- Writing More Code by Writing Less Code with Android Studio Live Templates
- An Android Tool Time Pro Tip
- What is this magic I speak of? Live Templates!
- Android Studio Live Templates: A Handy Reference
- Create Your Own Live Templates
- Top 7: Best free code editors apps for Android
- Recommendations
- 7. Dcoder
- 6. Quoda Code Editor
- 5. QuickEdit
- 4. anWriter Free
- 3. Pocket Editor
- 2. Turbo-Editor
- 1. DroidEdit Free
- Honorable mentions
- Our Code Editor Free
- Codeanywhere
- Enlightened
- Understanding Clean Code in Android
- Before you start writing your code, it’s better that you understand how to manage your code and how to make your code scalable.
- What is “Clean Code”?
- — Must I care about it?
- Characteristics of a Clean code
- Create Meaningful Names
- — Class Names
- — Method Names
- — Use Problem Domain Names
- Writing your code using S.O.L.I.D Principles
- Single Responsibility Principle — SRP
- Open-Closed Principle — OCP
- Liskov Substitutions Principle — LSP
- Interface Segregation Principle — ISP
- Dependency Inversion Principle — DIP
- Conclusion
Writing More Code by Writing Less Code with Android Studio Live Templates
An Android Tool Time Pro Tip
If you’ve written much Android code, you’ve probably made this mistake at least once:
What if I told you there was a way to guarantee you can avoid this mistake, and also use fewer keystrokes?
What is this magic I speak of? Live Templates!
If you’re an experienced IntelliJ user, you’re probably already aware of Live Templates — in which case skip ahead to the Android-specific templates included in Android Studio
Unless you’re getting paid by the keystroke, no one wants to write repetitive boilerplate code. It’s easier to show than explain, so here’s how they work.
As you can see, Live Templates are shortcuts displayed as code-completion options that, when selected, insert a code snippet that you can tab through to specify any required arguments.
For example, as shown above — typing “Toast” then hitting the Tab key inserts the code for displaying a new Toast with argument placeholders that you can enter, before hitting tab and moving on to the next argument.
Android Studio Live Templates: A Handy Reference
IntelliJ includes over dozens of Live Templates, and Android Studio features another 48 specific for Android development. Here’s a few of my favorites for easy reference
Live templates can also insert larger code snippets; such as starter which creates a static start(…) helper method to start an Activity:
Similarly, newInstance that creates a new Fragment instance with arguments, and ViewConstructors, adds generic view constructors to your custom View.
You can use the File > Settings > Editor > Live Templates menu option to see the full list.
Of course, if your favorite boiler plate isn’t already there, remember that you can:
Create Your Own Live Templates
Go to File > Settings > Editor > Live Templates. Click the Android group, and press the plus button to add a new Live Template.
You’ll want to choose an abbreviation to use the template, a description to remember what it does, and of course the code you’d like it to insert — like this example for writing a boolean Shared Preference value.
Notice that we’re fully qualifying the class paths, and most importantly that we replace the parts of our code snippet that will be different each time with variables indicated by wrapping the names with matching $ symbols.
With our new Live Template defined, we can type the abbreviation — select it from the autocompletion hint by pressing tab — and it will paste in our code snippet!
What code are you going to Live Templatize?
Источник
Top 7: Best free code editors apps for Android
Carlos Delgado
- September 23, 2021
- 240.4K views
See our top of 7 from the best free code editors applications for software developers.
As an enthusiast developer, I write and read a lot of code every single day without exception. However, not always you can take your laptop and work wherever you want for different reasons. Nowadays, everybody has a Smartphone that is small as a hand. Many developers say that that’s already an impediment because you can’t work comfortably, but we do not all think in the same way (i mean, not all of us have huge fingers).
In this top, we will share with you a collection of 7 from the best free code editors applications available for the Android Platform.
Recommendations
If you want to enjoy your development experience while you work with any of the apps in this top, we recommend you to use an appropriate keyboard like Hacker’s keyboard. This keyboard is available on the Play Store.
