- How to wirelessly charge your iPhone
- What you need
- Charge wirelessly
- Learn more
- How to use MagSafe Duo Charger with your iPhone and Apple Watch
- Get faster wireless charging for iPhone 12 and iPhone 13 models
- How to charge Apple Watch
- Qi and Magsafe — Everything an iPhone user needs to know about wireless charging
- What is Inductive Charging?
- Competing Standards
- Apple’s wireless charging history
- AirPower
- MagSafe
- What Apple products use wireless charging?
- Best Practices
- Comments (12)
- lilpir8
- multimedia
- ivanh
- avon b7
- entropys
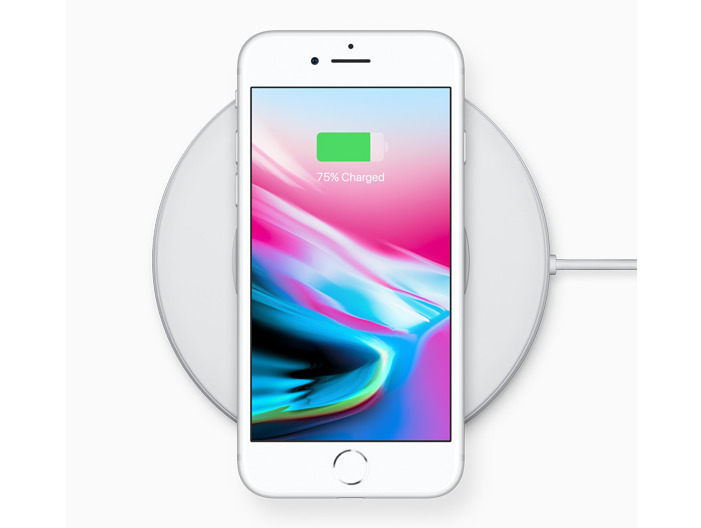
How to wirelessly charge your iPhone
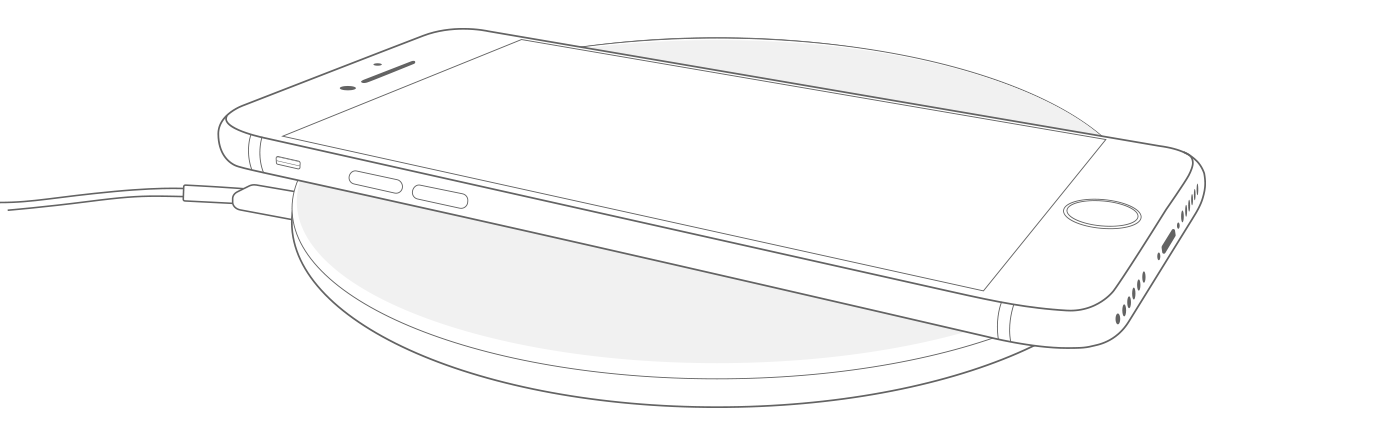
Learn how to wirelessly charge your iPhone with Qi-certified charging accessories.
What you need
Your iPhone features integrated wireless charging that allows for an easy and intuitive charging experience. Your iPhone works with Qi-certified chargers that are available as accessories and in cars, cafes, hotels, airports, and furniture. Qi is an open, universal charging standard created by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC).
