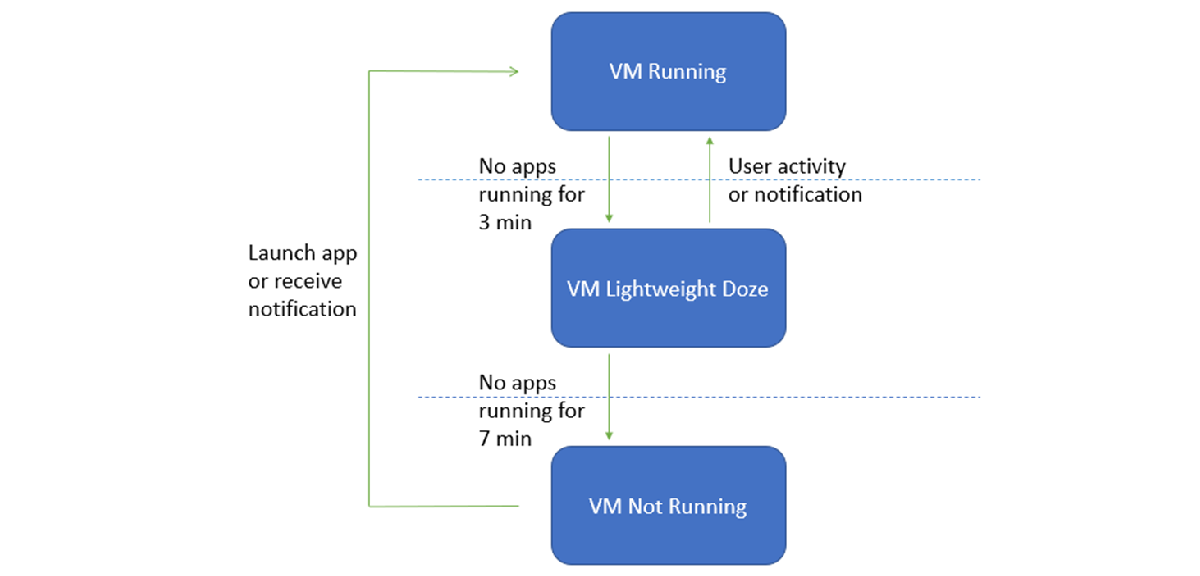
VM lifecycle considerations
Windows Subsystem for Android utilizes a virtual machine (VM) which provides compatibility with the AOSP framework and devices like keyboards, mice, touch, pen, etc.
There are three possible states for the VM running apps with Windows Subsystem for Android:
- Running
- Lightweight Doze: Activated after no app activity for 3 minutes. Deactivated by user activity or an app notification.
- Not Running: Activated after no app activity for 7 minutes.
Transitions between these states are triggered by user activity, such as launching or interaction with the Android app or an app notification. Android apps are paused and then stopped when their window is minimized.
VM Properties
The properties for the Windows Subsystem for Android VM are listed below. Hardcoding these values is not recommended as that could cause future incompatibilities.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Build.MANUFACTURER | Microsoft Corporation |
| Build.MODEL | Subsystem for Android |
| Build.VERSION.SDK_INT | 30 |
| Build.BOARD | windows |
Security
Windows Subsystem for Android performs per-file encryption that is software-based.
Both Windows kernel-mode drivers and Windows applications running at medium integrity level (IL) can inspect arbitrary Android containers and Android app memory. There are no plans to add detection for cheats/macro/bot/suspicious behaviors detection in the short-term.
Developers querying getSecurityLevel will get SECURITY_LEVEL_SW_SECURE_CRYPTO . Learn more about getSecurityLevel in the Android API Reference guide.
Amazon Appstore
In order to be available on a Windows 11 device, an Android app must be published to the Amazon Appstore. Currently, only a small set of apps selected by Microsoft and Amazon are available.
Developers should refer to the Amazon Device Targeting guidance for information on targeting APKs to specific devices.
Troubleshooting issues with Amazon Appstore
If you encounter issues specific to the Amazon Appstore on Windows, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Select Windows search from the Windows task bar.
- Search for “Amazon Appstore” and right-click on the Amazon Appstore icon.
- Select “App Settings” in the dropdown options.
- Select “Storage and Cache” and click both “Clear Storage” and “Clear cache”.
- Go back and select “Force Stop”.
- Close the Amazon Apptore Settings window.
- Relaunch the Amazon Appstore.
For further troubleshooting steps relating to the Windows Subsystem for Android Settings app or to leave feedback using Feedback Hub, see Troubleshoot mobile apps on Windows.
Building Universal APKs
Windows Subsystem for Android utilizes Intel Bridge Technology to emulate ARM applications on x86 based processors. ARM applications will of course run on ARM based processors natively. The emulation layer will induce a performance overhead – for optimal performance, please submit your application for both the x86-64 and ARM64 architectures.
Uninstalling Windows Subsystem for Android
You can uninstall the Windows Subsystem for Android, but note that all associated apps will also be uninstalled.
- Uninstalling the Amazon Appstore will uninstall the Windows Subsystem for Android and all other Amazon apps.
- Uninstalling an Amazon Appstore app will only uninstall the app (same behavior as Windows apps).
- Uninstalling the Windows Subsystem for Android will uninstall the Amazon Appstore and all Amazon apps.
Источник