- Android Certificate: Generate, Sign And Verify An Apk App
- Looking At A Decompile APK File
- Generating An Android Certificate
- Method 1:
- Method 2:
- Method 3:
- Signing An Android Applicaiton
- Verifying An Android Application
- How To Protect Your Android Phone From Harmful Apps
- Android 4.2 ‘Verify apps’ security feature explained by Google
- В Android появилась постоянная верификация приложений
- Implement In-app Update In Android
- Make sure every user of your app is on the new version.
- What is In-App Update:
- Flexible Update:
- Benefits:
Android Certificate: Generate, Sign And Verify An Apk App
Apk signing has been a part of Android from the beginning of the Android evolution, and android requires all Apks should be signed before it can be installed on the device, There have been numerous articles regarding on how to generate a key and also how to sign an Apk, but we will be looking at it from a Security Perspective, After you decompile or reverse-engineer an Apk file, What file should you look into, To get more info about the Developer who originally sign the app.
Looking At A Decompile APK File
After you unzip the file or using apktool, depending on how you decompile the file, if you unzip the file, The file structure will look like this.
We are looking at the META-INF folder,
Looking at a decompile Apk using Apktool, It includes the certificates details about the developer and the type of hashing algorithm used and so on in the original folder and checking the META-INF folder.
Using keytool to check for the certificate while you are still currently in the META-INF folder.
depending on the name of your certificate alias name, You will see different information of the Owner, Country, Issuer, Certificate Validity from both the date the certificate is issue and when the certificate is set to be expired.
Certificate fingerprints in MD5, SHA1 and SHA256 and also the Signature algorithm used.
Before, I talk about Generating a certificate, lets look at it from security perspective, In analyzing an Android application which you download from third party web site, You can decompile the App and look at the certificate and compare it with the original App, Look at the hashing algorithm used, compare it if probably the application has been modified or tamper with, I wont be talking about analyzing an APK file but may be later.
Generating An Android Certificate
If you decompile your android application and compile it back, You will need to sign the app, and if you don’t sign it the Application wont be installed on the user device. There are different ways of generating a certificate but, we will look at three ways to generate a certificate using keytool.
Method 1:
Open your terminal:
where awwal — is the keystore name, alias — hafsa is the certificate alias name, which after you use it will be added to META-INF folder, -keysize 2048 , but you can use 4096 size, but there are issues regarding that from devices or so. but just use 2048, validity is in days.
Method 2:
Using apk-signer.jar which can be downloaded here https://shatter-box.com/knowledgebase/android-apk-signing-tool-apk-signer/
This is a GUI written in Java that allows generating a certificate and also signing an apk file. Though there’s also an Android App for that in Playstore.
Method 3:
I created a bash script that automate the task of using method 1, As method might require you installing Java Runtime, Just run the script i created which uses keytool and jarsigner.
Download the script here: https://github.com/ShehuAwwal/Apk-Signer
After that follow the instruction which will be prompted to generate your key.
Signing An Android Applicaiton
After you already generate your android application, we will look at how to sign the app, run your terminal:
Where -sigalg is the signature algorithm used, You can find some Apps using MD5 but use SHA1 as when you are verifying the app it will tell you the hashing algorithm used and how weak the algorithm used is.
keystore — awwal is the name of the keystore name used when generating the certificate, and hafsa is the alias name of the certificate, and medium.apk is the name of the app to be sign.
Note: if you MD5 the application will be treated as an unsign app because the algorithm use to sign the App is weak.
And the easier way is to use the Apk-signer.sh which i wrote to make the task easier.
Run the script, and press 2 for signing the app, Also completes also work there for file name and certificate name.
Or also you can make use of the apk-signer.jar also provide the options to sign the app.
Verifying An Android Application
Verify the app using jarsigner, to see the list of resources sign, the hashing algorithm with keysize.
Open your terminal:
where verify only will show either it is sign or unsign and using the verbose options to see the full details of the certificate.
Or you can use Apk-signer to verify the App with auto completion of file name.
Источник
How To Protect Your Android Phone From Harmful Apps
The Google Play store for Android apps store has been dealing with a few sketchy programs lately, like the recent flashlight app that was caught selling personal user data without permission.
But Google has a nifty feature that can help protect your Android phone with a feature called Verify Apps. This tool can prevent you from downloading dangerous apps from Google Play and other sources. It also continuously scans your device for harmful apps.
Here’s how it works:
The settings to activate this feature will vary based on your Android software.
If you are using something lower than Android 4.2, go to the settings menu and navigate to Google Settings > Verify App. Go to Settings > Security > Verify apps if you are running Android 4.2 or higher.
The program can work two ways.