Many Qi-certified chargers charge iPhone with the latest version of iOS at rates up to 7.5 watts. These chargers are available at the Apple Online Store and Apple Stores.
Other Qi-certified chargers might vary in functionality and performance. If you have questions, contact the manufacturer.
Charge wirelessly
- Connect your charger to power. Use the power adapter that came with your accessory or a power adapter recommended by the manufacturer.
- Place the charger on a level surface or other location recommended by the manufacturer.
- Place your iPhone on the charger with the display facing up. For best performance, place it in the center of the charger or in the location recommended by manufacturer.
- Your iPhone should start charging a few seconds after you place it on your wireless charger.
You should see in the status bar.
Learn more
- Learn about charging with the MagSafe Charger and MagSafe Duo Charger.
- Wireless charging uses magnetic induction to charge your iPhone. Don’t place anything between your iPhone and the charger. Magnetic mounts, magnetic cases, or other objects between your iPhone and the charger might reduce performance or damage magnetic strips or RFID chips like those found in some credit cards, security badges, passports, and key fobs. If your case holds any of these sensitive items, remove them before charging or make sure that they aren’t between the back of your iPhone and the charger.
- If your iPhone isn’t charging or is charging slowly and your iPhone has a thick case, metal case, or battery case, try removing the case.
- If your iPhone vibrates—when it gets a notification, for example—your iPhone might shift position. This can cause the charging mat to stop providing power to your iPhone. If this happens often, consider turning off vibration, turning on Do Not Disturb, or using a case to prevent movement.