7. Dcoder
Dcoder is a mobile coding IDE especially designed to hone your coding skills on mobile. It is a complete package to learn and comprehend the programming languages from a wide range e.g from C to Ruby. It includes Rich text editor supporting syntax highlight and packed with all the necessary tools required to give you all the edge an IDE or Code Compiler can give. The compile process is made through cloud APIs, that means that these features aren’t available without internet.
Not only you can code, you can debug the code to see compilation errors and Result on the same screen. Its more alike port of your favourite Code Editors like Notepad++ or Sublime Text with compilation power. It offers Custom Themes too, Editable font Size for the Editor and much more. This app offers in-app purchases.
6. Quoda Code Editor
Quoda is a sophisticated and easy to use source code editor or IDE, much like Notepad++, Textmate or Sublime Text, with integrated support for SFTP/FTP(S) servers and cloud storage (Dropbox and Google Drive). Other features include downloading URL source code, Code-completion, auto-encoding detection, brace matching, auto-indentation, line bookmarking, colour picker, HTML formatting, and even more — many of these unmatched by other Android IDEs or text editors.
If you want to code productively away from your PC, Quoda is a must have, allowing you to carry a text editor and IDE like Notepad++, Textmate or Sublime Text in your pocket to code when on the move.
5. QuickEdit
QuickEdit is a fast, stable and full featured text editor for Android devices. It has been optimized for both phone and tablet, it’s of high performance and real time feedback on large text files (more than 10,000 lines). The speed and responsiveness is very good if you compare it with other text editor apps on Google Play. It can be used as a text editor or code editor for normal text files and programming files. It will automatically detect the character encoding of your files, but you can still change it as you wish.
QuickEdit allows you to Access files from recently opened or added files collections, FTP, Google Drive, Dropbox and OneDrive and has syntax highlight for more than 40 languages like C++, C#, Java, XML, Javascript, Markdown, PHP, Perl, Python, Ruby, Smali, Swift, etc. QuickEdit has the ability to edit system files on rooted devices too.
4. anWriter Free
anWriter HTML editor helps you to write code: It offers an autocompletion support for: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, LaTeX (PHP, SQL in pro version). It supports modern technologies: It offers an autocompletion support for HTML 5, CSS 3, jQuery, Bootstrap, and Angular It supports FTP: You can download a file from the FTP server, send a file to the FTP server, and browse directories on the FTP server. It allows previewing web pages in application: Allow you to get a quick preview of your web page in an internal viewer. You don’t need to open a browser. The integrated viewer has a JS error console.
With anWriter you will significantly increase your coding speed, compared with a usual notepad. anWriter is much lighter than most IDE, but at the same time much more powerful, than most of notepad like editors.
3. Pocket Editor
Pocket Editor is meant to be used as an integrated development environment (IDE), text editor, and code editor for Android. It offers syntax highlighting, code completion, and other features for languages like:
- JavaScript, HTML, CSS, JSON, XML, and SQL
- PHP
- SQL
- Java, C, C++, C#, Objective-C, Swift, Kotlin
- Ruby
- Python, R, Perl, Lua
- Go, Rust, Elixir, Elm, TypeScript
- Cobol, Fortran, Pascal, Ada, and Assembly
- YAML, TOML, and Markdown
And many more. It offers many features to enhance your performance while you work. Although this app is closed-source, it is totally free and it doesn’t have ads. Pocket Editor is a product by Our Code World.
2. Turbo-Editor
Simple, Powerful and Open Source Text Editor for Android. Built following the latest Android Guidelines to make the experience the most intuitive on the Phone but also on Tablets.
1. DroidEdit Free
DroidEdit is a text and source code editor (similar to Notepad++ or gedit) for android tablets and phones. Take your work everywhere with this application, code while you’re waiting for the bus or when you’re relaxing in a nice beach (i don’t know why someone would code on vacations but, whatever). Don’t rush to your office if you receive an emergency call asking you to change some code. Just pick your mobile phone and edit everything you need. This app supports Emmet Tools, expand simple expressions into full fledged HTML code automagically.