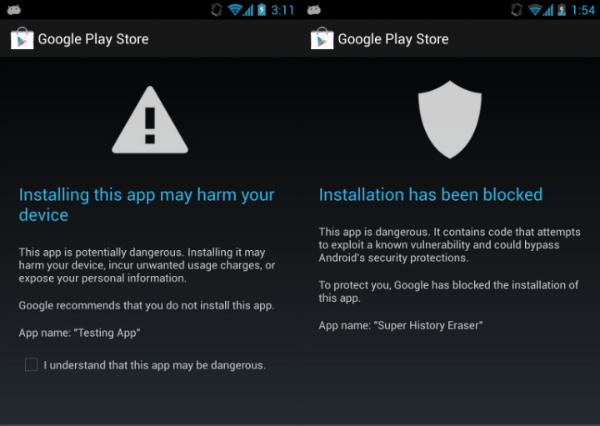
If you decide to download an app from an unknown source, Google will give you a warning that this could be dangerous. It recommends that you shouldn’t install the app, but you can choose to ignore this warning at the bottom.
If the program is too dangerous, Google can automatically block the app from being installed.
Unfortunately, a few apps can slip through the cracks. Verify Apps continuously scans your device for dangerous programs. This warning should appear if there is an app on your phone or tablet containing malware that Verify couldn’t detect upon installation.
If you keep ignoring the warnings, Google will automatically remove the app from your device.
Источник
Android 4.2 ‘Verify apps’ security feature explained by Google
Since we inevitably keep talking about malware in the Android ecosystem, and since we have already told you a bunch of times that Android 4.2 comes with some enhanced anti-malware security features, it’s time to look at Google’s official explanation regarding one of the new Google Play security protections that has been built into the new OS version, app verification.
Even before Android 4.2 became official, we heard that Google may be looking to improve the security of its app ecosystem by introducing new security measures in Android 4.2 meant to better protect users against unwanted attacks.
Those features were confirmed once Android 4.2 was announced, and can be taken advantage of right away by any Android 4.2 device user, including the apps verification process.
As long as it’s enabled – because it can be disabled by the user and it’s not mandatory to be used – the new security feature will scan the apps you want to download against Google’s database of apps. In case Google finds the apps to be harmful in any way, installing them will not be possible. Such a feature is especially useful if you plan to install lots of apps from other sources than Google’s own Play Store.
What data does Google get when communicating with your handset? Google explains:
Even though the feature is enabled by default on the device, it won’t transmit any data until you expressly agree for it to do so. A dialog message will appear asking for permission the first time you install an app for an unknown source.
In order to manage apps verification, you can head to Settings > Security > Verify apps on your smartphone or tablet running Android 4.2.
Источник
В Android появилась постоянная верификация приложений
В Android появилась постоянная проверка подлинности и безопасности приложений. Об этом инженер по безопасности Рич Каннингс сообщил 11 апреля в официальном блоге Android. В основе обновления лежит уже имеющийся в Android сервис верификации (Verify Apps), предупреждавший о вредоносных приложениях при их инсталляции.
Verify Apps был доступен уже на Android 2.3 Gingerbread (и более поздних версиях) и предназначался для проверки приложений, установленных за пределами Google Play. В 2013 году сервисом воспользовались 4 миллиарда раз — при установке приложений. Обновленный сервис верификации будет сканировать ваши приложения и после установки. Если одно из них окажется занесенным в черный список Google, на экране появится предупреждение «Google рекомендует деинсталлировать это приложение» или «Google деинсталлировала это приложение».
Первая контрмера предназначена для приложений, занимающих лишние ресурсы устройства, увеличивающих трафик и грозящих обнародовать ваши личные данные. Вторая — автоматическая деинсталляция — предназначена для борьбы с приложениями, пытающимися вытянуть из вас пароли и прочую ценную информацию. Чтобы включить (или отключить) постоянную верификацию, нужно зайти в «Настройки > Безопасность > Верификация приложений» («Settings > Security > Verify apps») и поставить (или снять) там галочку.
Читайте о мобильных приложениях в нашем разделе APPS. Новые материалы — каждый день.
Источник
Implement In-app Update In Android
Make sure every user of your app is on the new version.
Apr 6, 2020 · 8 min read
In this article, we will learn about the In-app update feature in Android what is all about In-app update, what are the benefits of using the In-app update in your android application. Recently I’ve been working on a product in which I need to Implement an In-app update Why we need to Implement this?.
As a Developer we always want our users to have the updated version of their application but there are a lot of people who actually turned off their auto update from google play store and he/she doesn’t know about any update available or not.
To overcome the problem Google Introduced this feature called In-app update from this feature you can easily prompt the user to update the application and with the user permission you can update the application also while updating the app user can be able to interact with the application. Now the user doesn’t need to go to google play store to check there is any update available or not.
What is In-App Update:
An In-app update was Introduced as a part of the Play Core Library, which actually allows you to prompts the user to update the application when there is any update available on the Google Play Store.
There are two modes of an In-app update.
- Flexible Update
- Immediate Update
Flexible Update:
In Flexible update, the dialog will appear and after the update, the user can interact with the application.
This mode is recommended to use when there is no major change In your application like some features that don’t affect the core functionality of your application.
The update of the application is downloading in the background in the flexible update and after the completion of the downloading, the user will see the dialog in which the user needs to restart the application. The dialog will not automatically show, we need to check and show to the user and we will learn how later.
Benefits:
The major benefit of the flexible update is the user can interact with the application.
Источник