- Depending on the charging mat you have, you might hear faint noises while your iPhone charges.
- Your iPhone might get slightly warmer while it charges. To extend the lifespan of your battery, if the battery gets too warm, software might limit charging above 80 percent. Your iPhone will charge again when the temperature drops. Try moving your iPhone and charger to a cooler location.
- Your iPhone won’t charge wirelessly when connected to USB. If your iPhone is connected to your computer with USB, or if it’s connected to a USB power adapter, your iPhone will charge using the USB connection.
Information about products not manufactured by Apple, or independent websites not controlled or tested by Apple, is provided without recommendation or endorsement. Apple assumes no responsibility with regard to the selection, performance, or use of third-party websites or products. Apple makes no representations regarding third-party website accuracy or reliability. Contact the vendor for additional information.
Источник
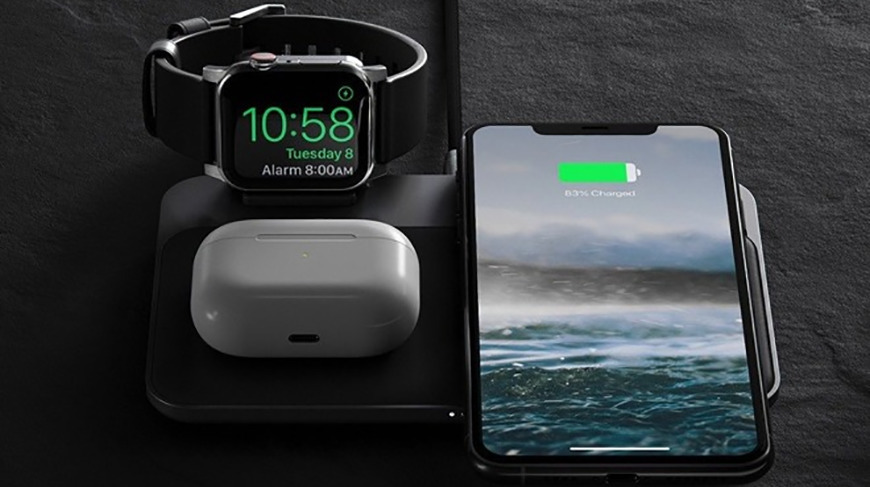
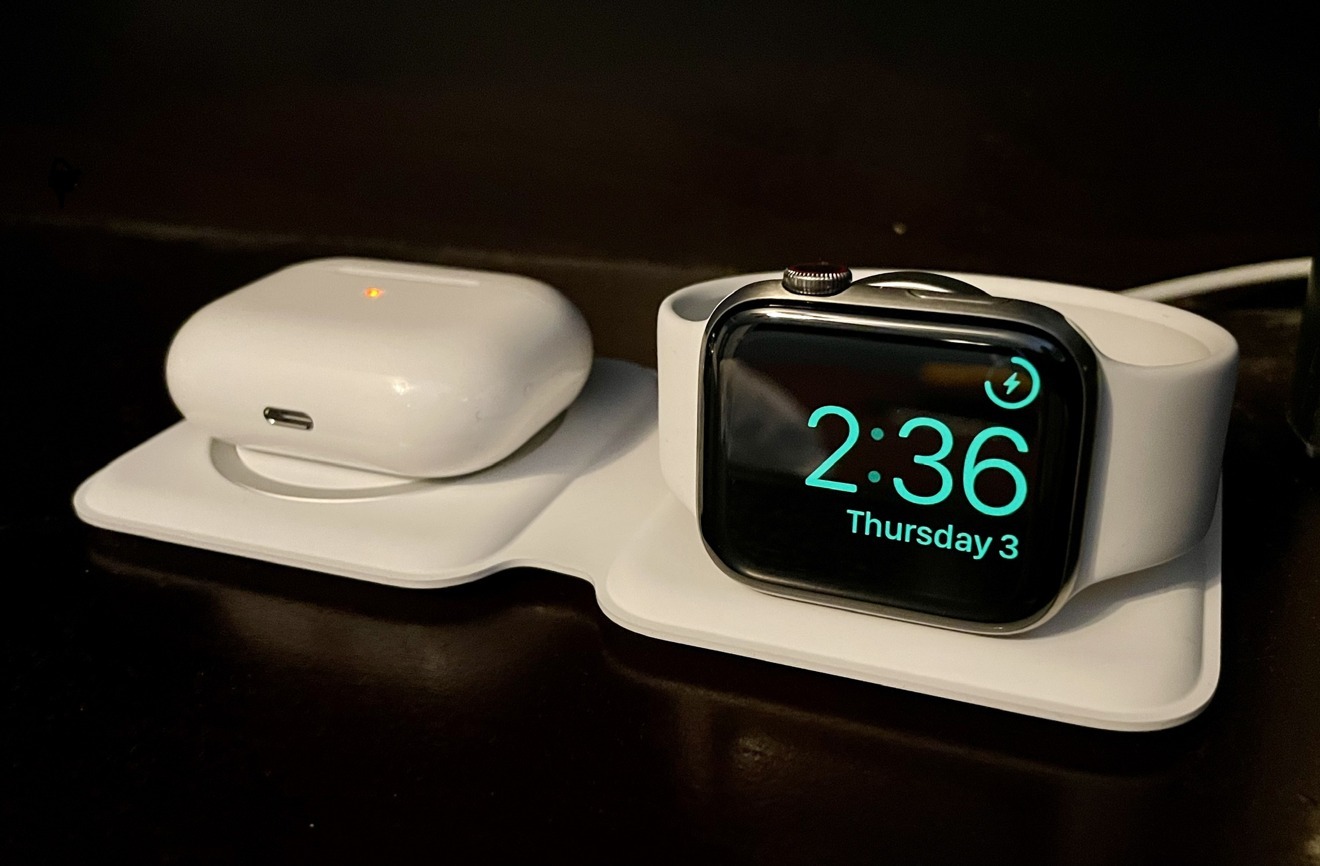
How to use MagSafe Duo Charger with your iPhone and Apple Watch
Learn how to charge your iPhone 12 or iPhone 13 and your Apple Watch wirelessly with MagSafe Duo Charger.
Your MagSafe Duo Charger is designed to work with all iPhone 12 and iPhone 13 models, all Apple Watch models, Apple MagSafe accessories, and Qi-certified devices and accessories.
Use the included USB-C to Lightning cable to plug in your MagSafe Duo Charger to a recommended 20 watt (W) or greater Apple USB-C power adapter* or a compatible third-party USB-C adapter. You can also connect to a USB-C port on a Mac or PC.
Place your MagSafe Duo Charger face up—as shown—on a flat surface, clear of any metal objects or other foreign material.
* The Apple 29W USB-C Power Adapter isn’t compatible with the MagSafe Duo Charger.