The ad supported version has exactly the same functionality as the paid version except it doesn’t have SFTP support, Dropbox support, Custom themes and root mode.
Honorable mentions
These are some applications that although they aren’t listed in the top, they deserve to be mentioned as they still rock !
Our Code Editor Free
Our Code Editor Free is an integrated development environment (IDE),text editor, code editor for Android. Our Code Editor offers many features to enhance your performance while you work. Download and edit files from many sources (sftp,dropbox), an useful autocomplete and many highlight themes. Ideal for tablets, cell phone and other android devices. No account or internet connection required (excluding dropbox and SFTP), just download, install run and start coding ! The code files will be managed locally on your device.
Our Code Editor supports code folding, Live syntax checker (for a couple of languages), cut, copy, and paste functionality, Search and replace with regular expressions
Although this app is closed-source, it is totally free and it doesn’t have ads. Our Code Editor Free was written by Our Code World .
Codeanywhere
Codeanywhere is a text, code and markup editor, that has been redesigned and reengineered to be light, fast, and mobile-friendly. Connect to your FTP, SFTP Servers, Dropbox or Github account and easily manipulate your resources, folders or files just with the swipe of your finger. Share and collaborate on projects or just a single file — from wherever you are, and of course quickly edit code with our keyboard that has been customised for developers on the go. Codeanywhere also works on the desktop (Mac and PC).
Apparently the Codeanywhere app doesn’t allow to edit local files from your device, only from remote sources.
Enlightened
Enlightened is an elegant, minimalist code editor for Android. Its purpose is similar to that of other lightweight code editors: it allows you to edit text and code of many different languages. Think of it as a kind of Notepad++ for Android devices. At the same time, its goal is to stay minimalistic and intuitive. It has absolutely no ads, intrusive permissions, or other nonsense. This app is not stable and have some bugs, however the app has potential and its improvable, that’s why it’s worth to mention it.
If you know another awesome free code editor application, please share it with the community in the comment box.
Источник
Understanding Clean Code in Android
Before you start writing your code, it’s better that you understand how to manage your code and how to make your code scalable.
As Uncle Bob said in his book,