Get faster wireless charging for iPhone 12 and iPhone 13 models
The MagSafe Duo Charger is designed to quickly and safely wirelessly charge your iPhone 12 or iPhone 13 and your Apple Watch simultaneously. The system intelligently adapts to conditions to optimize charging your compatible iPhone at up to 14W of peak power delivery. The actual power delivered to the iPhone will vary depending on the wattage of the power adapter and system conditions. For iPhone 12 mini and iPhone 13 mini, the MagSafe Duo Charger delivers up to 12W of peak power delivery.
It’s important to plug into a power source before placing your iPhone on the MagSafe Duo Charger. This allows MagSafe to verify that it’s safe to deliver maximum power. If you happen to place your iPhone on the MagSafe Duo Charger before plugging into a power source, remove your iPhone from the MagSafe Duo Charger, wait three seconds, and then put it back on to resume maximum power delivery.
The MagSafe Duo Charger is designed to negotiate the maximum power up to 9 volt (V) and 3 amp (A) with a USB PD compatible power adapter. MagSafe will dynamically optimize power delivered to the iPhone. The power delivered to the iPhone at any moment will vary depending on various factors including temperature and system activity.
All power adapters have different ratings for the amount and rate of power delivery. The MagSafe Duo Charger requires the following ratings to deliver faster wireless charging:
- USB-C connector (USB-A is not supported)
- 9V/2.22A power adapter provides up to 11W of power
- 9V/3A and higher power adapter provides up to 14W of power
- iPhone 12 mini and iPhone 13 mini can get up to 12W for faster wireless charging with at least 9V/2.62A
- Higher wattage adapters at or above 9V/3A will also deliver a maximum of up to 14W peak power to your iPhone
To use both the iPhone and Watch charger at the same time, the MagSafe Duo Charger requires at least 15W (5V/3A or 9V/1.67A), but this will result in slower charging.
When Lightning accessories such as headphones are connected, charging is limited to 7.5W to comply with regulatory standards.
How to charge Apple Watch
You can charge your Apple Watch in a flat position with its band open, or on its side, by lifting the inductive charging connector. When docked on its side, your Apple Watch automatically goes into nightstand mode, so you can also use it as your alarm clock.
Place the back of your Apple Watch on the charging connector, with the connector upright or flat. When your Apple Watch starts to charge, you’ll see the charge indicator on the display.
Источник
Qi and Magsafe — Everything an iPhone user needs to know about wireless charging
AppleInsider is supported by its audience and may earn commission as an Amazon Associate and affiliate partner on qualifying purchases. These affiliate partnerships do not influence our editorial content.
The introduction of MagSafe in the iPhone 12 range has cemented wireless charging as a core technology for smartphones, but not everyone knows how the technology works. Here’s what you need to know about wireless charging systems and how Apple uses them.
In a world that is so used to plugging charging cables into ports to recharge devices, the creation of wireless charging has been useful for many different reasons. From being able to charge without needing to struggle to plug the cable in, the ease of charging at all, and the seeming magical nature of power being transferred without a wire being used, wireless charging has its benefits.
With Apple’s adoption of the technology in its iPhone lineup, more people have been exposed to the idea of wireless charging. Add in the wealth of wireless chargers made by various vendors you can pick up quite cheaply, and the barrier to entry is remarkably low.
In this article, we explain what it is, how it reached its current form, and how Apple embraced the technology in its products.
What is Inductive Charging?
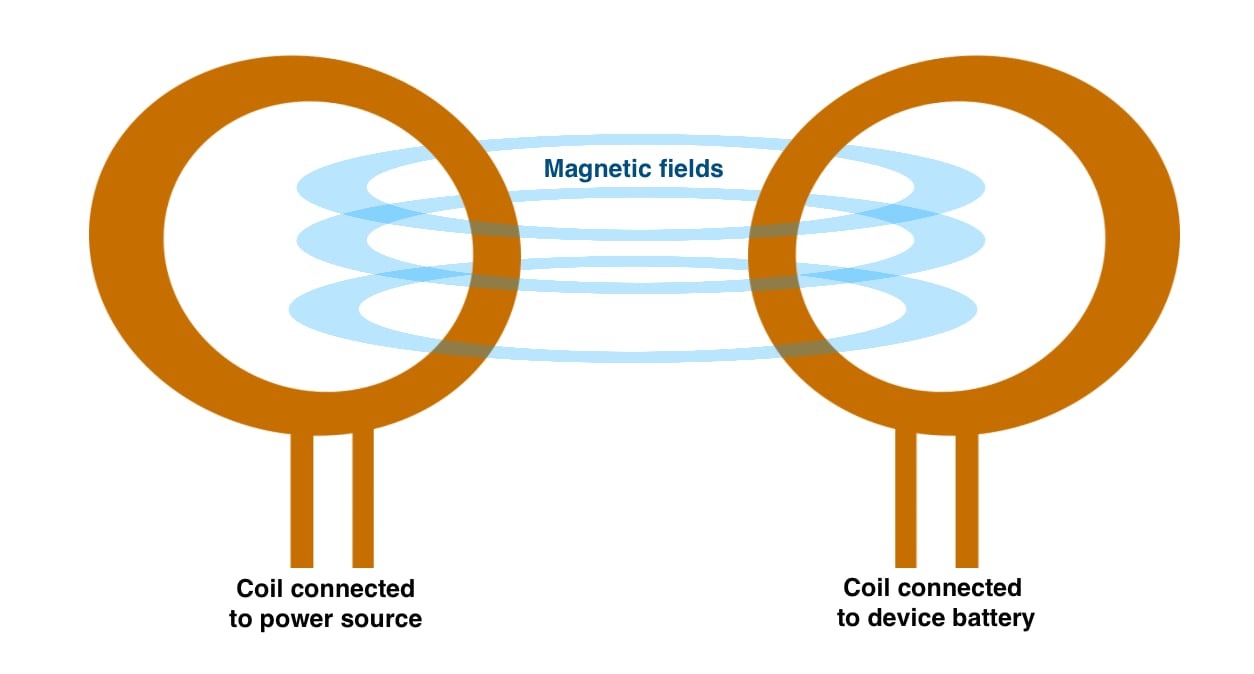
At its core, modern wireless charging relies on the properties of magnetic fields and their ability to influence other magnet-sensitive things. The simplest example of this would be a magnet passing through a coil of wire, with the movement of the magnet creating a current in the wire, which could be used to power a small light bulb.
Inductive charging follows the same principle but goes quite a few steps further.
For a start, instead of using a magnet to influence a coil of wire without touching it, inductive charging instead uses its own coil of wire, with the passing of current able to generate a magnetic field. If close enough, the magnetic field generated by the current in one coil could create a current in a second nearby coil.
Over short distances, such systems are quite useful, but the current of the «receiving» coil will always be lower than the «transmitting» coil. These can be rectified by increasing the coils’ size and increasing the power, but there’s only so far you can take it realistically.
To consumer devices, this has resulted in a system where a charging puck, stand, or other point includes a coil, which can interact with another coil contained within a host device, like a smartphone. The coils typically range from the size of a large coin to maybe two inches, depending on hardware. In contrast, the distance between the two coils tends to be less than a centimeter, separated by plastic or other materials not affected by magnetic fields.
Of course, the system can be scaled up, potentially to allow an electric car to recharge from a parking bay equipped with a larger coil, which could be useful in a future Apple Car. For the moment, devices with smaller coils are the type you will see with wireless charging.
Competing Standards
While the history of inductive charging goes back to the 1800s and Nikola Tesla, the modern history of device-based wireless charging is defined by the battle to be the dominant standard used by the electronics industry.
There are quite a few different standards out there for wireless charging technology, but for our purposes, we will cover the main two key standards groups working on competing wireless charging systems. The Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) offered its Qi charging system from 2008, and PMA technology championed by Power Matters Alliance (PMA) and Airfuel Alliance, licensed by Powermat.
Each of the groups had support, and their technology adopted by different companies, such as Google, Samsung, and various smartphone producers for Qi, while PMA included companies such as AT&T, Duracell, and Starbucks.
Since the two standards were warring with each other, there are some compatibility issues between the two, but they are similar in concept and implementation. The only real differences preventing them from working with each other were using different wavelength bands for the magnetic field and software.
The public battle for wireless charging played out with supporters of each side implementing the technology differently. The smartphone producer-heavy Qi enjoyed mobile devices’ support, the most apparent device category to use wireless charging.
On the other side of the fence, PMA benefited from more corporate-focused support, with Duracell being a significant name in batteries, a critical component. Starbucks did its bit by rolling out PMA-supporting charging points across the United States.