You are reading this “article” for two reasons. First, you are a programmer. Second, you want to be a better programmer. — Robert C. Martin
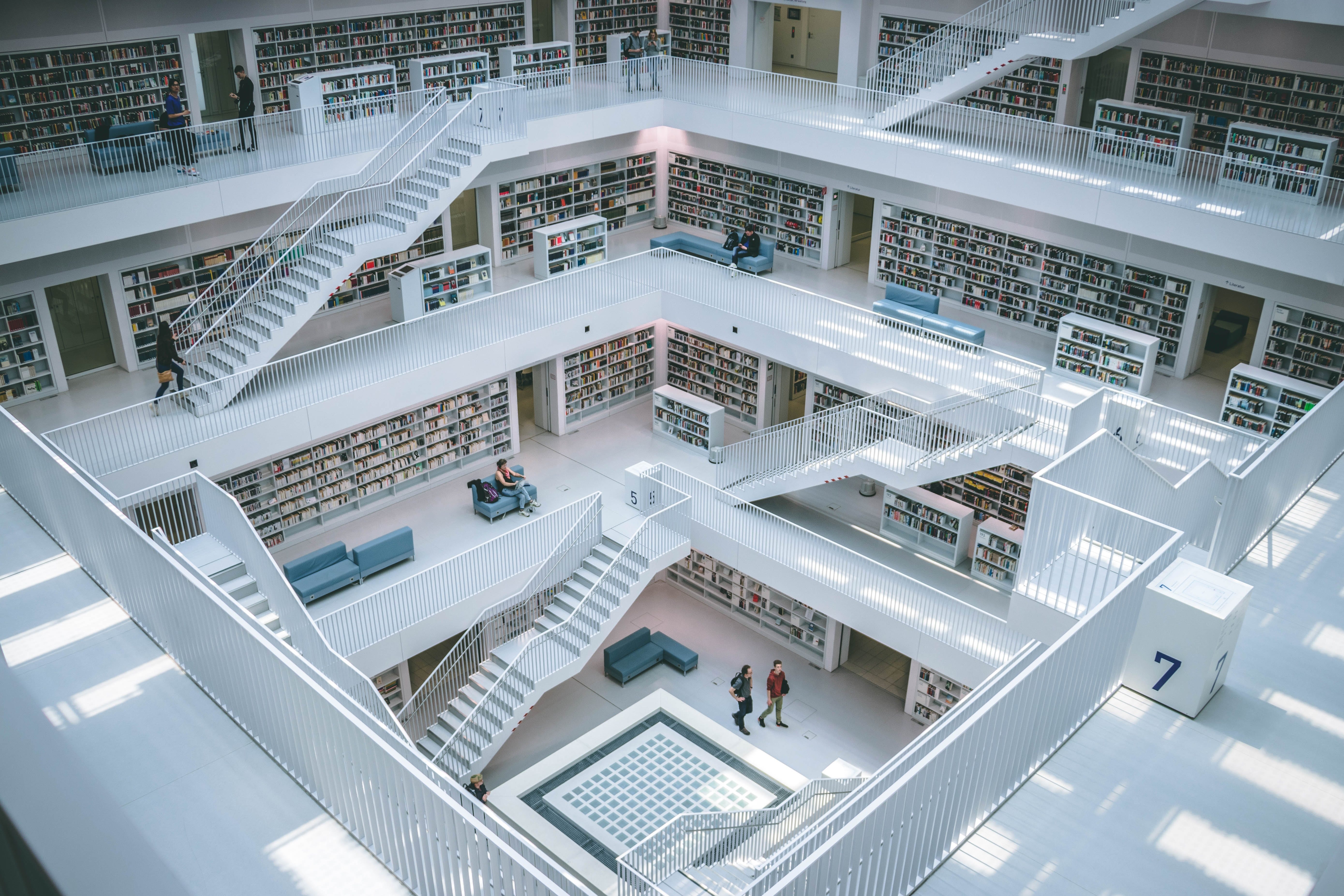
Like what he said, imagine that you are in a library, and you are looking for some books. If the library sorted and categorized their books, you will find your books faster. In addition, the cool interior design & architecture will make you feel comfortable inside the library while you are searching for your books.
Just like writing books, if you want to build something great, you have to know how to write and organize your code neatly. If you have team members or someone else that has your (legacy) code, they just need to see the variable names or packages or classes and they will understand right away. They don’t need to say “F**k” this code and start it again from zero.
What is “Clean Code”?
As you can see, it is not good enough if you finish your development faster if others cannot understand your code, because it will become another tech debt.
Your code has a definition of “Clean” if it can be understood easily by everyone on the team. Clean code can be read and enhanced by a developer other than its original author. With understandability comes readability, changeability, extensibility, and maintainability.
— Must I care about it?
The reason why you must care about your code is that your code will describe your thought process to others. That is why you have to start thinking about making your code more elegant, simple and readable.
Characteristics of a Clean code
- Your code should be elegant: Your code should make you smile the way a well-crafted music box or well-designed car would.
- Your code has been taken care of: Someone has taken the time to keep it simple and orderly. They have paid appropriate attention to details. They have cared.
- Your code has to be focused: Each function, each class, each module exposes a single-minded attitude that remains entirely undistracted, and unpolluted, by the surrounding details.
- Contains no duplication
- Runs all the tests
- Minimize the number of entities such as classes, methods, functions, and the like.
One difference between a smart programmer and a professional programmer is that the professional understands that clarity is king. Professionals use their powers for good and write code that others can understand. — Robert C. Martin
Create Meaningful Names
Choosing good names takes time but saves more than it takes. The name of a variable, function, or class, should answer all the big questions. It should tell you why it exists, what it does, and how it is used. If a name requires a comment, then the name doesn’t reveal its intent.