While Qi had a narrow lead over PMA, things didn’t change until 2017, when Apple decided to join the WPC as a member. At the time, rumors circulated that the iPhone 8 would have wireless charging, a rumor that would be confirmed later that year alongside the iPhone X having Qi support.
With Apple on board, things swung more heavily in Qi’s favor, to the point that a software update was rolled out to the Starbucks Powermat charging plates to make them compatible with Qi in late 2017, followed by Powermat formally joining the WPC in 2018.
Since then, Qi has practically become the dominant technology in use for mobile wireless charging. The vast majority of wireless charging accessories support it, as do most portable devices offering the feature. To consumers, this makes things considerably easier to acquire and use wireless charging hardware without needing to do much research beforehand.
Apple’s wireless charging history
While Apple’s iPhones were the main product to capture the public’s attention, it wasn’t the first to do so. The Apple Watch has provided wireless charging capabilities since the release of the first generation in 2015, predating the iPhone’s use by two years.
Using the supplied small charging puck, the wearable device line can be charged within a few hours or left overnight and ready to wear in the morning. Opting for an overnight charge also allows the use of Nightstand mode, which will turn the time on the display 90 degrees to be seen more clearly while recharging.
Though the core technology used to charge the Apple Watch wirelessly is fundamentally the same as Qi wireless charging in mechanics, you cannot use a Qi charger to recharge the Apple Watch. There are chargers on the market that have both a charging pad for an iPhone and a puck for an Apple Watch, but you can’t switch those two charging points around.
AirPower
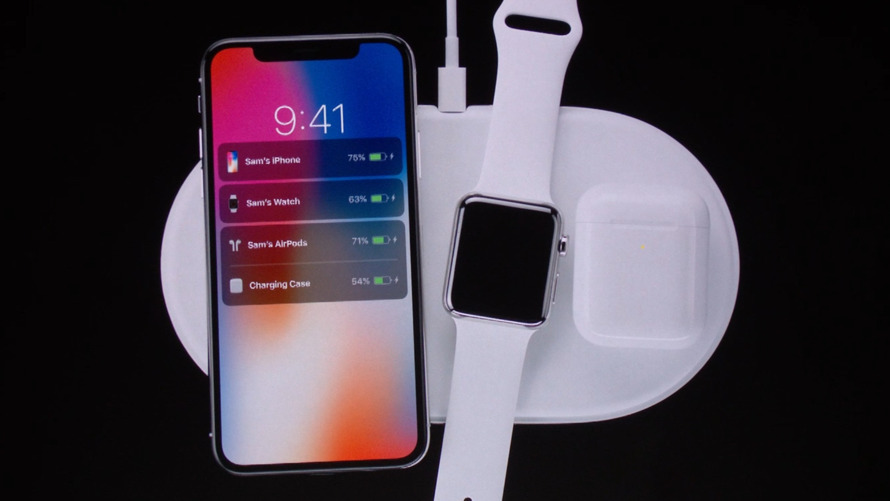
An exploration into Apple’s history of wireless charging wouldn’t be complete without mention of its seeming failure, AirPower.
Teased at the 2017 iPhone launch, AirPower promised a charging mat that did away with the usual rules of wireless charging. Instead of needing to place the iPhone in a specific position on the pad, the use of multiple coils would allow you to set the smartphone anywhere without worrying about alignment issues.
There was also the possibility of recharging three devices at the same time, including an iPhone, an Apple Watch, and an AirPods charging case, in any order and orientation.
However, development troubles, including thermal limitations, charging wattage limits, and fire hazards, caused enough problems before Apple’s release to effectively kill it off. In September 2018, Apple removed all mentions of AirPower from its website, and then admitted 19 months after its initial tease that it had «canceled the project.»
At the time of that announcement, Apple hinted it continued to «believe that the future is wireless and are committed to push the wireless experience forward.»
Arguably it has met the brief of a multi-device wireless charging station in the form of the MagSafe Duo, a foldable pad that offers MagSafe-based charging and power to an Apple Watch.
MagSafe
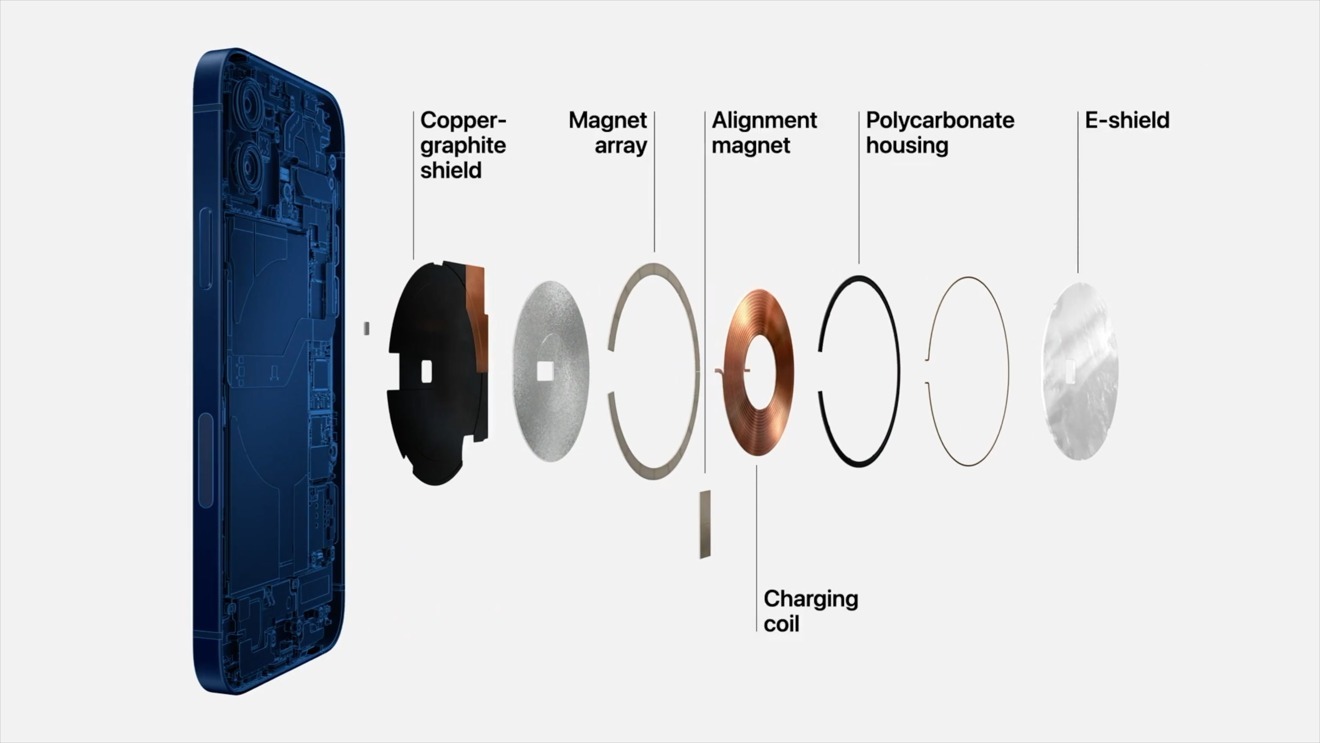
Formerly a name used for a magnetic mechanism to attach a charging cable to a MacBook, Apple revived the MagSafe brand for its modified form of wireless charging. Introduced alongside the iPhone 12, MagSafe was an improved version of its existing Qi charging support, adding rings of magnets to the equation.
By surrounding the charging coil inside the iPhone with magnets, this meant it was easier to correctly align the coil in the iPhone with a supported charger, as the MagSafe Charger would snap into place.
Another advantage was Apple’s decision to allow MagSafe to function at a higher level of watts, moving up from the 7.5-watt support for Qi chargers and allowing up to 15W charging on the iPhone 12 and Pro models, or up to 12W at peak on the iPhone 12 mini. Doing so required both the use of a MagSafe-compatible charger and a 20W or greater power adapter.
Since MagSafe still supports Qi chargers, it will continue to function with any existing Qi charging mats and pucks that a user may already own.
As an added benefit, the inclusion of magnets on the back of the iPhone means magnetic accessories can easily be placed and removed. Apple’s offerings include cases and covers, and a wallet attachment, with each also showing a color-matched graphic on the screen when applied.
What Apple products use wireless charging?
There are three product categories that you can use wireless charging with, consisting of iPhones, AirPods Wireless Charging Cases, and Apple Watch.