Let’s take a sample:
— Class Names
Classes and objects should have noun or noun phrase names like Customer, WikiPage, Account, and AddressParser. Avoid words like Manager, Processor, Data, or Info in the name of a class. A class name should not be a verb.
— Method Names
Methods should have verb or verb phrase names like postPayment, deletePage, or save. Accessors, mutators, and predicates should be named for their value and prefixed with get, set, and is according to the javabean standard.
— Use Problem Domain Names
When there is no “ programmer-eese” for what you’re doing, use the name from the problem domain. At least the programmer who maintains your code can ask a domain expert what it means.
Before we continue, take a break and make some coffee or grab some snacks. 😀
OK, now we continue about the writing your code using S.O.L.I.D principles.
Writing your code using S.O.L.I.D Principles
This principles are invented by Robert C. Martin (Uncle Bob), SOLID is a term describing a collection of design principles for good code.
Single Responsibility Principle — SRP
It means every class should have a single responsibility. There should never be more than one reason for a class to change. Just because you can add everything you want into your class doesn’t mean that you should. Split big classes into smaller ones, and avoid God Classes.
Lets take a sample:
We have an RecyclerView.Adapter with business logic inside onBindViewHolder.
It makes RecyclerView.Adapter not having a Single Responsibility because it has a business logic inside onBindViewHolder. This method is only responsible for setting up data into its view binding implementation.
Open-Closed Principle — OCP
Software entities should be open for extension but closed for modification. What it means is that if you write a Class A, and then your teammates want to make a modification in a function inside Class A, They can easily do that by extending Class A, instead of making a modification inside Class A.
The easy example would be the RecyclerView.Adapter class. You can easily extend this class and create your own custom adapter with custom behavior without modifying the existing RecyclerView.Adapter class.
Liskov Substitutions Principle — LSP
Child classes should never break the parent class’ type definitions.
It means that a subclass should override the methods from a parent class that does not break the functionality of the parent class. For example, you create an interface class that has an onClick() listener, and then you apply the listener in MyActivity and give it a toast action when the onClick() is called.
Interface Segregation Principle — ISP
The interface-segregation principle (ISP) states that no client should be forced to depend on methods it does not use.
It means that if you want to make a Class A and implement it in another class ( (Class B), it should not override all Class A methods inside class B. To make it clear and easy to understand,
Let’s take a sample: inside your activity, you need to implement SearchView.OnQueryTextListener() and only need the onQuerySubmit() method.
How to achieve that? simple, you just create a callback and a class that extends to SearchView.OnQueryTextListener().
And here is how to implement in view:
Or, if you are using Kotlin, you can use the Extension Function:
And last, here is how to implement in view:
Dependency Inversion Principle — DIP
Depend on Abstractions. Do not depend on concretions.
Uncle Bob’s definition of the Dependency Inversion Principle consists of two points:
- High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions.
- Abstractions should not depend on details. Details should depend on abstractions.
High-level modules, which provide complex logic, should be easily reusable and unaffected by changes in low-level modules, which provide utility features. To achieve that, you need to introduce an abstraction that decouples the high-level and low-level modules from each other.
The easy example is in MVP pattern, you have an object of interfaces that help us to communicate with concrete classes. What it means is, UI classes (Activity/Fragment) don’t need to know the actual implementation of methods in Presenter. So, if you have any changes inside presenter, UI classes don’t need to know or care about the changes.
Let’s see it in this code example:
Now let’s see it in UserActivity:
So what we do is we create an interface which abstracts the implementation of a presenter and our view class keeps the reference of the PresenterInterface.
Conclusion
Mature programmers know that the idea that everything is an object is a myth. Sometimes you really do want simple data structures with procedures operating on them. From now, you have to start thinking about what to implement and about future perspective that will be easy to update.
I know that if you have created an app before with nonsense naming, God classes, Spaghetti code, trust me, I have done the same thing. That’s why I share my knowledge about the Clean Code from Uncle Bob to you, and it is also be a reminder for me and I hope I can help you to understand it.
Last but not least, Comments/Suggestions are welcome as always. Keep learning and keep sharing.
Источник