Out of the three, the Apple Watch has the most significant caveats, in that you can only use an Apple-approved Apple Watch charger, such as its own, to recharge your wearable device. This applies to all Apple Watch models so far and probably will do so for the future until Apple comes up with a better way to provide power to it.
If you own an iPhone with wireless charging support or an AirPods Wireless Charging Case, you can use any Qi-certified charging mat to apply power to it. For iPhones, this consists of laying it face up or facing outward on a stand-type charger, so the coil on the back gets as close as possible to the charger itself.
The AirPods Wireless Charging Case can be charged with the lid closed and the status light facing up. If you want to recharge both your AirPods and the charging case simultaneously, you can do so by leaving the AirPods inside the case, but you can also charge the case while you’re using the AirPods or AirPods Pro.
Wireless charging is available on all iPhone models from the iPhone X and iPhone 8 or later, including the second-generation iPhone SE. All will support charging rates of up to 7.5W with compatible chargers.
For the iPhone 12, iPhone 12 Pro, iPhone 12 Pro Max, and iPhone 12 mini, these models have MagSafe, which means they support both Qi chargers and MagSafe chargers. When attached to MagSafe, they can charge at up to 15W under ideal conditions, but will return to 7.5W when using non-MagSafe chargers.
Best Practices
When using wireless charging, there are a few things you should remember at all times.
For a start, alignment is critical. Optimal positioning of the device on the charging mat will result in better power reception and quicker charging times than misaligned devices. As charging only takes place when there is sufficient alignment, there is a chance that the iPhone won’t recharge at all if it’s placed incorrectly.
Typically placing an iPhone on a wireless charger will prompt a chime to be played and for the display to turn on, showing it is starting to recharge. Keep an eye or an ear out for these each time you place a device down on a pad to make sure it’s receiving power.
This is less of a problem for MagSafe due to its ring of magnets, as it will automatically align itself correctly.
Since distance is a factor, make sure there’s as little material as possible between the two charging coils. While a case may be OK, items such as the MagSafe card holder attachment could cause problems for charging to occur and could end up causing damage to the item in the middle.
It may also be worth removing the case from your iPhone, especially if it is a battery case or made of metal, as these could interfere with wireless charging.
You may also find the iPhone could get a little warm after a long charging session. This is normal, and Apple includes a software limit that can halt charging beyond 80 percent if the battery gets too warm as a safety mechanism.
As tempting as it may be to use both wired and wireless charging simultaneously for one device to speed up recharging, it’s not possible to do so. Apple disables wireless charging when the Lightning port is in use, so you would have to disconnect any physical connections beforehand.
Lastly, remember that wireless charging is not the most efficient way to recharge your iPhone. If you want to get as much power into your iPhone in as short a space of time as possible, you are better off using the Lightning port.
Comments (12)
lilpir8
Does the new silicone iPhone 12 mag safe case come in clear?
multimedia
I don’t want an iPhone that doesn’t have a Lightning Port. My wallet case is too thick to work wirelessly without removing the wallet’s contents or maybe even the case itself. Plus wireless charging is way too slow. I sure hope Apple keeps a Lightning port or at worst a USB C port for wired charging.
ivanh
THE FIRST THING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT WIRELESS CHARGING IS
WIRELESS CHARGING DOESN’T TRANSFER DATA.
Almost all these article fail to mention wireless charging doesn’t syncing and doesn’t backup. My friends were regretted just a day after using wireless charging pads.
avon b7
THE FIRST THING YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT WIRELESS CHARGING IS
WIRELESS CHARGING DOESN’T TRANSFER DATA.
Almost all these article fail to mention wireless charging doesn’t syncing and doesn’t backup. My friends were regretted just a day after using wireless charging pads.
That can’t really be considered a negative point because wireless charging is focused on charging convenience and mobility. For example if you use a car’s in built wireless charging mat, you probably wouldn’t be looking to sync data.
Data syncing is available via cable and wifi if necessary.
For my phone I much prefer wired fast charging but I aways charge my earbuds case wirelessly. My wife has problems with grip and uses a wireless charger on the bedside table for convenience. Alignment is easy as it’s impossible to misalign the phone.
I like options. My only niggle with Apple’s wireless charging options is that they are very slow when compared to other flagships.
entropys
Here is my cool story: five weeks of an iPhone 12 mini and I haven’t wirelessly charged once.
i prefer to charge at max speed and sync every night.
Источник